Distillation DefinitionDistillation is a process of separating and purifying a mixture of liquids into their individual components. This process is based on the principle of different boiling points of the components in the mixture. The mixture is heated, causing the components with lower boiling points to vaporize first. The vapour is then condensed and collected, effectively separating it from the remaining components with higher boiling points. The process of distillation is used in a variety of industries, including the production of alcohol, perfumes, essential oils, and fuel. In the alcohol industry, for example, fermented grain mash is distilled to produce whiskey, gin, and other spirits. The process of distillation removes impurities, such as water, and concentrates the alcohol content, resulting in a much stronger and purer product. 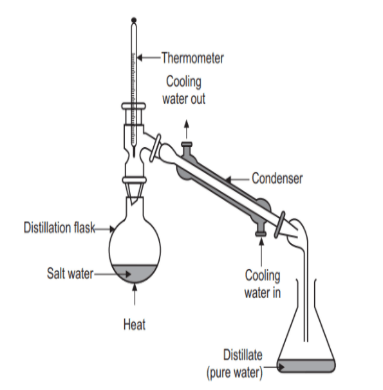
Distillation can also be used to purify water and other liquids, by removing impurities such as salts, minerals, and contaminants. The process works by heating the liquid to a boiling point, at which point the vapour rises and is condensed, leaving the impurities behind. Distillation is a critical process in many industries and has numerous applications. It is a proven method for purifying and separating liquids and has been used for centuries to produce a wide range of products. With the ongoing development of new technologies and techniques, distillation remains a key tool in the production of high-quality and pure products. Principle of DistillationDistillation is a separation technique based on the difference in boiling points of the components of a mixture. It is a thermodynamic process that involves heating a mixture to its boiling point, collecting the vapour produced, and condensing the vapour back into a liquid. The principle of distillation is based on the fact that different components of a mixture have different boiling points and vapour pressures. When a mixture is heated, the component with the lowest boiling point will vaporize first and the component with the highest boiling point will vaporize last. The vapour produced is then condensed and collected, resulting in a separation of the components of the mixture. This process can be repeated multiple times to increase the degree of separation. The efficiency of distillation is determined by the difference in boiling points between the components of the mixture. The greater the difference in boiling points, the easier it is to separate the components. The process can also be optimized by controlling the temperature and pressure conditions during distillation. Distillation is a widely used process in a variety of industries, including the production of alcohol, essential oils, fuel, and other products. The process is also used in air and water purification, as well as in chemical processing. Process of DistillationDistillation is a separation process that involves heating a mixture of liquids to create vapour, which is then cooled and condensed to separate and purify the individual components. This process is based on the differences in boiling points between the components in the mixture. The distillation process can be used to separate liquids with similar boiling points and can also be used to purify liquids by removing impurities. 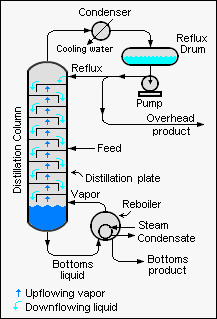
The process of distillation begins with the heating of the mixture in a still or distillation column. As the temperature of the mixture increases, the components with the lowest boiling points will vaporize first. This vapour rises and is captured in a condenser, where it is cooled and condensed back into a liquid form. The condensed liquid, also known as the distillate, is then collected in a separate container. The distillation process continues until the temperature of the mixture reaches the boiling point of the next component in the mixture. This process is repeated until all of the components have been separated. The resulting distillates are then analysed and characterized to determine their composition and purity. One of the most important aspects of the distillation process is the design of the still or distillation column. The design of the still determines the efficiency of the separation and the purity of the distillates. In a simple distillation setup, the still is typically a single vessel, while in a fractional distillation setup, it is a multi-tray column. The fractional distillation column allows for the gradual separation of the components in the mixture, resulting in a more precise and efficient separation. Uses of DistillationDistillation is a process used for separating and purifying liquids into their individual components. The process has a wide range of uses across a variety of industries, including:
Types of DistillationDistillation is a process used to separate mixtures of different substances based on their boiling points. It is a fundamental process in the chemical industry and is used to purify, concentrate, and extract various substances. There are several types of distillation, and following are the most common ones:
ConclusionIn conclusion, distillation is a versatile and powerful process that has been used for centuries to purify liquids. From the creation of alcohol and essential oils to the production of fuel, the process of distillation has transformed the world in countless ways. Its ability to separate and purify liquids has made it an indispensable tool in various industries and has allowed for the creation of some of the most important products that we use in our daily lives.
Next TopicManagement Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









