Excel text functionAlthough Excel is mostly all about numeric data, but it also contains text and string data. To manage and perform operations with text data, we require text functions to simplify things. Excel offers various text functions, such as Len(), Replace(), left(), right(), concatenate(), text(), trim(), and many more. These functions are available Text dropdown list inside the Formula tab. They help to manipulate the text data in Excel. Besides these text functions, a function named TEXT() is also offered by Excel that is used for number to text conversion. In this chapter, we will discuss the TEXT() function of Excel rather than all the text functions. TEXT() functionExcel TEXT() function is a function that allows the users to convert the number to text in Excel spreadsheets. It is an Excel built-in function. You can use this function within the Excel spreadsheet for the number to text conversion. "Data converted using TEXT() function cannot be used for calculation as they changed into the text format. So, if you want to use them in calculation, also keep the original data in another cell." This function is categorized into the text/string functions category. With the help of this function, a numeric value can be converted into a text string. SyntaxThe TEXT() function accepts two parameters: value and formating_text. Following is the formula of TEXT() function - ParametersValue - It takes the value to which you would like to format. Formating_text - It is a format in which way you want to format the value. Or you can understand it as - it contains the formatting code that you want to apply on value. Return ValueThe TEXT() function returns the values after converting to a specific text format. Why this function is required?The TEXT() function is used in the following circumstances:
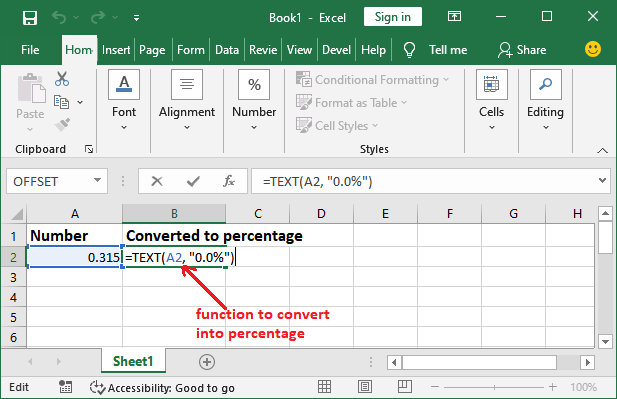
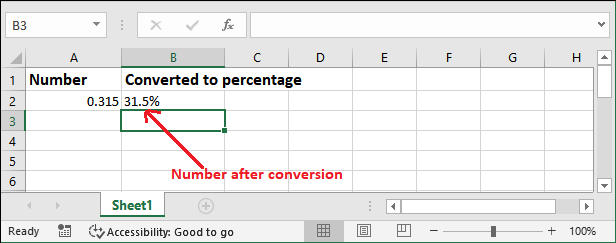
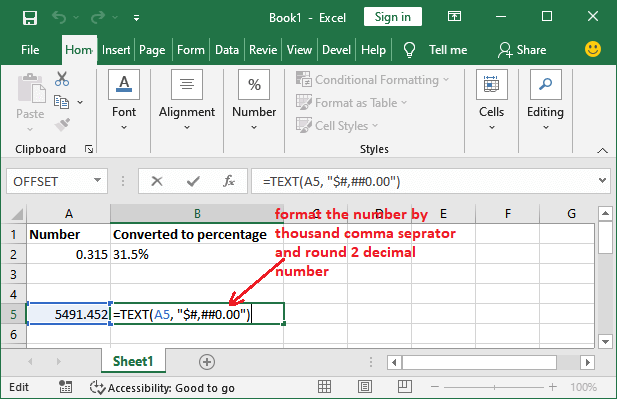
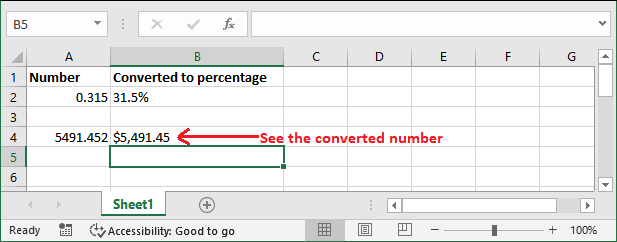
Basic Example: Format numbersWe have taken a simple example to format the numbers using the TEXT() function.
Note: When the TEXT() function applies to any type of value, it converts to the text format. Thus, you cannot use these values further for numeric calculation.Similarly, you can do more number formatting using this function. Formatting codesExcel offers some formatting codes to be used with the TEXT() function. These codes are used while formatting numbers into text.
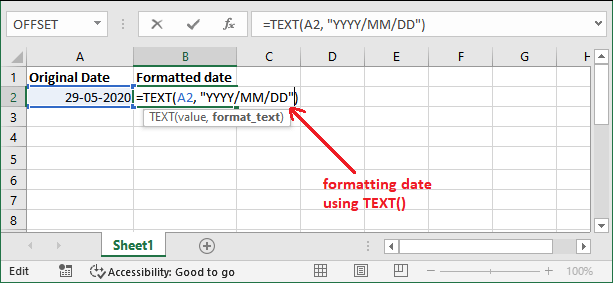
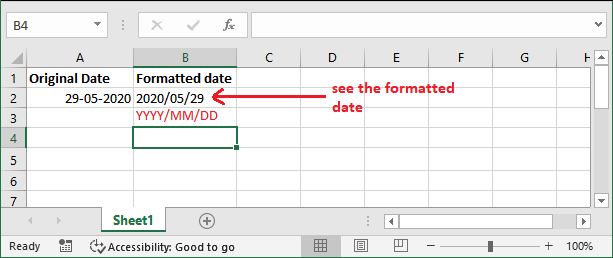
You can use them within the TEXT() function to format your Excel worksheet data however you want. Basic Example: Format dateThis is a simple example to format a date in a specific format using the TEXT() function. We will show you to format the date into YYYY/MM/DD text format in this example. We have a date stored in an A2 cell.
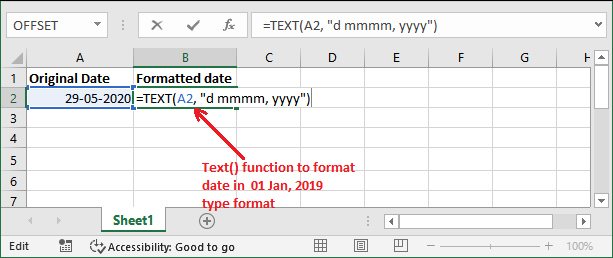
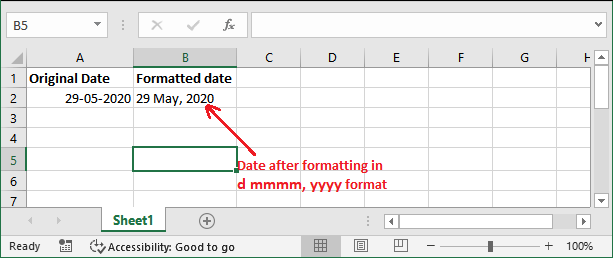
Example 2: date in date, month name, year formatIn this example, we will format the date in date, month, year format. But the month will be the month name instead of month number. It is a special date format. We have to provide formatting_text value d mmmm, yyyy.
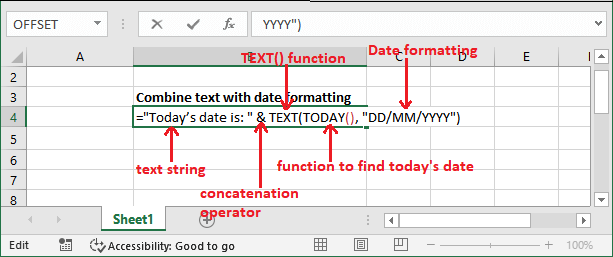
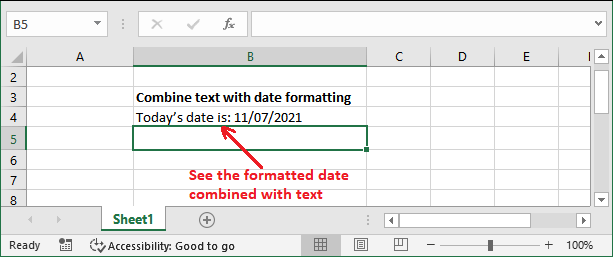
Example: Combining text with dateAs we told you that the TEXT() function allows to combine the numbers with text/string. Similarly, we can also combine text/ string with a date. In this example, we will format the date with a text string with the help of TEXT() function. We will do with today's date. If you try to do it by simply combining the string using the formula like this - ="Today's date is: " & TODAY() 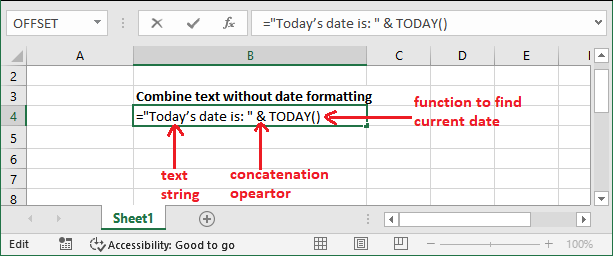
The result will be something like without date formatting: 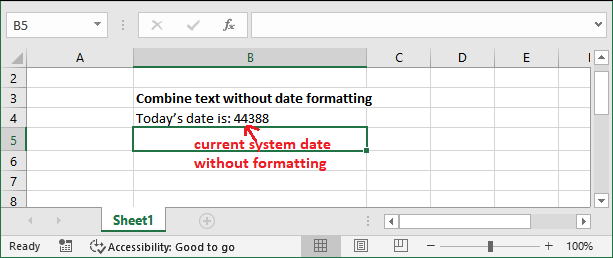
Without apply any formatting to the date, the returned resultant date is unreadable. Although it has been combined with the text string. Hence, add the formatting with date using the TEXT() function. Add the formatting with dateFirstly, we will get today's date using the TODAY() function that will be nested inside the TEXT() function with a date format. That date will be then concatenated with text string using & operator. Now, see how it will take place to get today's formatted date with text data.
Popular ExamplesThe TEXT() functions can be used alone and with other functions. This means it can also be used with other functions by nesting them inside it. Here, we have some popular examples with their description to see that how the TEXT() function works with different data.
In the same way, TEXT() function helps to achieve different results. You can use it anywhere you need and do more tasks as you want. #NAME? ErrorYou may get this #NAME? Error while using TEXT() function. This error usually occurs when you skip the quotation mark (" ") around the formatting code in second parameter value. For example, You have provided a date format without quotation marks like this dd-mm-yyyy. It is incorrect that is why the TEXT() function will return #NAME? Error. Let's understand with a complete example - If you write a TEXT() formula =TEXT(A2, dd-mm-yyyy) to format a date, it would give #NAME? Error because the formula is incorrect. You need to write the formula this way: =TEXT(A2, "dd-mm-yyyy") Remember that the formatting text always be passed inside double-quotes.
Next TopicExcel LOOKUP() function
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share