Android Service Tutorial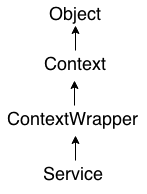
Android service is a component that is used to perform operations on the background such as playing music, handle network transactions, interacting content providers etc. It doesn't has any UI (user interface). The service runs in the background indefinitely even if application is destroyed. Moreover, service can be bounded by a component to perform interactivity and inter process communication (IPC). The android.app.Service is subclass of ContextWrapper class. Note: Android service is not a thread or separate process.Life Cycle of Android ServiceThere can be two forms of a service.The lifecycle of service can follow two different paths: started or bound.
1) Started ServiceA service is started when component (like activity) calls startService() method, now it runs in the background indefinitely. It is stopped by stopService() method. The service can stop itself by calling the stopSelf() method. 2) Bound ServiceA service is bound when another component (e.g. client) calls bindService() method. The client can unbind the service by calling the unbindService() method. The service cannot be stopped until all clients unbind the service. 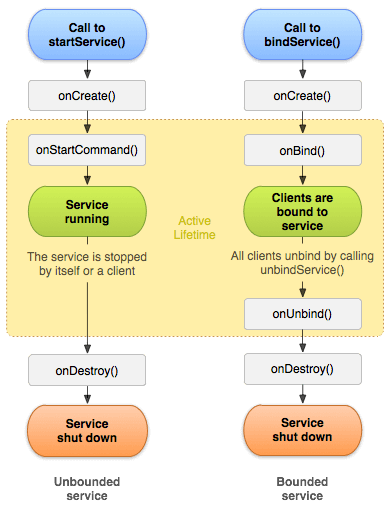
Understanding Started and Bound Service by background music exampleSuppose, I want to play music in the background, so call startService() method. But I want to get information of the current song being played, I will bind the service that provides information about the current song. Android Service ExampleLet's see the example of service in android that plays an audio in the background. Audio will not be stopped even if you switch to another activity. To stop the audio, you need to stop the service. 
activity_main.xmlDrag the 3 buttons from the pallete, now the activity_main.xml will look like this: File: activity_main.xml
activity_next.xmlIt is the layout file of next activity. File: activity_next.xml
It contains only one textview displaying the message Next Page Service classNow create the service implemenation class by inheriting the Service class and overridding its callback methods. File: MyService.java
Activity classNow create the MainActivity class to perform event handling. Here, we are writing the code to start and stop service. Additionally, calling the second activity on buttonNext. File: MainActivity.java
NextPage classNow, create another activity. File: NextPage.java
Declare the Service in the AndroidManifest.xml fileFinally, declare the service in the manifest file. File: AndroidManifest.xml
Let's see the complete AndroidManifest.xml file Output: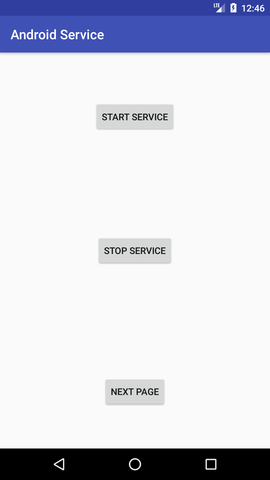
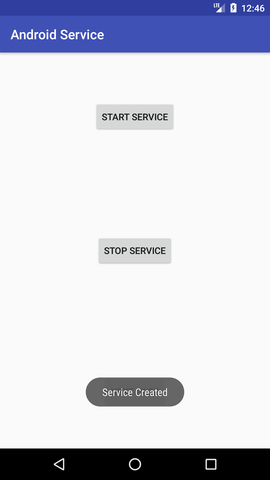 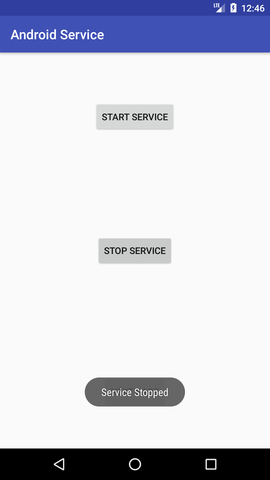
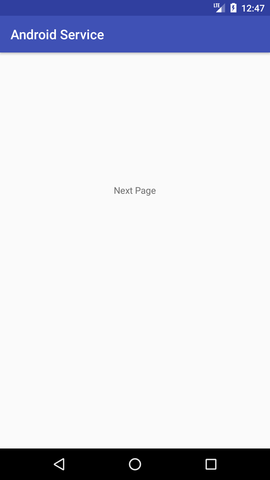
Next TopicAndroid AlarmManager
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









