Red-black tree in Data StructureThe red-Black tree is a binary search tree. The prerequisite of the red-black tree is that we should know about the binary search tree. In a binary search tree, the values of the nodes in the left subtree should be less than the value of the root node, and the values of the nodes in the right subtree should be greater than the value of the root node. Each node in the Red-black tree contains an extra bit that represents a color to ensure that the tree is balanced during any operations performed on the tree like insertion, deletion, etc. In a binary search tree, the searching, insertion and deletion take O(log2n) time in the average case, O(1) in the best case and O(n) in the worst case. Let's understand the different scenarios of a binary search tree. 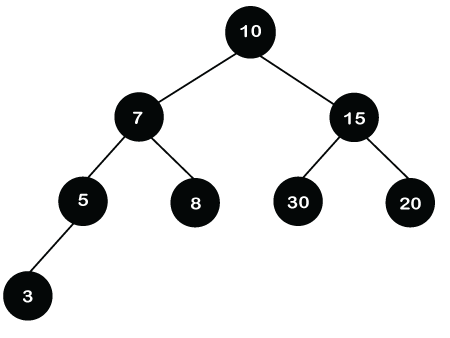
In the above tree, if we want to search the 80. We will first compare 80 with the root node. 80 is greater than the root node, i.e., 10, so searching will be performed on the right subtree. Again, 80 is compared with 15; 80 is greater than 15, so we move to the right of the 15, i.e., 20. Now, we reach the leaf node 20, and 20 is not equal to 80. Therefore, it will show that the element is not found in the tree. After each operation, the search is divided into half. The above BST will take O(logn) time to search the element. 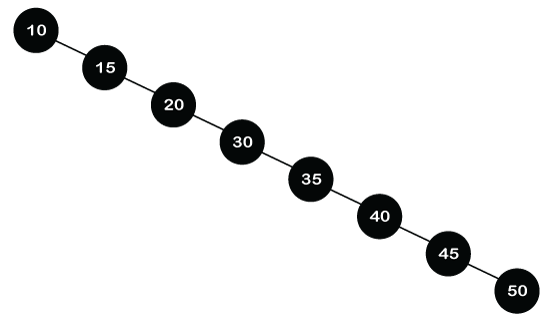
The above tree shows the right-skewed BST. If we want to search the 80 in the tree, we will compare 80 with all the nodes until we find the element or reach the leaf node. So, the above right-skewed BST will take O(N) time to search the element. In the above BST, the first one is the balanced BST, whereas the second one is the unbalanced BST. We conclude from the above two binary search trees that a balanced tree takes less time than an unbalanced tree for performing any operation on the tree. Therefore, we need a balanced tree, and the Red-Black tree is a self-balanced binary search tree. Now, the question arises that why do we require a Red-Black tree if AVL is also a height-balanced tree. The Red-Black tree is used because the AVL tree requires many rotations when the tree is large, whereas the Red-Black tree requires a maximum of two rotations to balance the tree. The main difference between the AVL tree and the Red-Black tree is that the AVL tree is strictly balanced, while the Red-Black tree is not completely height-balanced. So, the AVL tree is more balanced than the Red-Black tree, but the Red-Black tree guarantees O(log2n) time for all operations like insertion, deletion, and searching. Insertion is easier in the AVL tree as the AVL tree is strictly balanced, whereas deletion and searching are easier in the Red-Black tree as the Red-Black tree requires fewer rotations. As the name suggests that the node is either colored in Red or Black color. Sometimes no rotation is required, and only recoloring is needed to balance the tree. Properties of Red-Black tree
Is every AVL tree can be a Red-Black tree?Yes, every AVL tree can be a Red-Black tree if we color each node either by Red or Black color. But every Red-Black tree is not an AVL because the AVL tree is strictly height-balanced while the Red-Black tree is not completely height-balanced. Insertion in Red Black treeThe following are some rules used to create the Red-Black tree:
4a) If the color is Black, then we perform rotations and recoloring. 4b) If the color is Red then we recolor the node. We will also check whether the parents' parent of a new node is the root node or not; if it is not a root node, we will recolor and recheck the node. Let's understand the insertion in the Red-Black tree. 10, 18, 7, 15, 16, 30, 25, 40, 60 Step 1: Initially, the tree is empty, so we create a new node having value 10. This is the first node of the tree, so it would be the root node of the tree. As we already discussed, that root node must be black in color, which is shown below: 
Step 2: The next node is 18. As 18 is greater than 10 so it will come at the right of 10 as shown below. 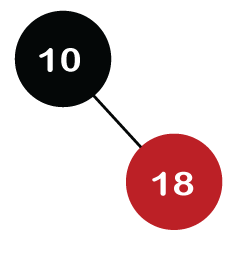
We know the second rule of the Red Black tree that if the tree is not empty then the newly created node will have the Red color. Therefore, node 18 has a Red color, as shown in the below figure: Now we verify the third rule of the Red-Black tree, i.e., the parent of the new node is black or not. In the above figure, the parent of the node is black in color; therefore, it is a Red-Black tree. Step 3: Now, we create the new node having value 7 with Red color. As 7 is less than 10, so it will come at the left of 10 as shown below. 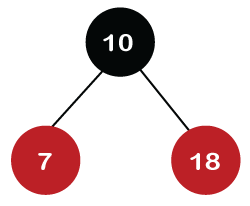
Now we verify the third rule of the Red-Black tree, i.e., the parent of the new node is black or not. As we can observe, the parent of the node 7 is black in color, and it obeys the Red-Black tree's properties. Step 4: The next element is 15, and 15 is greater than 10, but less than 18, so the new node will be created at the left of node 18. The node 15 would be Red in color as the tree is not empty. The above tree violates the property of the Red-Black tree as it has Red-red parent-child relationship. Now we have to apply some rule to make a Red-Black tree. The rule 4 says that if the new node's parent is Red, then we have to check the color of the parent's sibling of a new node. The new node is node 15; the parent of the new node is node 18 and the sibling of the parent node is node 7. As the color of the parent's sibling is Red in color, so we apply the rule 4a. The rule 4a says that we have to recolor both the parent and parent's sibling node. So, both the nodes, i.e., 7 and 18, would be recolored as shown in the below figure. 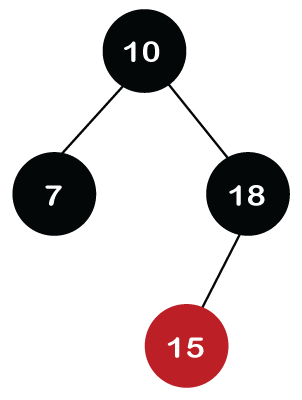
We also have to check whether the parent's parent of the new node is the root node or not. As we can observe in the above figure, the parent's parent of a new node is the root node, so we do not need to recolor it. Step 5: The next element is 16. As 16 is greater than 10 but less than 18 and greater than 15, so node 16 will come at the right of node 15. The tree is not empty; node 16 would be Red in color, as shown in the below figure: 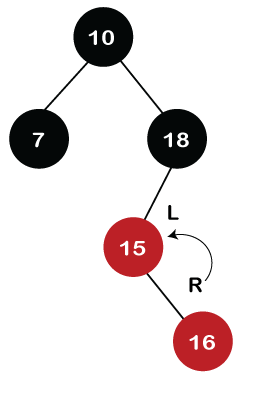
In the above figure, we can observe that it violates the property of the parent-child relationship as it has a red-red parent-child relationship. We have to apply some rules to make a Red-Black tree. Since the new node's parent is Red color, and the parent of the new node has no sibling, so rule 4a will be applied. The rule 4a says that some rotations and recoloring would be performed on the tree. Since node 16 is right of node 15 and the parent of node 15 is node 18. Node 15 is the left of node 18. Here we have an LR relationship, so we require to perform two rotations. First, we will perform left, and then we will perform the right rotation. The left rotation would be performed on nodes 15 and 16, where node 16 will move upward, and node 15 will move downward. Once the left rotation is performed, the tree looks like as shown in the below figure: 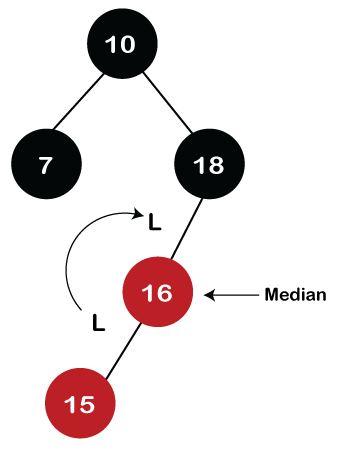
In the above figure, we can observe that there is an LL relationship. The above tree has a Red-red conflict, so we perform the right rotation. When we perform the right rotation, the median element would be the root node. Once the right rotation is performed, node 16 would become the root node, and nodes 15 and 18 would be the left child and right child, respectively, as shown in the below figure. 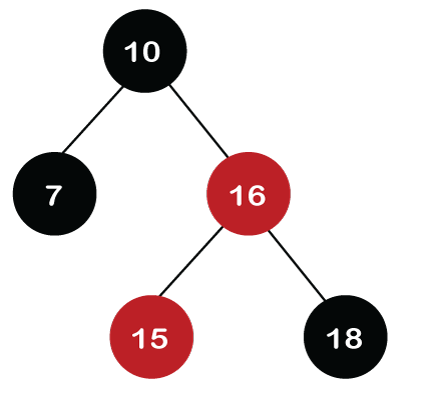
After rotation, node 16 and node 18 would be recolored; the color of node 16 is red, so it will change to black, and the color of node 18 is black, so it will change to a red color as shown in the below figure: 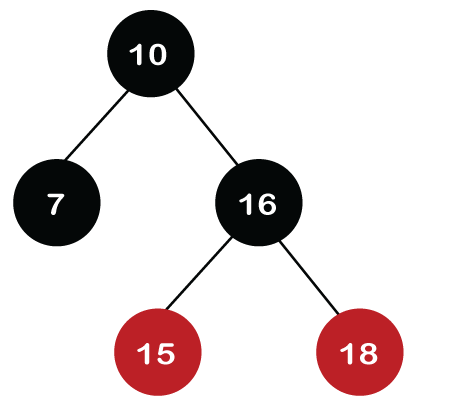
Step 6: The next element is 30. Node 30 is inserted at the right of node 18. As the tree is not empty, so the color of node 30 would be red. 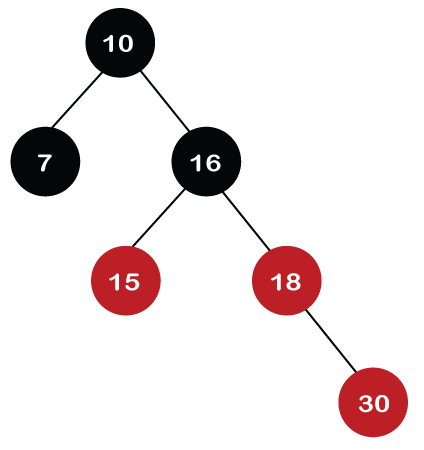
The color of the parent and parent's sibling of a new node is Red, so rule 4b is applied. In rule 4b, we have to do only recoloring, i.e., no rotations are required. The color of both the parent (node 18) and parent's sibling (node 15) would become black, as shown in the below image. 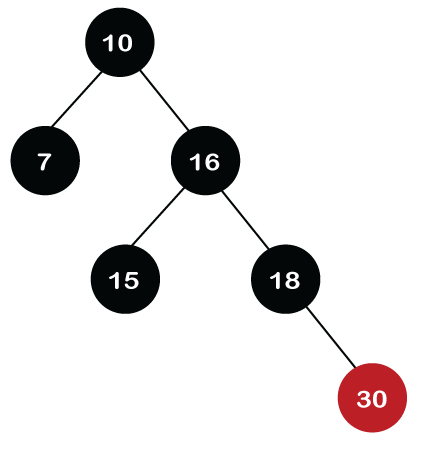
We also have to check the parent's parent of the new node, whether it is a root node or not. The parent's parent of the new node, i.e., node 30 is node 16 and node 16 is not a root node, so we will recolor the node 16 and changes to the Red color. The parent of node 16 is node 10, and it is not in Red color, so there is no Red-red conflict. 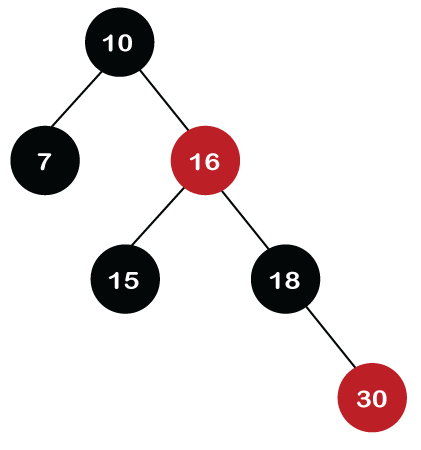
Step 7: The next element is 25, which we have to insert in a tree. Since 25 is greater than 10, 16, 18 but less than 30; so, it will come at the left of node 30. As the tree is not empty, node 25 would be in Red color. Here Red-red conflict occurs as the parent of the newly created is Red color. Since there is no parent's sibling, so rule 4a is applied in which rotation, as well as recoloring, are performed. First, we will perform rotations. As the newly created node is at the left of its parent and the parent node is at the right of its parent, so the RL relationship is formed. Firstly, the right rotation is performed in which node 25 goes upwards, whereas node 30 goes downwards, as shown in the below figure. 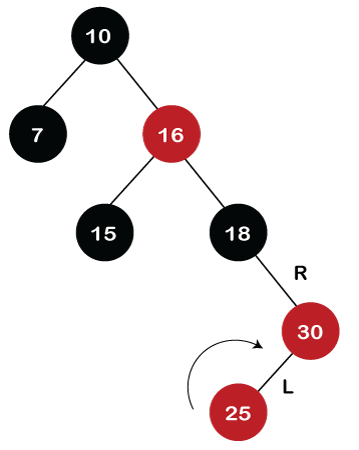
After the first rotation, there is an RR relationship, so left rotation is performed. After right rotation, the median element, i.e., 25 would be the root node; node 30 would be at the right of 25 and node 18 would be at the left of node 25. 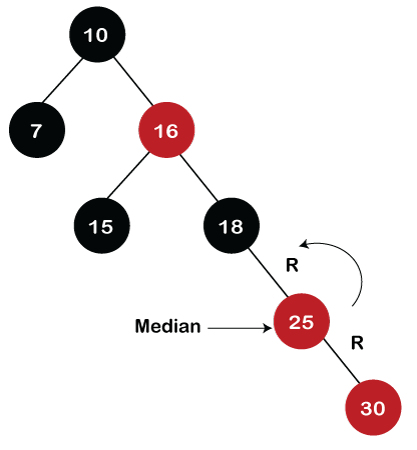
Now recoloring would be performed on nodes 25 and 18; node 25 becomes black in color, and node 18 becomes red in color. 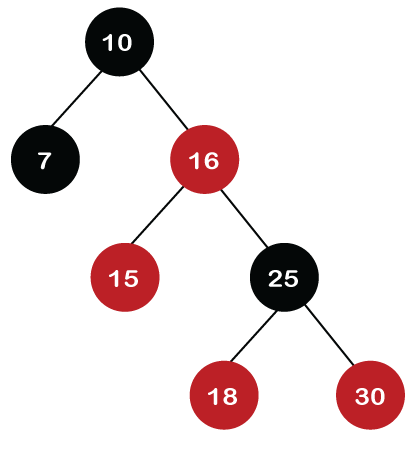
Step 8: The next element is 40. Since 40 is greater than 10, 16, 18, 25, and 30, so node 40 will come at the right of node 30. As the tree is not empty, node 40 would be Red in color. There is a Red-red conflict between nodes 40 and 30, so rule 4b will be applied. 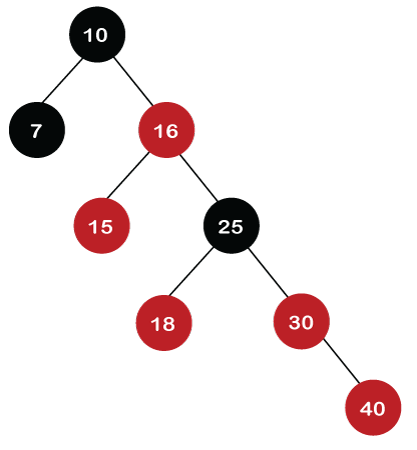
As the color of parent and parent's sibling node of a new node is Red so recoloring would be performed. The color of both the nodes would become black, as shown in the below image. After recoloring, we also have to check the parent's parent of a new node, i.e., 25, which is not a root node, so recoloring would be performed, and the color of node 25 changes to Red. After recoloring, red-red conflict occurs between nodes 25 and 16. Now node 25 would be considered as the new node. Since the parent of node 25 is red in color, and the parent's sibling is black in color, rule 4a would be applied. Since 25 is at the right of the node 16 and 16 is at the right of its parent, so there is an RR relationship. In the RR relationship, left rotation is performed. After left rotation, the median element 16 would be the root node, as shown in the below figure. 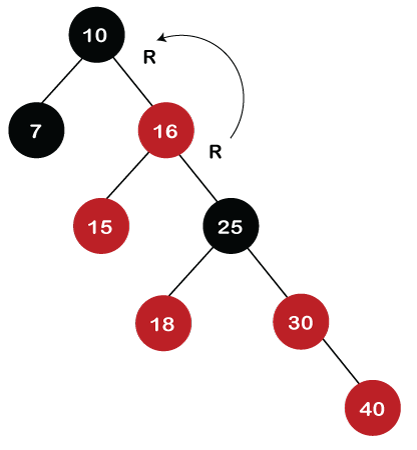
After rotation, recoloring is performed on nodes 16 and 10. The color of node 10 and node 16 changes to Red and Black, respectively as shown in the below figure. 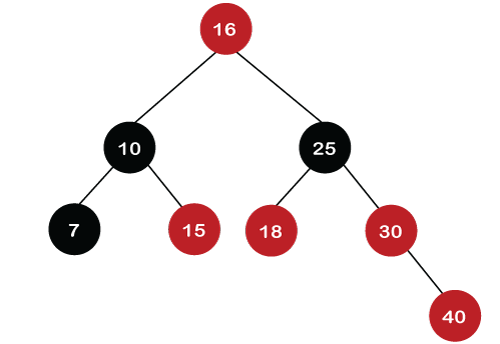
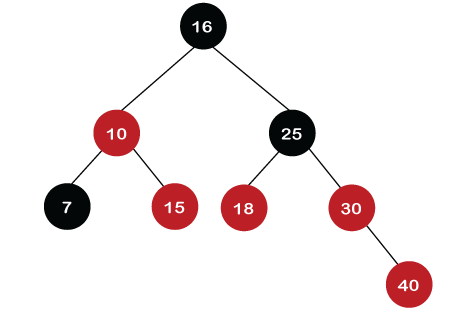
Step 9: The next element is 60. Since 60 is greater than 16, 25, 30, and 40, so node 60 will come at the right of node 40. As the tree is not empty, the color of node 60 would be Red. As we can observe in the above tree that there is a Red-red conflict occurs. The parent node is Red in color, and there is no parent's sibling exists in the tree, so rule 4a would be applied. The first rotation would be performed. The RR relationship exists between the nodes, so left rotation would be performed. 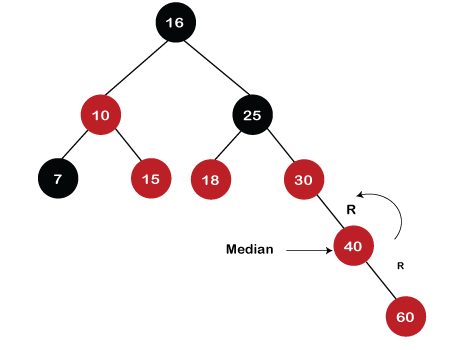
When left rotation is performed, node 40 will come upwards, and node 30 will come downwards, as shown in the below figure: 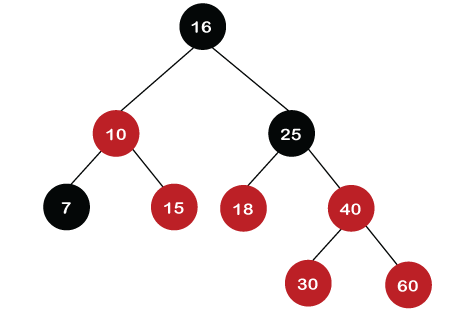
After rotation, the recoloring is performed on nodes 30 and 40. The color of node 30 would become Red, while the color of node 40 would become black. 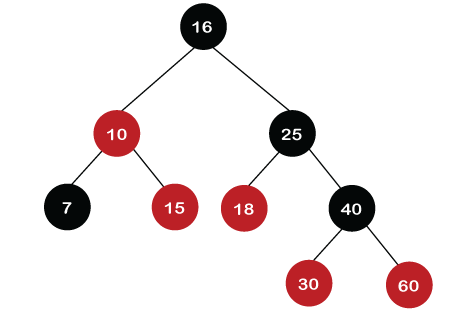
The above tree is a Red-Black tree as it follows all the Red-Black tree properties. Deletion in Red Back treeLet's understand how we can delete the particular node from the Red-Black tree. The following are the rules used to delete the particular node from the tree: Step 1: First, we perform BST rules for the deletion. Step 2: Case 1: if the node is Red, which is to be deleted, we simply delete it. Let's understand case 1 through an example. Suppose we want to delete node 30 from the tree, which is given below. 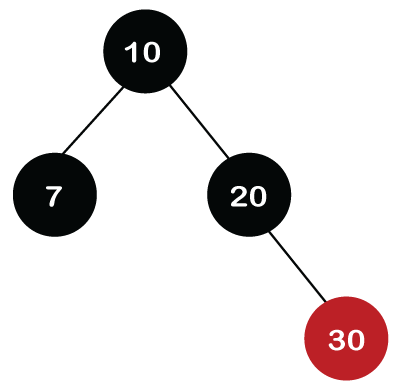
Initially, we are having the address of the root node. First, we will apply BST to search the node. Since 30 is greater than 10 and 20, which means that 30 is the right child of node 20. Node 30 is a leaf node and Red in color, so it is simply deleted from the tree. If we want to delete the internal node that has one child. First, replace the value of the internal node with the value of the child node and then simply delete the child node. Let's take another example in which we want to delete the internal node, i.e., node 20. 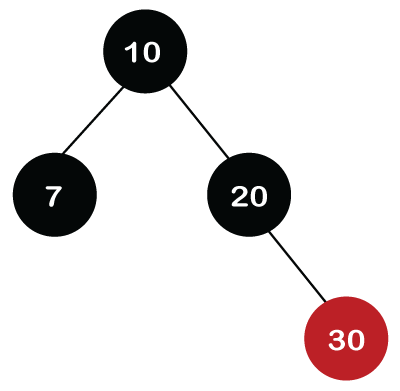
We cannot delete the internal node; we can only replace the value of that node with another value. Node 20 is at the right of the root node, and it is having only one child, node 30. So, node 20 is replaced with a value 30, but the color of the node would remain the same, i.e., Black. In the end, node 20 (leaf node) is deleted from the tree. 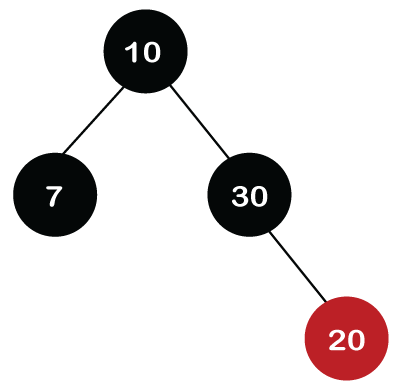
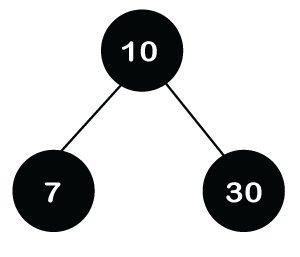
If we want to delete the internal node that has two child nodes. In this case, we have to decide from which we have to replace the value of the internal node (either left subtree or right subtree). We have two ways:
Suppose we want to delete node 30 from the tree, which is shown below: 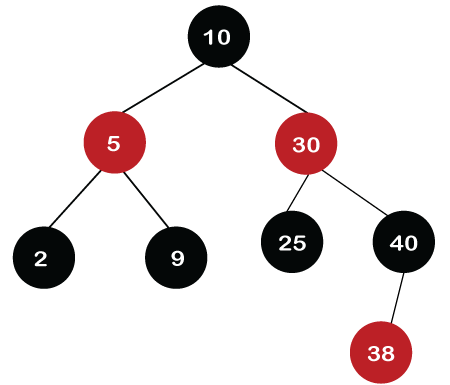
Node 30 is at the right of the root node. In this case, we will use the inorder successor. The value 38 is the smallest value in the right subtree, so we will replace the value 30 with 38, but the node would remain the same, i.e., Red. After replacement, the leaf node, i.e., 30, would be deleted from the tree. Since node 30 is a leaf node and Red in color, we need to delete it (we do not have to perform any rotations or any recoloring). 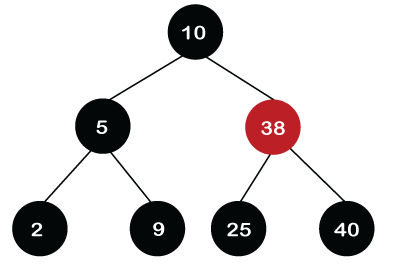
Case 2: If the root node is also double black, then simply remove the double black and make it a single black. Case 3: If the double black's sibling is black and both its children are black.
Let's understand this case through an example. Suppose we want to delete node 15 in the below tree. 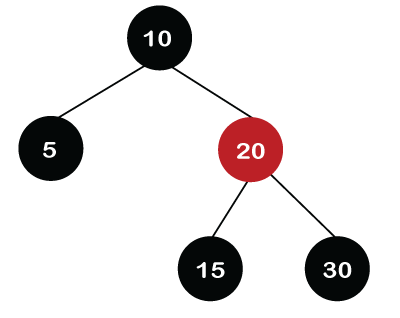
We cannot simply delete node 15 from the tree as node 15 is Black in color. Node 15 has two children, which are nil. So, we replace the 15 value with a nil value. As node 15 and nil node are black in color, the node becomes double black after replacement, as shown in the below figure. 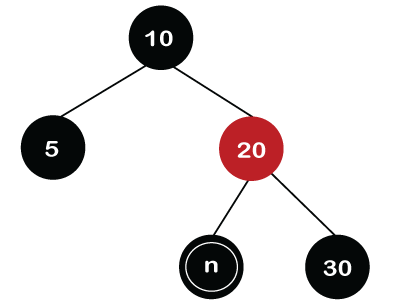
In the above tree, we can observe that the double black's sibling is black in color and its children are nil, which are also black. As the double black's sibling and its children have black so it cannot give its black color to neither of these. Now, the double black's parent node is Red so double black's node add its black color to its parent node. The color of the node 20 changes to black while the color of the nil node changes to a single black as shown in the below figure. 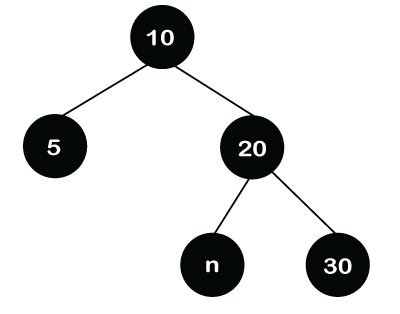
After adding the color to its parent node, the color of the double black's sibling, i.e., node 30 changes to red as shown in the below figure. In the above tree, we can observe that there is no longer double black's problem exists, and it is also a Red-Black tree. Case 4: If double black's sibling is Red.
Let's understand this case through an example. Suppose we want to delete node 15. 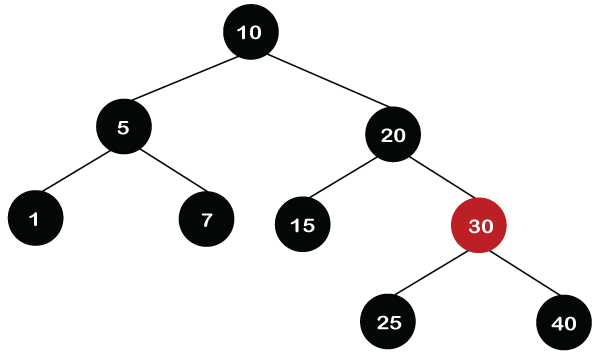
Initially, the 15 is replaced with a nil value. After replacement, the node becomes double black. Since double black's sibling is Red so color of the node 20 changes to Red and the color of the node 30 changes to Black. Once the swapping of the color is completed, the rotation towards the double black would be performed. The node 30 will move upwards and the node 20 will move downwards as shown in the below figure. 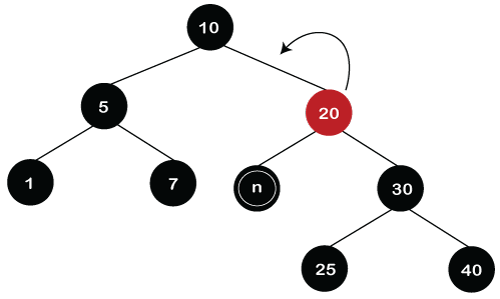
In the above tree, we can observe that double black situation still exists in the tree. It satisfies the case 3 in which double black's sibling is black as well as both its children are black. First, we remove the double black from the node and add the black color to its parent node. At the end, the color of the double black's sibling, i.e., node 25 changes to Red as shown in the below figure. 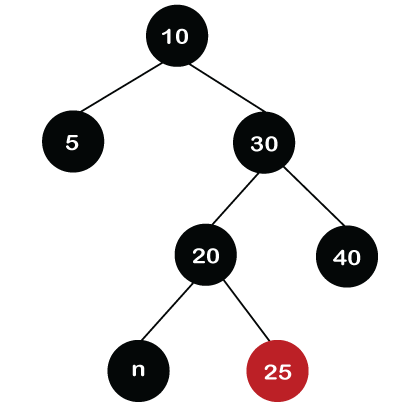
In the above tree, we can observe that the double black situation has been resolved. It also satisfies the properties of the Red Black tree. Case 5: If double black's sibling is black, sibling's child who is far from the double black is black, but near child to double black is red.
Suppose we want to delete the node 1 in the below tree. 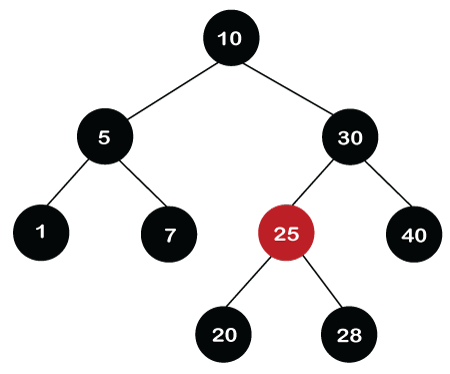
First, we replace the value 1 with the nil value. The node becomes double black as both the nodes, i.e., 1 and nil are black. It satisfies the case 3 that implies if DB's sibling is black and both its children are black. First, we remove the double black of the nil node. Since the parent of DB is Black, so when the black color is added to the parent node then it becomes double black. After adding the color, the double black's sibling color changes to Red as shown below. 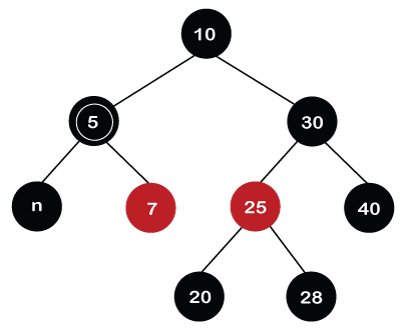
We can observe in the above screenshot that the double black problem still exists in the tree. So, we will reapply the cases. We will apply case 5 because the sibling of node 5 is node 30, which is black in color, the child of node 30, which is far from node 5 is black, and the child of the node 30 which is near to node 5 is Red. In this case, first we will swap the color of node 30 and node 25 so the color of node 30 changes to Red and the color of node 25 changes to Black as shown below. 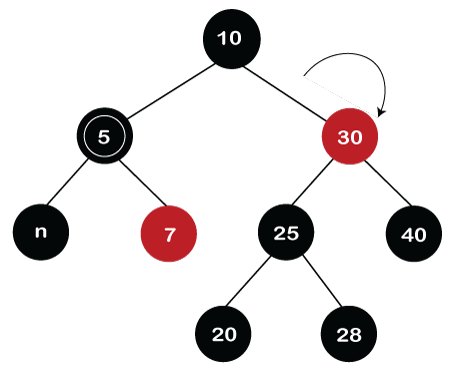
Once the swapping of the color between the nodes is completed, we need to rotate the sibling in the opposite direction of the double black node. In this rotation, the node 30 moves downwards while the node 25 moves upwards as shown below. 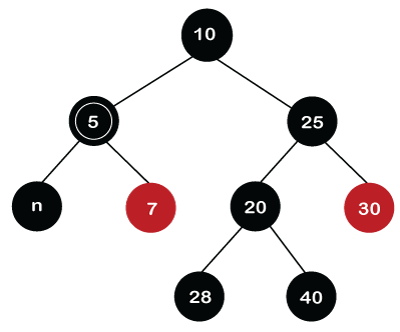
As we can observe in the above tree that double black situation still exists. So, we need to case 6. Let's first see what is case 6. Case 6: If double black's sibling is black, far child is Red
Now we will apply case 6 in the above example to solve the double black's situation. In the above example, the double black is node 5, and the sibling of node 5 is node 25, which is black in color. The far child of the double black node is node 30, which is Red in color as shown in the below figure: 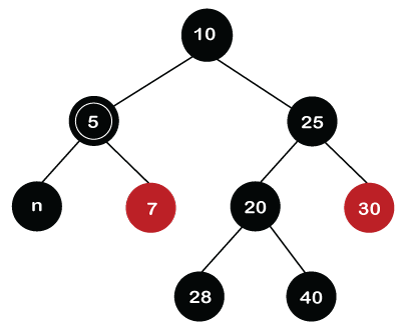
First, we will swap the colors of Parent and its sibling. The parent of node 5 is node 10, and the sibling node is node 25. The colors of both the nodes are black, so there is no swapping would occur. In the second step, we need to rotate the parent in the double black's direction. After rotation, node 25 will move upwards, whereas node 10 will move downwards. Once the rotation is performed, the tree would like, as shown in the below figure: 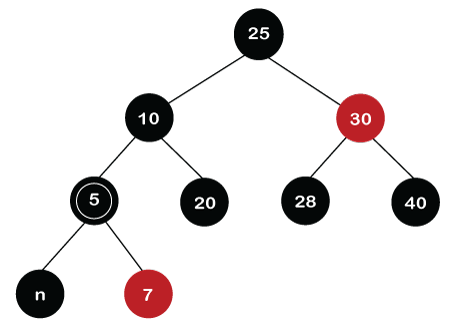
In the next step, we will remove double black from node 5 and node 5 will give its black color to the far child, i.e., node 30. Therefore, the color of node 30 changes to black as shown in the below figure. 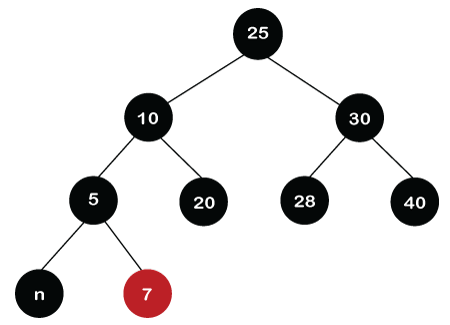
Now let us implement the Red-black tree Data Structure in the java programming language. Java Code:Output: Red Black Tree Test The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 10 RBT in Post-order: 10B RBT in Pre-order: 10B RBT in In-order: 10B Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 18 RBT in Post-order: 18R 10B RBT in Pre-order: 10B 18R RBT in In-order: 10B 18R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 45 RBT in Post-order: 10R 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10R 45R RBT in In-order: 10R 18B 45R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 33 RBT in Post-order: 10B 33R 45B 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45B 33R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 33R 45B Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 87 RBT in Post-order: 10B 33R 87R 45B 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45B 33R 87R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 33R 45B 87R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 90 RBT in Post-order: 10B 33B 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 87B 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 33B 45R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 31 RBT in Post-order: 10B 31R 33B 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 31R 87B 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 31R 33B 45R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 1 Enter integer node_data to insert 77 RBT in Post-order: 10B 31R 33B 77R 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 31R 87B 77R 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 31R 33B 45R 77R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 2 Enter integer node_data to search 18 Search result: true RBT in Post-order: 10B 31R 33B 77R 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 31R 87B 77R 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 31R 33B 45R 77R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 3 Nodes = 8 RBT in Post-order: 10B 31R 33B 77R 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 31R 87B 77R 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 31R 33B 45R 77R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 4 Empty status = false RBT in Post-order: 10B 31R 33B 77R 90R 87B 45R 18B RBT in Pre-order: 18B 10B 45R 33B 31R 87B 77R 90R RBT in In-order: 10B 18B 31R 33B 45R 77R 87B 90R Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 5 Tree Cleared RBT in Post-order: RBT in Pre-order: RBT in In-order: Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? y The options list for Red Black Tree:: 1. To add a new node in the Red-Black Tree 2. To search the Red-Black Tree for a node 3. To get node count of nodes in Red Black Tree 4. To check if the Red_Black_Tree is Empty or not? 5. To Clear the Red_Black_Tree. 4 Empty status = true RBT in Post-order: RBT in Pre-order: RBT in In-order: Wanna proceed further(Type y or n)? n Now let us see a code in C++ language to implement RBT data structure. C++ Code:Output:
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 1
Key value for the node_of_the_red_black_tree to insert_a_node_to_rbt in RBT: 12
New node_of_the_red_black_tree added.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 1
Key value for the node_of_the_red_black_tree to insert_a_node_to_rbt in RBT: 45
New node_of_the_red_black_tree added.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 1
Key value for the node_of_the_red_black_tree to insert_a_node_to_rbt in RBT: 23
New node_of_the_red_black_tree added.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 1
Key value for the node_of_the_red_black_tree to insert_a_node_to_rbt in RBT: 98
New node_of_the_red_black_tree added.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 4
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 23
Colour: Black
Parent: 12
Right Child: 45
Left Child: 12
Left:
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 12
Colour: Black
Parent: 23
no right child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
Right:
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 45
Colour: Black
Parent: 23
Right Child: 98
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
Right:
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 98
Colour: Red
Parent: 45
no right child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 2
Enter key of the node_of_the_red_black_tree to be search_rbt_nodeed: 98
FOUND node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 98
Colour: Red
Parent: 45
no right child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 3
Enter the key of the node_of_the_red_black_tree to be del_rbt_nodeeted: 45
del_rbt_nodeeted Element: 45
Colour: Black
Parent: 23
Right Child: 98
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
node_of_the_red_black_tree del_rbt_nodeeted.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 4
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 23
Colour: Black
Parent: 12
Right Child: 98
Left Child: 12
Left:
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 12
Colour: Black
Parent: 23
no right child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
Right:
node_of_the_red_black_tree:
Key: 98
Colour: Red
Parent: 23
no right child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
no left child node_of_the_red_black_tree present.
The options list for Red Black Tree::
1. To add a new node_of_the_red_black_tree in the Red-Black Tree
2. To search_rbt_node the Red-Black Tree for a node_of_the_red_black_tree
3. To del_rbt_nodeete an existing Red-Black tree node_of_the_red_black_tree
4. To display all the node_of_the_red_black_trees of the Red-Black Tree
5. To exit the code execution.
Input: 5
Next TopicDS Graph
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









