Homophones DefinitionHomophones are words that are pronounced the same way but have different meanings and spellings. They are a typical source of confusion for language learners and native speakers alike, as they can be difficult to distinguish in spoken language. Homophones are a type of homonym, which refers to a word that shares almost the same spelling or pronunciation with another word but has a different meaning. 
Examples of homophones include "bare" and "bear", "write" and "right", and "hear" and "here". In each of these pairs, the two words are pronounced almost the same way, but they have different meanings and spellings. Homophones can be confusing because they can be used in similar contexts, and it is important to use the correct one to avoid misunderstandings. Homophones can also vary by dialect and accent. For example, "cot" and "caught" are homophones in some dialects of English, but in others, they are pronounced differently. Homophones can be a challenge for language learners because they need a good ear to hear the pronunciation and understand the nuances of the English language. To avoid confusion, it is important to learn the correct spelling and usage of homophones. Homophones are commonly used in puns and wordplay, as well as in poetry and literature. They can add humour and depth to a text, as well as create interesting word associations. One way to learn homophones is to create a list of words that are commonly confused. Some common homophones include "their", "they're", and "there"; "to", "two", and "too"; and "break" and "brake". Once you have identified the homophones, you can practice using them correctly in sentences to reinforce your understanding. 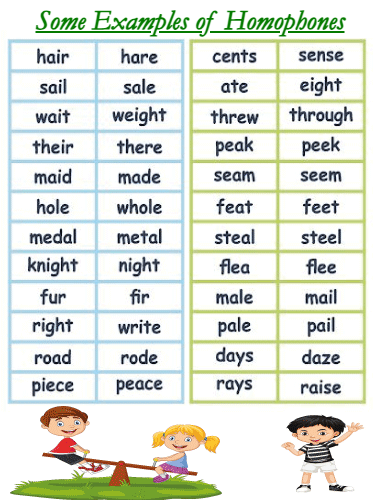
Some Common HomophonesConfusing "Their", "They're", and "There"One of the most commonly confused homophone sets is "their, they're, and there". 'Their' is a possessive pronoun that indicates ownership, as can be seen in the example: "Their house is beautiful." 'They're' is a contraction of "they are", as can be seen in the example: "They're coming over for dinner tonight." 'There' is an adverb that indicates location, as can be seen in the example: "The store is over there." To use these homophones correctly, remember that 'their' shows possession, 'they're' is a contraction of "they are", and 'there' indicates a location. Confusing "Your", and "You're"Another frequently confused homophone pair is "your and you're". 'Your' is a possessive pronoun that shows ownership, as can be seen in the example: "Your car is parked outside." 'You're' is a contraction of "you are", as can be seen in the example: "You're going to love this restaurant." To use these homophones correctly, remember that 'your' indicates possession, while 'you're' is a contraction of "you are". Confusing "To", "Too", and "Two""To, too, and two" refers to another set of commonly confused homophones. 'To' is a preposition used to indicate direction or movement, as can be seen in the example: "We are going to the park." 'Too' means "also" or "excessively", as can be seen in the example: "I want to go too." or "It's too hot outside." 'Two' is the number that comes after one (1) and before three (3). To use these homophones correctly, remember that 'to' indicates direction or movement, 'too' means "also" or "excessively", and 'two' is the number that comes between one (1) and three (3). Confusing "Its", and "It's"'Its' and 'it's' are two homophones that are frequently misused. 'Its' is a possessive pronoun that indicates ownership, as can be seen in the example: "The cat licked its paw." 'It's' is a contraction of "it is", as can be seen in the example: "It's raining outside." To use these homophones correctly, remember that 'its' indicates possession, while 'it's' is a contraction of "it is". Confusing "Here", and "Hear"'Here' and 'hear' refers to homophones that sound alike but have different meanings. 'Here' is an adverb that indicates location, as can be seen in the example: "I am here." 'Hear' is a verb that means to perceive sound, as can be seen in the example: "I can hear the birds singing." To use these homophones correctly, remember that 'here' indicates location, while 'hear' means to perceive sound. Confusing "Brake", and "Break"Finally, 'brake' and 'break' are two homophones that often confuse people. 'Brake' refers to a device used to slow or stop a vehicle. The use of the term 'brake' can be seen in an example: "The car's brake failed." In contrast, 'Break' is a verb that means to fracture or separate, as can be seen in the example: "I need to take a break from work." Confusing "Bare" and "Bear""Bare" and "bear" are two homophones that can easily be mixed up by listeners. "Bare" means uncovered or naked, while "bear" can be a verb meaning to carry or support, or a noun referring to a large carnivorous mammal. The use of the term 'bare' can be seen in the example: "The house is bare, but will feel like home after being decorated." The use of the term 'bear' can be seen in the example: "The table could hardly bear the weight of so many things kept on it." Besides, in the sense of an animal, the term 'bear' can be used as: "In summer, bears eat a lot so that they can hibernate for months." Confusing "Flour" and "Flower""Flour" and "flower" are two homophones that people can easily be confused with, even when writing. "Flour" is a powder made from ground grains, while "flower" refers to a plant's reproductive organ. Examples of the words 'flour' and 'flower' can be seen in the following examples: "One should put flour in his cake." and "This is a flower I picked out for you." Homophones can be confusing, but with practice and attention to detail, they can be used correctly. By learning the correct meanings and spellings of commonly confused homophones, you can communicate more effectively and avoid misunderstandings. Remember to pay attention to context when using homophones, and always double-check your work to avoid errors. 
How to improve our understanding and usage of homophones?Confusing one word for another can lead to misunderstandings and miscommunications, so it's essential to improve your understanding and usage of homophones. In this section, we will provide some tips on how to improve your knowledge and usage of homophones. They are: Learn the Meanings of HomophonesThe first step to improving your understanding and usage of homophones is to learn the meanings of each word. Homophones often have different meanings, so it's crucial to understand each word's definition to use them correctly. For example, "meet" means to come together, while "meat" refers to animal flesh used as food. Once you have a clear understanding of the meaning of each homophone, you can use them more effectively in your writing and communication. Read and Listen to Homophones in ContextReading and listening to homophones in context can help you understand how they are used in real-life situations. You can find examples of homophones in literature, news articles, and everyday conversations. Pay attention to how homophones are used in different contexts, and try to identify the meaning of each word. By reading and listening to homophones in context, you can improve your understanding of how they are used in everyday communication. Memorize the Spellings of HomophonesMemorizing the spellings of homophones is essential to avoid confusion and ensure that you are using the correct word. Many homophones have different spellings, so it's crucial to remember the correct spelling of each word. For example, "piece" and "peace" sound the same, but they have different spellings and meanings. By memorizing the spellings of homophones, you can avoid errors and communicate more effectively. Use Homophones in Your Writing and CommunicationUsing homophones in your writing and communication is an effective way to improve your understanding and usage of them. By using homophones correctly, you can develop a better understanding of how they are used in context. It's important to pay attention to the meaning of each word and to use them in the appropriate context. By using homophones in your writing and communication, you can become more comfortable with using them correctly. Get Feedback from OthersGetting feedback from others can be a helpful way to improve your understanding and usage of homophones. Ask a friend, teacher, or colleague to review your writing or communication and identify any errors or confusion with homophones. By getting feedback, you can learn from your mistakes and improve your ability to use homophones correctly. Homophones and AccentsAccents are variations in the way a language is spoken. They can be influenced by a variety of factors, such as geography, ethnicity, social class, and education. Accents can be regional, such as the Southern accent in the United States or the Cockney accent in England. They can also be influenced by a speaker's first language, leading to what is known as a "foreign accent". When it comes to homophones, accents can make a big difference in the way words are pronounced and perceived. For example, the words "cot" and "caught" are homophones in some accents but not in others. In many American accents, the two words are pronounced the same way, with a short "o" sound. However, in some British accents, "cot" and "caught" are pronounced differently, with a longer "o" sound in "caught". Accents can also impact the way homophones are spelled. For example, in some accents, the words "flower" and "flour" are pronounced the same way, with a silent "w". In these accents, it's easy to see how someone could confuse the two words when spelling them after listening. Another challenge of accents and homophones is that they can impact the way people are perceived in society. Accents can be associated with stereotypes and biases, leading to discrimination and prejudice. For example, someone with a Southern accent in the United States may be perceived as less educated or less intelligent than someone with a standard American accent. This can lead to assumptions about their abilities and opportunities, and even affect their job prospects and social interactions. Accents can also play a role in language learning and teaching. For non-native speakers, learning a new accent can be as challenging as learning a new language. It can take time and practice to master the nuances of a particular accent, especially when it comes to homophones. For language teachers, it's important to be aware of the different accents that exist in the English language and how they can impact the perception of homophones. Teachers can also help students learn to recognize and understand different accents, and to adapt their pronunciation to different contexts. Homophones in Literature and Popular CultureHomophones, words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings, have been used creatively in literature and popular culture for centuries. From puns to wordplay, homophones have been used to add humour, depth, and complexity to storytelling. In literature, homophones have been used in many famous works. In Shakespeare's play "Romeo and Juliet", the character Mercutio uses a series of puns based on the homophones "grave" and "grove" to mock Romeo's melancholy mood. In Lewis Carroll's "Alice in Wonderland", the White Rabbit mistakes Alice for his maid Mary Ann, leading to a series of misunderstandings based on the homophones "Mary Ann" and "Marry a Man." In popular culture, homophones have been used in a variety of ways, from advertising slogans to song lyrics. Overall, homophones have played an important role in literature and popular culture, adding humour and complexity to storytelling and entertainment. Their use in creative works highlights the importance of language and the power of words to convey different meanings, even when they sound similar.
Next TopicInsect Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










