Excel FV FunctionFuture planning is essential for making your personal and corporate finances. It is one of the most significant factors of success to understand the future perspective and growth of today's investment. To make this step easy, Excel has provided an inbuilt function known as FV (stands for future value). In this tutorial, we will cover the definition, syntax, and the steps to build correct FV formula for a series of cash flows, various examples, and more! What is FV function?The Excel FV function tells the future worth of constant payments at a fixed interest rate (fixed value). It operates for both types of payments, whether a series of periodic payments or a single lump-sum payment. The FV function is categorized under Excel Financial functions. This function is used to return the future value of an investment for a constant rate of interest. The future value (FV) is one of the prime elements that help in various financial modeling and benefits in financial planning. In other words, FV defines how much specific money or asset will rise or grow in the future if it is invested for a specific time. Generally, the Future Value is calculated based on a predicted growth rate or rate of return. Determining a future value is quite easy when the money is deposited in a saving account with a fixed interest rate such as FD (Fixed deposit, RD, etc.). Though some investments have a volatile rate of return, and their interest rate also fluctuates, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities. These kinds of investments are hard to calculate accurately. Fortunately, Microsoft Excel has introduced a special function that does all the necessary calculation for you based on your given parameters. The function was introduced with Excel 2007 and since then has been available in all versions, including Excel 2010, Excel 2013, Excel 2016, Excel 2017, and Excel 365. Syntaxof that number.ParametersRate (required)- This argument represents the rate of interest per period. If you pay once a year, supply an annual interest rate; if you pay the amount each month, then you should supply a monthly interest rate, and so on. Nper (required) - This argument represents the total number of payment periods for the length of an annuity. pmt (required)- This argument represents the payment made for each period. If this parameter is omitted, the default value is 0 but in that case the pv parameter must be included. pv [optional]: This argument represents the current value, or total value of all payments now. Since it is an optional parameter therefore its default value is 0. But if it is omitted in that case the pmt argument must be included. type [optional]: This argument provides the information regarding when payments are due.
Points to Remember about FV FunctionKindly have a look at the below given point to efficiently utilize the FV function in your worksheets and bypass common mistakes in Excel:
ExamplesExample 1: Calculate the present value of the annuity using FV function for the data given in the below table.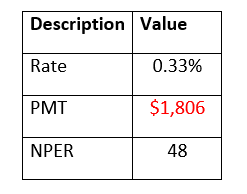
NOTE: In the above example, the pmt parameter is negative (represented by red) as we are investing the amount.To determine the future value for the given rate, pmt and nper follow the below given steps: Step 1: Add helper row at the bottom of table Put your cursor below the table and add your helper row i.e., "Future Value". In this row we will type the FV formula and will fetch the future value for the given data. Refer to the below image: 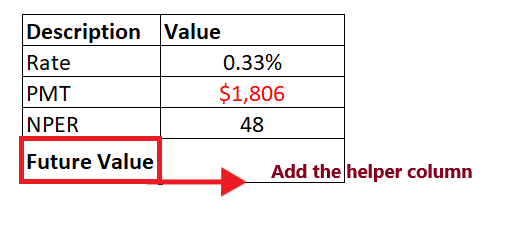
Step 2: Enter the FV formula Move to next cell of your helper row and start typing the formula = FV( It will look similar to the below image: 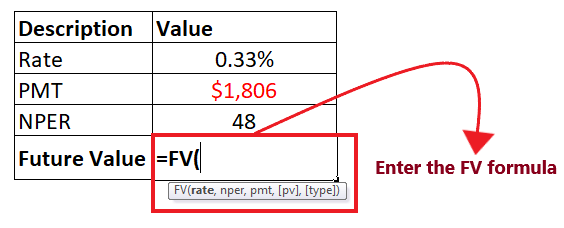
STEP 3: Add the parameter to your formula
The overall formula will look similar to the below image: 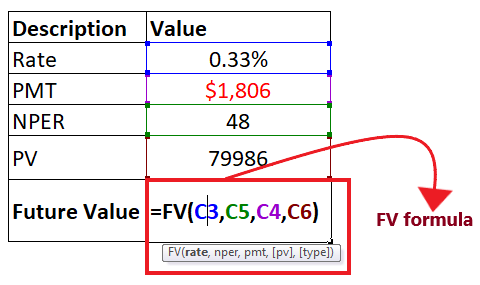
STEP 4: FV will return the output Press the enter button as soon as you are done typing the formula. Excel will return the output for your PV formula. As shown below it will return 0 as an output of your periodic payment. FV is $0, it implies that we will be able to repay the loan of $80,000 we had initially taken by paying 48 monthly installments of $1,806 each. 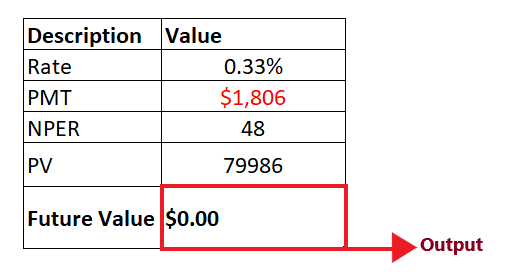
Example 2: Using the FV formula build a common calculator that calculates the future value and work well for both periodic and lump-sum investments.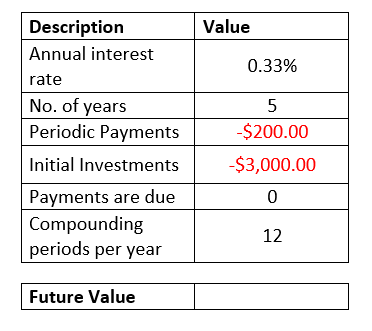
NOTE: In the above example, the pmt (periodic payments) and nper (initial investments) parameters are negative (represented by red) as we are investing the amount.For setting up a future value calculator in Excel below the given steps: Step 1: Add helper row at the bottom of table Put your cursor below the table and type the heading of your helper row i.e., "Future Value". In this row we will type the FV formula and will fetch the future value for both periodic and lump-sum payments with either annuity type. Refer to the below image: 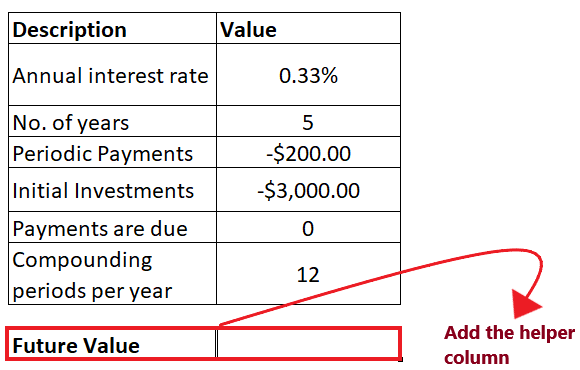
Step 2: Enter the FV formula Move to next cell of your helper row and start typing the formula = FV( It will look similar to the below image: 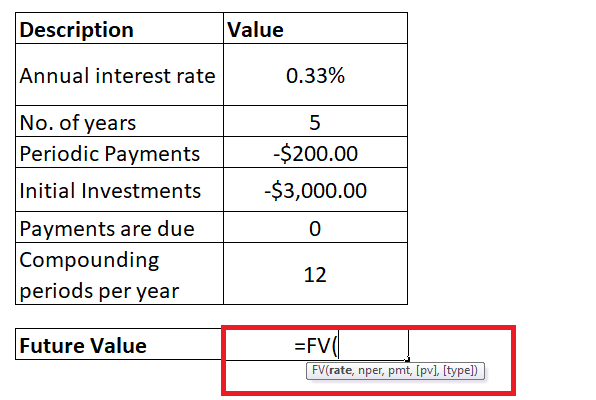
STEP 3: Add the parameter to your formula
NOTE: Always remember to convert annual interest rate to periodic interest rate while working with Excel FV formula for monthly cash flows.
The overall formula will look similar to the below image: 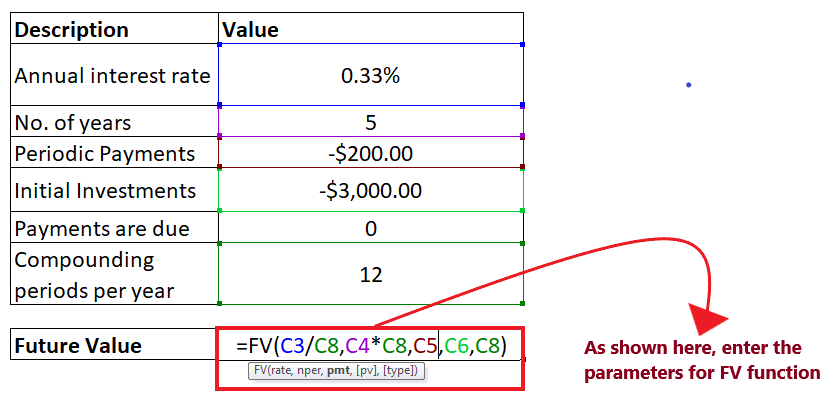
STEP 4: FV will return the output Press the enter button as soon as you are done typing the formula. The FV calculator will return the Future value for the given data. As shown below it will return $15,151.10 as an output of your periodic payment. 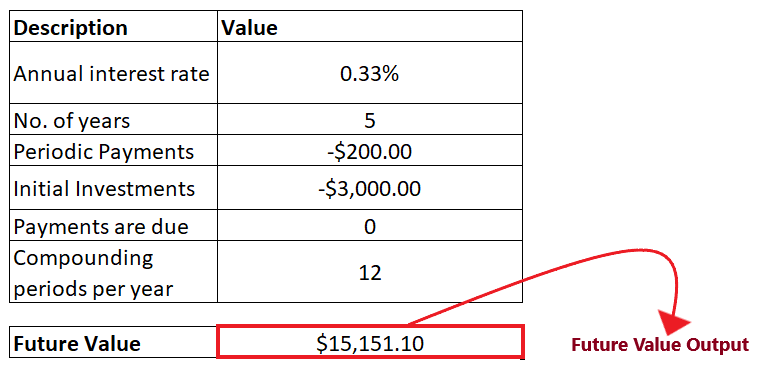
Therefore, we can conclude that the Future Value will be 15,151.10 at the end of 12 years. Tips
Example 3: In the below table, few of the arguments are non-numeric. Let's see what happens if you specify non-numeric arguments in NPER formula.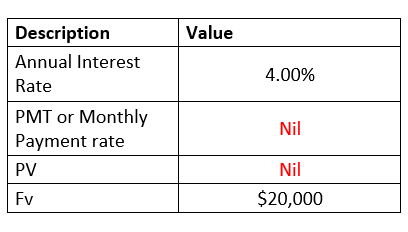
To fetch the FV output for the above table follow the below given steps: Step 1: Add helper row at the bottom of table Put your cursor below the table and add your helper row. In this row we will type the NPER formula and will fetch the periodic payment for the given data. Refer to the below image: 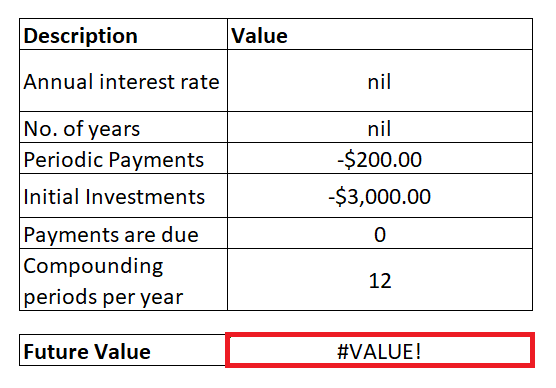
STEP 2: Add the FV formula and insert its parameters
NOTE: We have omitted the type parameter as we have assumed the payments are due at the end of the period.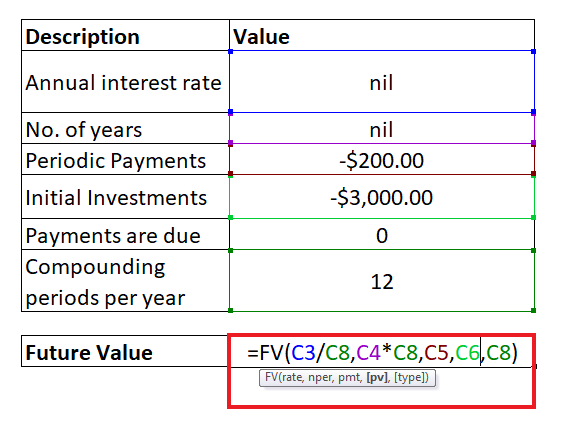
STEP 3: FV function will return #VALUE! error as Output Press the enter button as soon as you are done typing the formula. Excel will return the output for your FV formula. As shown below it will throw the #VALUE! error. Refer to the below image: 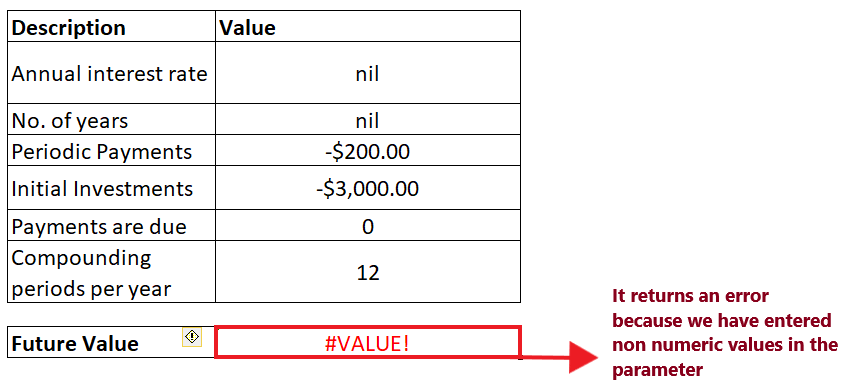
This error occurs if any of the arguments specified in your FV formula is non-numeric. To fix this error in Excel, always ensure that all the parameters are numeric and all the specified numbers are not formatted as text. Excel FV function not workingSometimes while working with the FV function, there are possibilities you might run into an error or a wrong result, and it mostly occurs because of one of the following reasons:
This error occurs if any of the arguments specified in your FV formula is non-numeric. To fix this error in Excel, always ensure that all the parameters are numeric and all the specified numbers are not formatted as text.
This problem occurs in the FV formula when you have used positive numbers to represent the outflow payments. For example, when you calculate the payment periods for a loan, provide the pv (loan value) parameter as a positive number and the pmt argument as a negative number.
Next TopicExcel NPV Function
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









