Social Change DefinitionChange can be defined as any change, variation, or modification that occurs through time in a condition or an object. The phrase "social change" refers to changes in how people interact. Since society is a "web of social relationships," "social change" necessarily refers to a change in the social relationship system. 
Social interactions, processes, and organizations are used to understand social relationships. Thus, "social change" refers to a desired change in social interaction, processes, and organizations. It involves changes to things like social structure and functions. Social ChangeSociologists describe social change as an evolution in cultures, institutions, and responsibilities. Most change takes time to be noticeable. Change in society is frequently slow. Various factors and forces are at play, most opposing changes to the status order. Some types of changes occasionally occur in every society. 
The idea of "social change" explains how time, interactions, and relationships between people can affect social and cultural institutions, norms, and values. The change has been described by sociology as a global phenomenon that happens slowly and gradually. Social changes are not instantaneous in the sense that you can immediately notice the change. Internal and external factors in any society contribute to shifting assumptions and changing society and culture. Social change shows how human behavior affects society and its long-term effects. Theories of Social ChangeA society will inevitably experience social change, but the reasons for these changes are not always clear. According to sociology, many social change theories could help clarify the topic of social movement and social change. 
One of the most well-known sociologists, Auguste Comte, supported the evolutionary theory of social change. Pareto and Spencer are two sociologists who have significantly contributed to this theory. Charles Darwin's Theory of Organic Evolution significantly influenced the sociology theory of social change, popular in the 19th century. It established the standard for describing social change, its root causes, and its social consequences. The fundamental idea of evolutionary theory is that change is gradual, inevitable, and happens in stages. It highlights the idea that society will develop linearly, moving from simple to more complex levels and that those who don't adapt quickly will fall behind. The evolutionary theory holds that evolution is progressive and ongoing in sociology. Every society will go through the same growth and development stages, and these social transformation stages are irreversible.
The functionalist theory of social change in sociology contrasts society to the human body, where each component is an essential organ, and each organ depends on the others to function. According to the philosophy, each component of society has a vital role to play and needs to coexist peacefully. A problem in one area of society will harm society, making it vulnerable and eventually collapsing. Emile Durkheim and Talcott Parsons are two important sociologists who contributed significantly to this sociological idea. According to the functionalist sociology theory, society always exists in equilibrium. According to this idea, society strives for a stable condition. When a problem arises, it will only last for a short while, and other components must pay attention to fix it. According to the functionalist theory of sociology, social change happens when things happen quickly, the equilibrium is threatened, and when the system experiences creative ideas.
According to the conflict theory of social change in sociology, social structure is competitive and unequal by nature and is always in a state of conflict. Because there are strong groups that can preserve the status order, many sociologists argue that institutions still have an impact on society. Fighting may continue between individuals and groups to fully utilize the advantages offered. Marx and Engels are two important authors who contributed significantly to conflict theory sociology. They held the opinion that conflict plays a significant role in social change and is in some way connected to all different kinds of social change. Social Change Characteristics
Features of Social Change
Social Change Types
Based on how much change they urge and whether they target specific people or the entire society, cultural anthropologist David F. Aberle has suggested four types of social reforms. The types are:
For example, campaigns against using a phone while driving aim to modify a small amount of behavior.
For example, religious campaigns against drunkenness are becoming more popular as they aim for dramatic personal transformation for a certain segment of the community.
For example, there is a movement to end the Sati system and to allow same-sex couples to marry.
For example, the Maoist Armed Revolution in Nepal (between 1996-2006 AD) and the French Political Revolution (1789-1799 AD). Social Change Source
Either a society's members or outsiders can bring about social change.
For example, biological variables (such as population and heredity), religion, the economy, and legal issues.
For example, the rise of globalization, the environment, etc. Social Change Factors
Numerous factors cause social change. Some significant factors are covered below:
Process of Social Change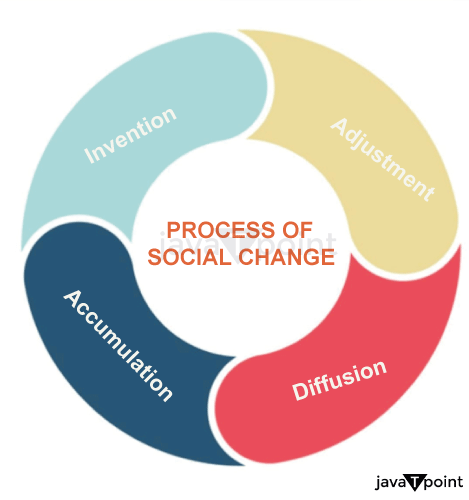
According to American sociologist William Fielding Ogburn, social change happens in culture, and cultural evolution is the consequence of the processes listed below:
"An invention is a new application of knowledge," according to Linton. Social change occurs when something already existing in culture is brought to attention and made visible to the general public. The following three factors all contribute to the invention: Mental Ability: A person in a culture has to be mentally capable of inventing something. The number of talented people would increase with population size. Therefore, a source of social change in society is mental ability. Demand: People's demands for limited resources lead to inventions, which bring about social change. The invention process would go faster as customers' demand for physical goods increased. Existence of Cultural Elements: Smaller cultures experience slower change than larger ones. The speed of invention will increase with the number of cultural components. For an invention and social change, cultural resources and elements are crucial.
More novel aspects are added to culture as a result of innovation. The accumulation process is brought about by fusing these cultural aspects with traditional elements. The accumulation will increase as new elements are created and merged with existing ones.
A significant factor in social change is cultural diffusion. The diffusion process begins when a cultural element or invention spreads from one culture to another. An invention or the diffusion of a cultural component to another civilization was made possible by quick transportation and communication.
Adjustment is the final component in the process of social change. After cultural elements have been invented, accumulated, and diffused, an individual must adapt to that culture. All cultural components are interconnected, yet as a culture undergoes a material shift, the material culture also slowly changes. However, the gap becomes filled as time passes, and new elements are adjusted in that society. So, due to adjusting to social change, the invention of new elements becomes a part of the culture. What Causes Social Change?Although no society remains the same forever, what motivates it? There are three basic causes of social change:
The history of the world demonstrates that social change is sparked by conflict. Dissatisfaction and rage are encouraged by inequalities due to class, race, gender, religion, and other factors. Groups band together to push for change to address their situation. Governments are subject to overthrow or transformation. Change can also occur suddenly though it often occurs gradually over time.
When the demographics of a society evolve, social change is unavoidable. When birth rates rise, or as people live longer, the demographics of society frequently alter. The availability of resources and their distribution is impacted by population growth. A rise in emigration and immigration has an impact on society as well.
Discoveries, innovations, and the spread of ideas influence cultural changes. Explore the influence of the internet. It has transformed the culture of particular nations and the globe. It has changed how we communicate and how many different industries are structured. Discoveries can impact a society's culture. Think at the rate things changed when Europeans "discovered" America. This illustration demonstrates how social change does not always benefit everyone. New perspectives on gender, racism, religion, the workplace, education, and other topics change society. Social Change ExamplesSocial movements frequently result in social change. Multiple examples can be found throughout history in every nation on the planet. The most well-known examples, many of which are still active or developing, include:
Next TopicDefinition Of Grammar In English
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










