Morbidity definition
Illness is part of our survival, a living being (animals and humans) gets ill due to various reasons. Illness can last one or two days, taking months, years, or even a lifetime. This state of being ill or the quality of being unhealthy full is considered morbidity. "Morbidity is the condition or state of a human being surviving a disease or medical condition which includes:
The term morbidity has no relationship with your likelihood of death or even how unwell or well you are instead, it is the condition of being ill or having some medical condition (physical or mental). This state can be progressive and affect a person's health and quality of life. It can be cured with medication and care but sometime may result in death. People with morbidities don't enjoy long life compared to others without. If this morbidities condition is well managed, it is less effective for human beings. Morbidity rateWhen the morbidity condition of the portion of people is measured in a specific geographical condition during a specific period is termed a morbidity rate. It is the frequency of the disease appearing in pollution or collective information of people suffering from it at a time. For example: When pandemic happened in 2019, the data of COVID infected person data is collected to keep a record track of the disease called morbidity rate and is shown in percentage. Morbidity rates calculationThe morbidity rate is calculated by dividing the number of cases of the affected person with injury, disease, or disability by the population at a specific disease period. 
Case: If a city with a population of 20 lacks in one year, 20,000 people suffer from a particular disease, then the morbidity rate is 0.01% (20,000/ 20,00,000). The morbidity rates are affected by climatic conditions, healthcare costs, sanitary conditions, and other factors like different geographical areas during different periods. The health and human services department collects all the data and reports morbidity rates on MMWR (morbidity and mortality weekly report). The department aims to prevent and control disease, injury, and disability to protect public safety and health. The term morbidity is incomplete without another term, "mortality," related to illness and Death. Let's discuss the term: 
MortalityWith morbidity, the term mortality also arises, even though both terms are a little confusing as these are discussed together but are quite different in meaning. Rather mortality is another term used for death. Still, it is the collection of several deaths caused by an illness or event over a specific period by the total population. Insurers and public health experts use these mortality rate statistics to determine the impact of disease on healthcare costs or where the health cost is best spent. For example: Suppose in condition 25, lung cancer happens in one year in a population of 30,000. Final mortality comes to 83 per 100,000. COVID-19 is one of the best examples that recorded excess mortality. Some of the causes of mortality are the same as morbidities like cancer, heart cause, diabetes, diabetes, chronic lower respiratory disease, kidney disease, suicide, pneumonia, and influenza. Types of mortality ratesa) Crude death rate: In this type of mortality rate, the death rate is calculated by the number of Deaths from all causes in a population during a specific period. The birth rate is also counted in this to conduct analysis. b) Age-specific mortality rate: Rate of mortality based on a particular age group. 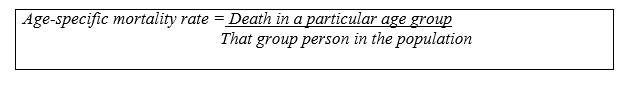
For example, A total number of deaths ( 130,761) in a particular year occurs among persons aged 25-44. So the mortality rate is 153.0 per 100,000 (25-44 years). c) Infant mortality rate: It measures the comparison of the health status of infants among nations. It is calculated annually to measure the health status of the mother and infant during the pregnancy and the year after that. Tracing of mother and infant health reflects the wide variety of factors like the prevalence of prenatal maternal health behavior (use of alcohol and tobacco and proper nutrition during pregnancy), access to prenatal care, sanitation, infection control, postnatal care, and behavior (including childhood immunizations and proper nutrition). 
d) Neonatal mortality rate: Birth ups are counted, and the mortality rate is calculated over 1,000 live births. 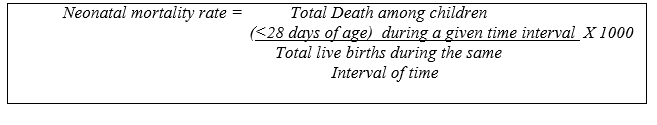
e) Post neonatal mortality rate: The period starts from the 28th day of birth but doesn't include one year of age. 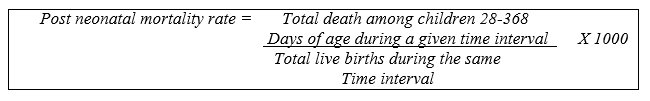
f) Maternal mortality rate: Counted the mortality rate during and at the site of pregnancy. 
g) Race-specific mortality rate: particular racial group mortality rate is calculated where the numerator and denominator are limited to a specified rate. h) Sex-specific mortality rate: Decide the male and female ratio among the population where the numerator and denominator are limited to one sex. i) Case fatality rate: It is calculated by measuring the number of deaths from a certain cause of the population to the population with that cause. For example: 
Morbidity and mortality overviewThe combined morbidity and mortality rate results provide a better picture of real problems facing services, healthcare facilities, and practices. Both analyses help identify these serious and potentially widespread issues, but their exact difference needs to be known by healthcare professionals. Morbidity is related to how illness affects everyone or some people, and mortality is related to how much only death affects some people. Compared with the effect of mortality, morbidity is long-lasting. Importance of morbidity and mortalityAccording to studies, both terms determine the public health burden of a disease or condition within a defined population. Therefore both equally provide different information or statics important for the health care department. But in some cases, both terms are used interchangeably because both are related to health care. One (morbidity) is best defined as several people ill or dying within a population, and the other (mortality) is the number of deaths during a given period. The morbidity and mortality can be calculated using statistical data from census records or registration systems. So, both are equally important. Preventive measures of morbidities and mortalityTo reduce the morbidity and mortality rate, a human must follow these preventing that keeps them healthy:
So, we can conclude that morbidities are an important factor in the healthcare industry to keep track of all diseases and prepare ourselves for future harmful aspects. It helps in taking preventive measures y the government regarding the health of human beings.
Next TopicAllergy Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










