Excel COUNT() Function in Microsoft ExcelWe all know that Microsoft Excel is currently the most popular spreadsheet program, with over 400 built-in functions. And Microsoft Excel is a part of the MS Office suite, and it allows us to perform various operations on the given data set in an Excel sheet as well. The COUNT() function is a popular built-in Excel function frequently used within the sheet. This article discusses the step-by-step procedure of applying the Microsoft Excel COUNT() function, including its syntax and examples. What is the COUNT Function in Excel?The "COUNT function" is one of the commonly used built-in functions in Microsoft Excel, and it can be used from a category of "Statistical Functions "on the ribbon in the MS Excel program. The COUNT function is primarily used to count the total number of cells with numeric values and the number of arguments with numeric values from the supplied range of cells. This function can accept a series of numeric values and determine the number of cells containing numerical values within the given range accordingly. The "COUNT function" is typically used as a traditional Excel worksheet function. This means that we can also use the Excel COUNT function as part of a formula for one or more desired cells within the Excel sheet. The "COUNT function" is found in all versions of MS Excel, including the latest Office 365, Microsoft Excel 2019, Microsoft Excel 2016, Microsoft Excel 2013, etc. The COUNT function was primarily introduced in Microsoft Excel 2000. Moreover, the respective COUNT function is helpful in financial analysis. It can help us determine or analyze the data if we want to count respective cells in a specified range.
Which values are counted as Numeric Values?Numbers and dates are specific numeric values effectively accepted by the Excel COUNT function. Furthermore, logical values and text representations are treated differently. The COUNT function's behavior depends upon how they are supplied to the COUNT function. Specifically, the COUNT function counts these values based on whether they are used as Excel cells, range, or directly within the function. The following table describes what values are and are not counted as numeric values by the "COUNT function" in Microsoft Excel:
Syntax The following is the syntax of the COUNT function, which is effectively used in Microsoft Excel: In the above syntax, the values are usually represented by the numeric data, arrays, named range, a reference to one or more desired cells, or a range with numbers. Arguments or ParametersThe "COUNT function" must be used with at least one argument, which means that one of the arguments is compulsory in the COUNT function. However, there can be more than one argument depending upon the requirements, but they are optional. The COUNT function has the following arguments or parameters:
In earlier versions of Microsoft Excel, such as Microsoft Excel 2003 and lower, the "COUNT function" accepts up to 30 arguments. However, the limit was increased in later versions. Thus, later versions, such as Microsoft Excel 2007 and higher, support a maximum of 255 individual arguments in the "COUNT function." In addition, we can quickly identify or represent each argument as an array of values or a range of cells, which may contain other values. Returns The "COUNT function" in Microsoft Excel returns the total count of numeric values from the selected or the supplied set of data cells or the ranges of numbers. In other words, it typically returns the count of cells that contain numeric values. How to use the COUNT Function in Excel?Counting the number of values in Microsoft Excel is one of the most basic and straightforward tasks. The "COUNT function" effectively performs this task when counting the number of numeric values within the supplied range. We can apply or use the "COUNT function" as other typical worksheet functions of Microsoft Excel. It means that the COUNT function can be used as a part of the formula in one or more desired cells within the Excel sheet. And to successfully apply the "COUNT function" in its simplest form, we can type it in any specific cell in an Excel sheet and supply random numbers as arguments.
=COUNT(1, 2, 3, 4) In this example, the COUNT function usually returns the output value 4, and it is very much clear that we have supplied four arguments in the COUNT function; thus, the total count of values is 4. Here, the arguments are directly provided to the function as numeric values. However, it is quite rare to work directly with the values in the function as arguments. Generally, we work on the data stored in cells or ranges within the Excel sheet. When working on values registered in Excel cells, we can perform the below steps to apply the "COUNT function" to count the total numeric values from the specified or selected range of cells or a range: Step 1: First of all, we must select a specific cell to store the calculated number of the cells containing numerical values within the desired range. Next, we need to start typing the COUNT function '=COUNT(' in a selected cell without quotation marks respectively. Step 2: After that, we have to type the opening parenthesis and select all the effective cells or range of cells for which we wish to count the number of cells with numeric values. We can also use the "drag feature" with the mouse and select the desired cells or ranges. Step 3: After that, we need to select all the desired cells or ranges and close the "COUNT function" by just typing the ending parenthesis ')' without quotation marks. Step 4: Finally, we must press the "Enter key" from our keyboard to retrieve the counted cells. And for instance, let us now assume that we have the following Excel sheet with some random numbers in cells of column A, and we want to calculate or count the total number of values present in these specific cells, effectively lying in the range A1:A9. Thus, we only need to use the "COUNT function" for this particular range. If we consider cell A10 a result cell, we need to apply the COUNT function in it, similar to the image below: 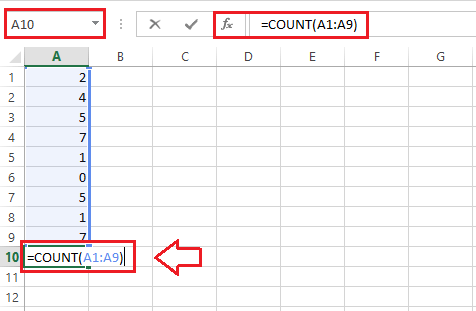
And finally, we need to press the "Enter key" from our keyboard to retrieve the corresponding result of the applied function. 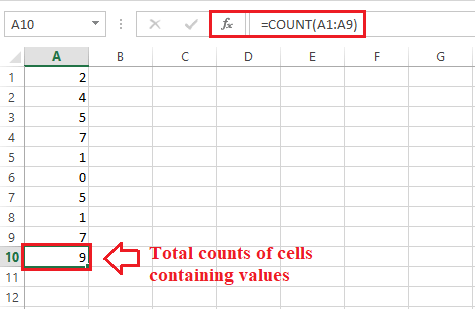
As in the above example, we have the zero value in cell A6; the "COUNT function" has included this in its result. This means the "COUNT function" counts the zero values respectively. This way, we can use the COUNT function and get the total number of values for the specified range of data in an Excel sheet. Let us now understand the different use cases of the COUNT function with the help of the following examples: Excel COUNT Function ExamplesThe following examples discuss the process on how we can use the COUNT function in different ways: Example 1: Counting the Numbers in the Specific Range It is the most common scenario using the "COUNT function" in Microsoft Excel. According to this example, we can easily use the COUNT function in a specified range and count the numbers in the given range. Let us now consider the following Excel sheet with some students' marks, names, and the corresponding subjects and in this, we are required to count the valid numbers in this Excel sheet respectively. 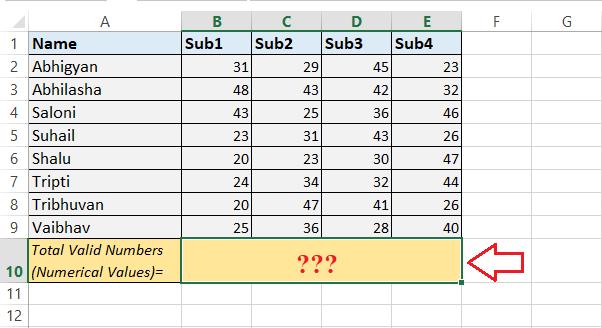
For this, we can efficiently perform the following steps to count the numbers in the given range as well: Step 1: First of all, we must select the cell to apply the "COUNT function" and get the results. We need to select cell B10 as the result cell respectively. 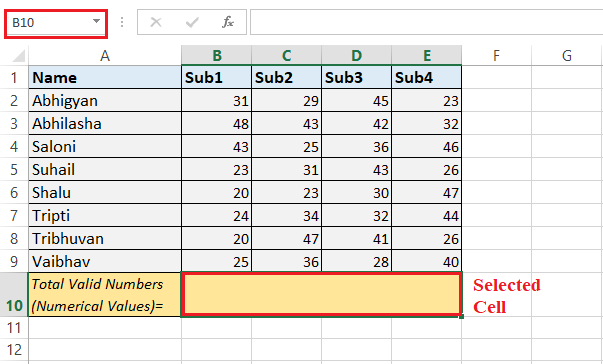
Step 2: Now, just after that, we must type the "COUNT function" in a particular selected cell. Since we want to count the numbers in the entire sheet, we must select the entire range of data ranging from cell A1 to E9 to supply the function. After that, we enter the ending parenthesis. 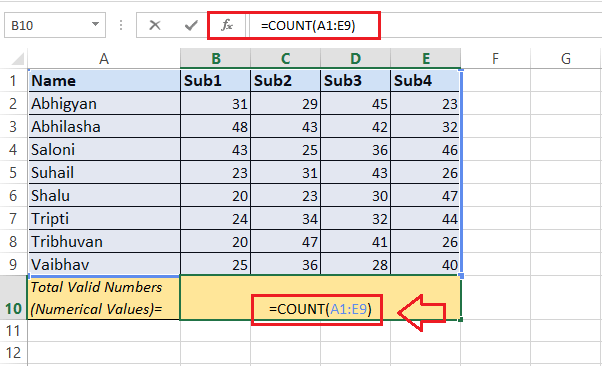
Step 3: Just after entering the "COUNT function" and selecting all the effective cells with data, we need to press the "Enter key" from our keyboard to obtain the result. We will get the total numbers of the cells with the valid numeric values in a result cell immediately, as depicted in the following image: 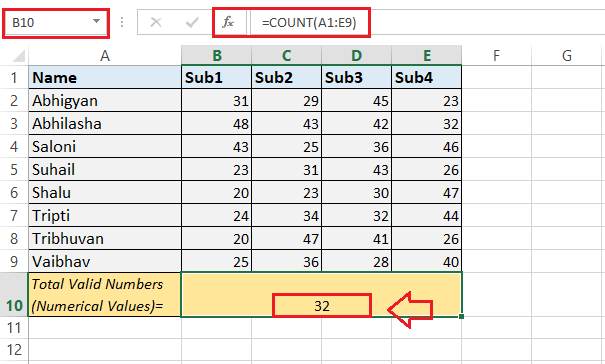
As in the above image, the COUNT function primarily returns 32 because the specified range A1:E9 contains only 32 valid numbers. And we can see that the valid numbers are only registered in a range B2:E9, and the rest of the cells have text values not counted by the "COUNT function." Example 2: Counting the Number of Valid Dates We can also use the "COUNT function" to count the valid dates registered within the Excel sheet respectively. The valid dates are identified in the default date formats present in the Excel configuration. Let us consider the following Microsoft Excel sheet with some ordered products and their delivery dates. As in this Excel sheet, we want to "count the number of valid dates" from the range of delivery dates, which are also effectively displayed in the given sheet. 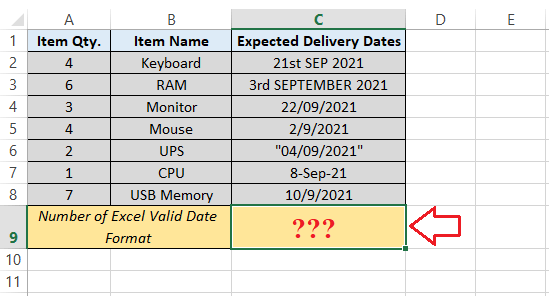
Now we can efficiently perform the following steps to count out the number of valid dates (delivery dates) in the given specified range of dates as well: Step 1: First, we must select a cell to record the number of "valid dates." And it is primarily termed to be the "result cell." For this, we need to select cell C9 respectively. 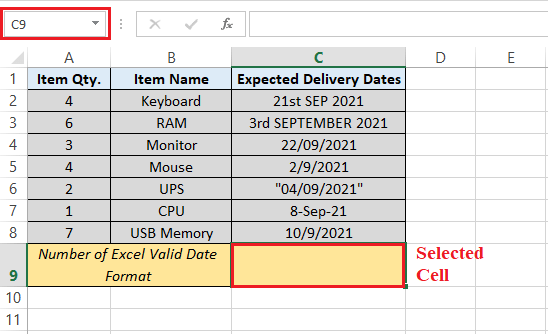
Step 2: Next, we need to type the "COUNT function" in a given result cell for a range of the cells C2:C8 (as it was depicted in the below-mentioned image): 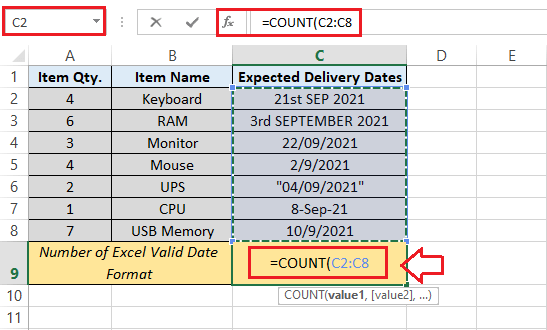
Step 3: After that, we need to type the ending parenthesis and press the "Enter key" from our keyboard to record the results obtained by applying the "COUNT function" respectively. Although the selected range C2:C8 has dates in various formats, few are valid. Specifically, only three dates, written in cells C4, C5, and C8, are valid. Hence, the function returns 3, as shown in the result cell C9 of the following image: 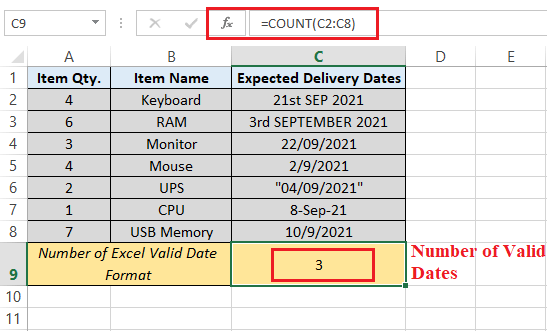
Example 3: Counting the Numbers with Multiple Parameters We can also apply the "COUNT function" to the respective range of the Microsoft Excel cells with multiple parameters, including the direct argument within the function, respectively. Let us consider the following Microsoft Excel sheet with the multiple values (parameters or arguments) in cells. Here, we wish to count the valid numeric values when the additional parameter is used directly in the function, i.e., 6. 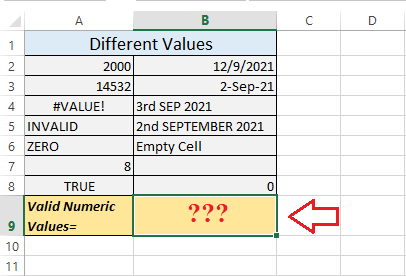
Since we have values in a given range of the cells A2:B8 (as depicted in the above image), we are required to apply the "COUNT function" to this entire range and another parameter 6 directly in the given function. If in case we consider the result cell B9, then we can easily apply the "COUNT function" like this: =COUNT (A2:B8,6) 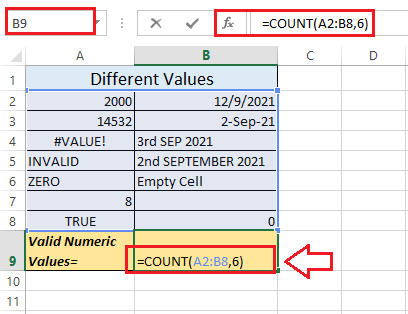
Next, we need to press the "Enter key" from our keyboard to get the results effectively. As in our example, the "COUNT function" returns 7. 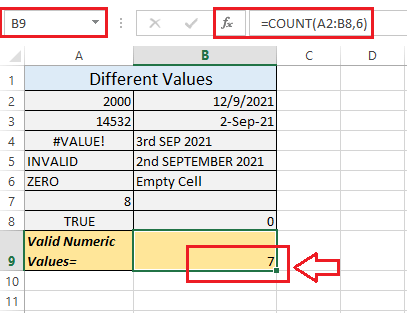
Let us now understand why the function only returns 7 valid numeric values in the above example: The selected range A2:B8 has 6 valid numeric values, written in cells A2, A3, A7, B2, B3, and B8. In addition to this, we have one numeric value (which is 6) in the function that we directly supplied as an argument. Thus, we have 7 valid numeric values in our example. Apart from the valid numeric values, the rest of the values are not counted by the COUNT function. They are text representations (cell A5, A6, and B6), errors (cell A4), invalid date formats (cell B4 and B5), logical value (cell A8) and a blank cell (B7). Some Important Points to RememberThe various essential points that need to be remembered by an individual while working with the "Excel Count ()" Function in Microsoft Excel is as follows: To use the "COUNT function" appropriately, an individual must need to keep the following points or facts in their mind:
Next TopicLine Chart Excel
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









