Serialize and Deserialize a Binary TreeData structures must also be able to be transformed into a format that can be stored and later reconstructed. A data structure is transformed into a series of bits through the process of serialization. The process of recreating the data structure from the serialized sequence is known as deserialization. In order to create effective software, data structures are essential, and we frequently need to exchange them. Consider sharing a binary tree; if it's an inter - process interaction, the tree's root node can be exchanged directly. But if we need to share it over a network, this won't work. We can transform a data structure into a sequence using serialisation so that it can be transferred over a network or kept in a memory buffer. Deserialization is then performed to reconstruct the data structure at a later time. Let's look at a binary tree serialization and deserialization example. 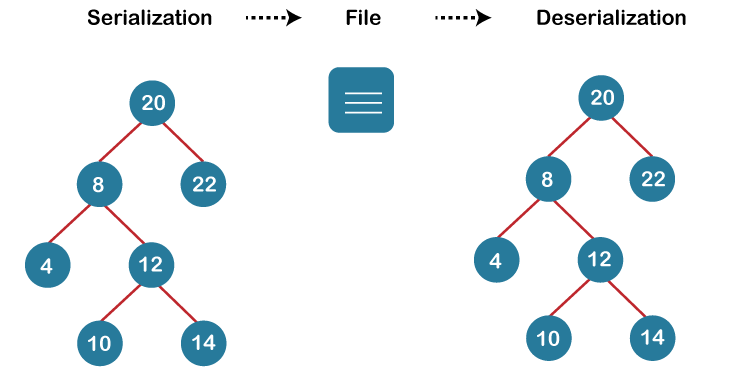
One simplistic method for doing this is to keep track of any two tree traversals and recreate the tree from scratch using both traversal sequences. Additionally, the nulls must be saved here in order to serialise the tree and restore it using a single tree traversal, either preorder or postorder. Let's first examine how to serialize a tree and the process of deserialize a tree separately before getting into the theory and implementation of serialising and deserializing a binary tree. Binary Tree SerializationA binary tree can be serialised by traversing it in a specific order and saving the relevant sequence. The objective is to have the ability to reconstruct the tree from the sequence as well as archive the tree nodes in a sequence (to be able to serialise and deserialize a binary tree). Now, this can be accomplished by traversing the tree in a particular way so that the same approach may be taken while deserializing. Pre-order, in-order, post-order, and other types of traversals are a few examples. First Technique: Pre-Order TraversalIn order to identify a null when reconstructing the tree, the concept is to do a preorder traversal of the tree and save the null values with integer minimum. The pre-order traversal algorithm is as follows:
Implementation The pre-order traversal implementation for serializing a binary tree in C++ is as follows: C++Code: Output Preorderseries follows as 1 2 4 -2147483648 -2147483648 -2147483648 3 5 -2147483648 -2147483648 -2147483648 Time Complexity This method traverses the tree, appending each node to the array. Time complexity is going to be O(N). Space Complexity This method maintains an internal recursion stack of size H and needs an array to store the serialized sequence (height of binary tree). As a result, the complexity of space will be O(H+N), where Technique 2: Post-Order TraversalIn order to identify a null when reconstructing the tree, the concept is to do post-order traversal of the tree and save the null values with integer minimum. The post-order traversal algorithm is as follows:
Implementation The post-order traversal implementation for serializing a binary tree in C++ is as follows: C++ Program: Output Postorderseries follows as -2147483648 -2147483648 4 -2147483648 2 -2147483648 -2147483648 5 -2147483648 3 1 Time Complexity This method traverses the tree, appending each node to the array. Time complexity is going to be O(N). Space Complexity This method maintains an internal recursion stack of size H and needs an array to store the serialized sequence (height of binary tree). As a result, the complexity of space will be O(H+N), where Binary Tree DeserializationOnce serialisation is complete, we will have a serialised sequence from which the original tree must be recreated. As was previously discussed, we ought to use the same traversal strategy as when the tree was serialized (to be able to serialize and deserialize a binary tree). By doing this, the deserialization method is able to maintain the original tree's state. Technique 1: Pre-Order TraversalThe goal is to continue adding nodes to a tree in the appropriate pre-order as we go through the specified sequence. Keep in mind that the specified sequence must equal the original tree's pre-order traversal. Otherwise, the original tree will not be recreated by the pre-order deserialization. The following is the deserialization procedure for a pre-order traversal sequence.
The pre-order traversal sequence used by the C++ implementation to deserialize a binary tree follows as: C++ Program: Output inorder traversal of deserialized tree follows as 4 2 1 5 3 Time Complexity This method goes over the entire sequence and generates a fresh node for each value. Because N is the length of the sequence, the time complexity will be O(N). Space Complexity However, this method effectively keeps a recursion stack of size O(H), in which H is the height of a binary tree, without the need for any additional space. Technique 2: Post-order TraversalThe expected procedure for deserializing a post-order traversal sequence is to first construct the left child, then construct the right child, and then construct the current node. However, without first building the current node, we are unable to access child nodes. As a result, we move through the sequence backwards while adhering to the current, right, and left directions. Keep in mind that the specified sequence must equal the original tree's pre-order traversal. Otherwise, the original tree will not be recreated by the pre-order deserialization. The following is the deserialization procedure for a post-order traversal sequence.
Implementation The post-order traversal sequence's binary tree deserialization in C++ is implemented as C++ Program: Output inorder traversal of deserialized tree follows as 4 2 1 5 3 Time Complexity This method goes over the entire sequence and generates a new node for each value. Because N is the length of the sequence, the time complexity will be O(N). Space Complexity However, this method effectively keeps a recursion stack of size O(H), in which H is the height of a binary tree, without the need for any additional space. Serialization and Deserialization Benefits
ConclusionLet's review the steps for serializing and deserializing a binary tree.
Next TopicApplication of Binary Tree
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









