8 Parts of Speech Definitions and ExamplesPicture that its your cleaning and re-arranging day. You plan to organize your almirah. To begin you take out all the clothes from your almirah and dump in on your bed. Then you begin sorting by separating the shirts; pants; socks and so on. No you fold the pants and create a stack of them; you do the same thing for your shirts; socks and other clothes. 
So, what did you just do? You organized your apparels on the basis of their functions and the purpose they serve. Similarly in English language ; we organize our words and terms on the basis of their functions ; purpose and features they have. And this categorization and re-organization of the words on the basis of the functions is known as parts of speech. Parts Of Speech - The First Step To English LanguageTo learn to run, you must first learn to take steps. The same may be said about learning English. To speak the language fluently, you must first understand the grammar and the associated rules. Words in the English language can be perplexing at times due to their propensity to have several meanings. As a result, we utilize a concept known as parts of speech to better comprehend and analyze words and their meaning. The term 'parts of speech' refers to a group of words with comparable grammatical qualities in conventional English grammar. A single word may serve as a distinct component of speech depending on the circumstances. The phrase 'parts of speech' is rarely used in current linguistics and is frequently substituted with terms such as syntactic category or word classes. There are eight parts of speech in the English language, and we will examine each one and provide an instance of how each is utilized in a phrase or a sentence. 
Introduction To Parts Of SpeechParts of speech are the first step in learning English. It is also an integral part for improving your spoken English abilities. The parts of speech in English are as follows: noun, verb, pronoun, adverb, adjective, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. Words in English can be categorised owing to their different forms, meanings, places, and functions. Every word in English is part of speech. The word's importance indicates where it fits in the parts of speech. A new student must understand the components of speech in English. The English language may be learned using the suitable way. The complete and methodical approach can aid with your English language mastery. Basic grammar subjects are being given more weight in various kinds of competitive examinations. You must be aware of the many parts of speech that might be used in your conversation. Language learning is not complete without a thorough understanding of the parts of speech. The parts of speech are given substantial weight in English as a language for both writing as well as communicating. If you want to develop your language abilities, you must start from the beginning from the fundamentals that form the basis of the English Language. Are you ready to take your first steps? When utilized in different contexts, the same word might serve as more than one part of speech. Only parts of speech can be used to determine the correct meaning of a word. The many roles that a word plays in a phrase are referred to as parts of speech. Form class words include nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, while the function class words include pronouns and conjunctions. What Exactly Is A Part Of Speech?The English language has numerous words, and each word serves a purpose. Some words are used to demonstrate activity, others to connect, and yet others to label something. Parts of speech encompass all of the roles played by words in the English language. Definition Of Parts Of SpeechParts of speech are "traditional grammatical groups to which words have been assigned in line with their syntactic processes, including noun, verb, adjective, adverb, and so on." They pertain, to the many functions that words might play in a phrase or a sentence and how they connect to one another depending on grammar and syntax. So what does Parts of Speech encompass ?

Examples of the Eight Parts of SpeechLearning the eight parts of speech is essential for language mastery. Each component serves a distinct role in sentence construction and meaning communication. These components serve as the foundation for good communication. Let us look at each part of speech, their purposes, and examples to help you understand their importance in creating meaningful and cohesive sentences. 1. NounA noun is a term that specifies the name of something, someone, a place, a concept, or an activity. Nouns are the most common type of word in the English language. There are two types of nouns: common and proper. Proper nouns refer to the name of an individual, item, or place, whereas common nouns imply to a location, thing, or individual. Singular and plural nouns are both acceptable. Singular nouns are frequently used in conjunction with an article (a, an, the). Nouns can function as a subject, an object, or subject complements in a statement. Gender, number, and case are all attributes of nouns. Concrete and abstract nouns are the two types of nouns. Concrete Nouns are nouns that express physical existence, such as titles of places and things. Examples of Noun
Some more examples
Now let us have a look at the examples Of Noun on the basis of its types or kinds.
Here are sentence examples of these ;
2. VerbA verb is a grammatical core and one of the most important sentence parts. Every statement has a subject and a predicate. The main element of the predicate is the verb, which is employed to describe an event, action, or state of being. Verbs simply describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. The most prevalent types of verbs are action verbs as well as linking verbs. Although the latter aids in visualizing the subject's action, the previous one conveys the subject's beings, identity, or existence. Verbs change shape and have new ends added to them. These ends demonstrate the verb's link to time, which is referred to as verb tense. The verb is also considered a doing verb. It's also classified as an action term. The verbs express actions. It may additionally explain a phenomenon's existence or occurrence. In addition, the verb can express ideas, imagery, mood, continuity, habit, condition, and sensory aspects. Transitive Verbs: Object-taking verbs are known as transitive verbs. Example: Krishna arranges folders. Intransitive Verbs: An intransitive verb is one that does not require an object. Example: Krishna sits by itself. Examples Of Verbs In Sentences On The Basis Of The Types ;
Examples Of Functions Of Verbs In Sentences
Examples Of Verb Voices In The Sentences
Here are some more examples of verbs in the sentences ;
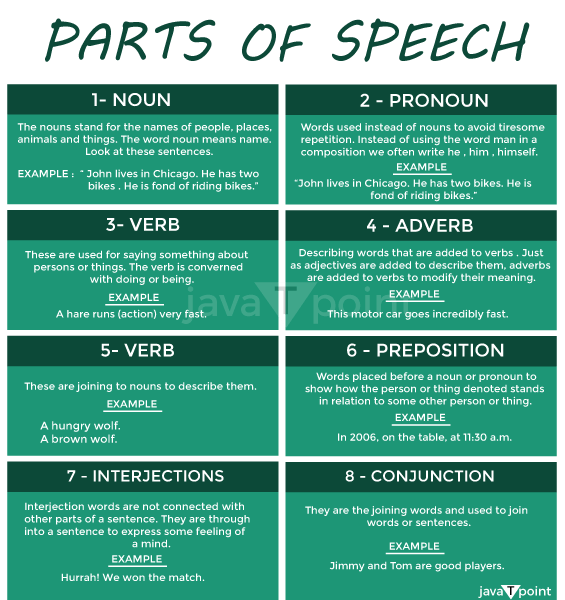
3. PronounA pronoun is a term that is utilized as a substitute for a noun in a statement. The pronoun should be utilized after a noun has been utilized in the sentence before. There are nine different types of pronouns in English. The various sorts of pronouns are classified according to their purposes and meanings. Possessive pronouns are utilized to convey ownership, personal pronouns are utilized when referring to a person or object, demonstrative pronouns are utilized for pointing to the noun, reflexive pronouns are utilized to highlight another pronoun or a noun, while relative pronouns are utilized when introducing a subordinate clause. Examples Of Pronouns On The Basis Of Its Types Personal Pronouns Personal pronouns are classified into three types: first-person pronouns, second-person pronouns, as well as third-person pronouns. Examples
Reflexive Pronouns These are formed through the addition of -self in the singular as well as -selves in the plural to pronouns like your, my, him, her, in addition to it. Examples
Emphatic Pronouns Emphatic Pronouns are utilized to give emphasis whenever forms like -self and -selves are utilized. Examples
Interrogative Pronouns These pronouns are utilized to ask questions. Examples
Distribute Pronouns These Pronouns are utilized to refer to certain people or things. The distributive pronouns are each, any, and neither. Examples
Reciprocal Pronouns Those pronouns that indicate a mutual connection. Each other as well as one another are reciprocal pronouns. Examples
Indefinite Pronouns Those are utilized in a broad sense, without relation to specific items or people. Examples
Demonstrative Pronouns This kind of Pronouns are utilized to point out items or individuals. This, that, those, and these are examples of demonstrative pronouns.
Relative Pronouns The pronoun that relates to the noun prior to it. It contains the words whose, whom, who, whereas, and which. Examples
4. AdjectiveAn adjective is the statement's modifier; it characterizes the noun or pronoun. An adjective basically provides extra details about the statement's subject. It provides answers to inquiries such as what kind, how many, and so on. In English, adjectives can have superlative or comparative ends. There is usually an article - the prior to the adjective for superlative. Adjectives do not modify or agree with nouns. Adjectives can be used as nouns. They supplement the meaning of a noun. It can also be used to alter a noun. Adjectives are often utilized to describe things in both comparative as well as superlative ways. There are various types of adjectives. Examples
5. AdverbAdverbs, like adjectives, are used to alter or describe the verb, adjective, or adverb in a statement. Adverbs typically describe the time, condition, or state. It frequently finishes in -ly. However, several adverbs do not end in -ly, such as also, never, frequently, again, too, well, soon, and very. When employed in a question, the terms why, where, when, and how are referred to as interrogative adverbs. The adverb qualifies the verb. It provides additional information regarding the manner of a specific activity. It can change not just verbs but also adjectives and adverbs. Adverbs are classified into several categories. Examples of various kinds of Adverb in sentences
Some more examples of Adverb in sentences
6. PrepositionA preposition is a term in a statement that demonstrates the link between the a noun or pronoun as well as another word. The relationship formed by a preposition can be directional, spatial, or temporal. Prepositional phrases are formed when pronouns are joined with nouns or pronouns. Prepositional phrases are typically used as an adverb or an adjective. Prepositions are words that come prior to a noun or a pronoun. A pronoun is utilized to indicate how a noun or pronoun is related to other words in a phrase. Let us have a look at examples of types of Prepositions;
Examples
7. ConjunctionA conjunction is a term that connects the statement's words, clauses, or other phrases. It also shows the link between the sentence's components. A conjunction can be divided into four types. Coordinating conjunctions, Subordinating conjunctions, Conjunctive adverbs, and Correlative conjunctions are all types of conjunctions.
Examples of Conjunctions in the Sentences on The Basis Of The Types ;
An interjection is a word that is introduced to a phrase to indicate emotion. An interjection is not grammar-wise related to the phrase; it can appear either prior to or following the main sentence, exists alone, and is frequently followed by an exclamation mark. The phrase interjection is derived from the Latin words inter (which means between) and jacre (which means to throw). So an interjection is a word that you insert between the remainder of the text when you're experiencing the need to exclaim. Interjections are commonly employed in informal writing but are uncommon in scholarly writing. Examples Of Interjection
Articles and determiners are they parts of speech?Articles (a, an, the) and determiners (that, my, some) are two more components of speech that exist in sentences. So, why are there just eight rather than ten parts of speech? Although some style guides and lists include articles and determiners as parts of speech, these are actually adjectives. They change nouns to make the sentence more detailed.
ConclusionUnderstanding the parts of speech is only the first step toward creating a proper sentence. However, parts of speech differ slightly from parts of sentences - and you must understand both to correctly organize your work. Otherwise, you can come across grammar errors like sentence fragments or run-on phrases.
Next TopicDeep Learning Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










