Transformation DefinitionWhat is Transformation?Transformation in science is the process of changing one thing into another. Transformation can be used to describe a wide variety of processes, from physical to chemical to biological. In physics, transformation usually refers to the transformation of energy, such as when energy is converted from one form to another. In chemistry, transformation can refer to a chemical reaction or changing a substance from one form to another. In biology, transformation can refer to changes in the structure or function of an organism, such as when a species evolves or adapts to its environment. 
Transformation in PhysicsIn physics, the most common form of transformation is that of energy. Energy can be converted from one form to another, such as when electrical energy is converted to heat or light energy. This process is sometimes referred to as energy conservation. The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed but can be transformed from one form to another. Transformation in ChemistryIn chemistry, transformations occur when a chemical reaction takes place. This occurs when one or more reactants are converted into one or more products. For example, in the combustion of hydrocarbons, oxygen is combined with carbon and hydrogen to produce carbon dioxide and water. This transformation is an exothermic reaction, meaning energy is released in the heat. Transformation in BiologyIn biology, transformation refers to an organism changing due to its environment. This can include changes in physical characteristics, such as size, colour, or shape, or changes in behaviour, such as learning or mating behaviour. Transformation can also refer to genetic changes, such as when a species evolves due to natural selection or genetic drift. In general, transformation can occur in physics, chemistry, and biology; each transformation is unique and has its purpose. Transformation can help us understand the world around us and can also be used to create new technologies and solutions to problems. How is Transformation Important?Transformation is important for a variety of reasons. It can be used to create new technologies that can help us better understand the world around us. For example, energy transformation can be used to create electricity, which is used to power our homes and businesses. Transformation can also be used to create new medicines and treatments and develop new materials with unique properties. Finally, transformation can be used to create new organisms or species, which can help us understand the evolutionary process. History of TransformationThe history of transformation can be traced back to ancient times when people first began understanding the concept of energy conversion. Ancient Greek philosophers such as Aristotle and Democritus were among the first to consider transforming energy from one form to another. In the 1600s, scientists such as Galileo, Kepler, and Newton began developing mathematical and physical energy transformation models. During the 1700s and 1800s, scientists and engineers significantly advanced in understanding energy transformation. This period saw the invention of the steam engine and the development of the laws of thermodynamics. In the 19th century, James Clerk Maxwell developed the theory of electromagnetic transformation, and the first electric motor was created. In the 20th century, scientists and engineers continued to expand upon the understanding of energy transformation. The invention of the transistor and the development of nuclear energy were two of the most important advances during this time. In the 21st century, scientists and engineers are continuing to develop new technologies and processes based on the principles of energy transformation. Transformation is essential in many fields, from physics and chemistry to biology and engineering. It has been studied and developed for centuries and is an important research area. As new technologies are developed, transformation will continue to be an important part of our lives. 
How is Transformation a Revolution in Science?The transformation has revolutionized science in many ways. In physics, energy transformation has enabled us to create new technologies, such as electricity and nuclear power. In chemistry, the transformation of substances has allowed us to create new materials with unique properties. In biology, the transformation has allowed us to understand the evolutionary process better and develop new medicines and treatments. The transformation has enabled us to create new products from raw materials and data in engineering. Finally, the transformation has allowed us to create new tools and solutions to problems in technology. The transformation has revolutionized science and has opened new doors for future discoveries. Types of Transformations?Types of transformations include Physical Transformation, Chemical Transformation, and Biological Transformation. Chemical transformation involves the conversion of one or more reactants into one or more products, such as in the combustion of hydrocarbons. Biological transformation involves changes in the structure or function of an organism, such as when a species evolves or adapts to its environment. Examples of TransformationsExamples of transformations include the following:
Advantages of Transformation
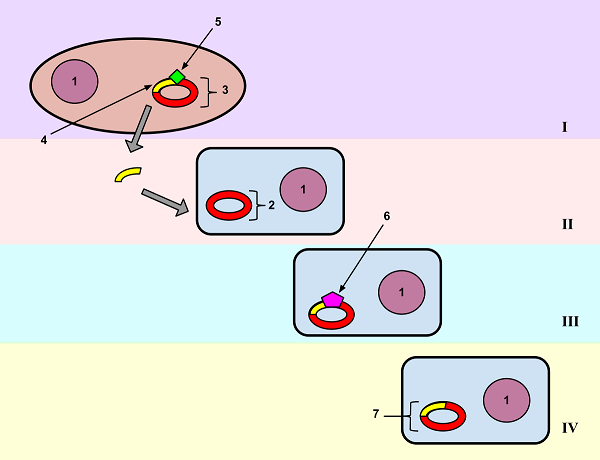
Disadvantages of Transformation
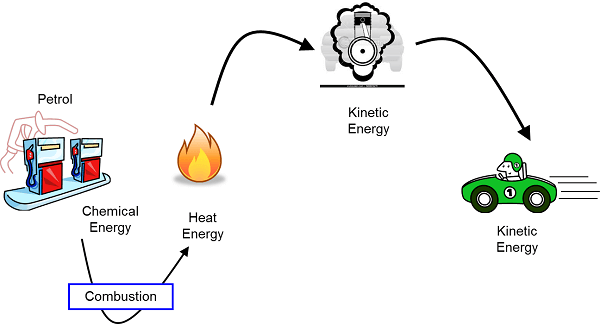
ConclusionOverall, transformation is a powerful tool that can be used for various purposes, such as gene therapy and cloning. However, it also has some drawbacks that should be considered before using it. These include potential unintentional gene transfer, difficulty controlling the amount of genetic material, expense and time requirements, and ethical concerns.
Next TopicVelocity Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









