Seasons DefinitionSeasons are parts of the year that have a recognizable set of weather patterns and day lengths. There are four seasons.
May exhibit a wide range of traits and influence changes in the environment. Here, we go further into these four seasons. Although the characteristics of the seasons may change depending on where you are, there are still general classifications that apply to most places. Winter
It becomes cool throughout the winter. While chilly rain falls in other places, certain regions may see snow or ice. Animals change their behaviour to remain warm and may change their appearance to fit in with the surroundings. Winter festivities, similar to the Autumnal theme, "celebrate the return of the light during a time of deepest physical darkness," said De Rossi." For instance, the Indian celebration of Diwali, which is observed between October and November, honors the victory of right over wrong and light over darkness. Spring
As soon as seeds sprout in the spring, vegetation begins to grow. The climate is more humid and warm. In many cases, animals who have recently left warmer climates awaken or return. According to the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), flooding along streams can result from melting snow from the previous season combined with more rain. Summer
The summer months might have some of the year's hottest days. If they reach dangerously high levels, droughts, and extreme heat can create problems for people, animals, and plants. For instance, in the 2003 summer extreme heat killed more than 30,000 lives. Additionally, certain places can get more rain. Forest fires might become more common and some people would get less water. Autumn or fall
Temperatures once again fall in the autumn or fall. Plants might start to become dormant. Animals may save food or leave for warmer climates in order to prepare for the coming winter weather. Annual celebrations have been held in a number of civilizations to commemorate abundant harvests. Thanksgiving is a prime illustration. "Thanksgiving in the United States is a historical commemoration, but it has a spiritual dimension strongly associated with homecoming and giving praise for what has been bestowed upon us," said Cristina De Rossi, an anthropologist at Barnet and Southgate College in London. Everywhere's Seasons are not Similar
Depending on where on Earth you are, the seasons change at different times and have different features. Warm winters and hot summers are hardly distinguishable in areas close to the equator, which has relatively stable temperatures throughout the year. This is because, according to the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) program, it is situated on the outer curve of the Earth, where it receives relatively consistent light from the sun. The seasons can vary more dramatically in regions to the north and south. In contrast to people who live closer to the equator, individuals who live closer to the poles may endure hotter summers and icier, more icy winters. The weather and temperature can be influenced by other things as well. Some regions enjoy hot, dry summers, while others may refer to summer as their "wet season." According to the Met Office, the bulk of the yearly precipitation in a nation or area falls during the rainy season. Mountainous areas may receive more snowfall than plains within the same latitude, and when the weather changes, properties near the coast may face an increase in severe tropical storms. The season a location experience is determined by whether it is in the northern or southern hemisphere. Winter is experienced in the Southern Hemisphere while summer is experienced by its northern neighbours; the northern Hemisphere witnesses the sluggish spring flowering while the southern hemisphere brings in the fall harvest. What are the Reasons for the Seasons?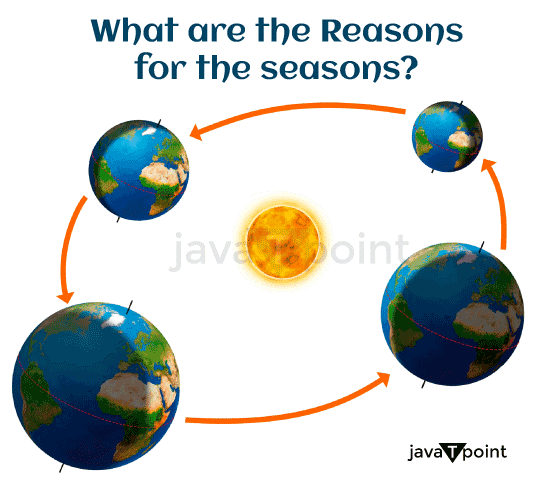
Because of Earth's tilt toward the sun, there are four distinct seasons. The Earth rotates on an invisible axis, with either the northern or southern axis closer to the sun, depending on the season. This phenomenon results in one hemisphere experiencing summer while the other hemisphere experiences winter, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). In contrast, neither hemisphere is inclined towards or away from the sun during other times of the year, leading to spring and fall. According to astronomy, each season corresponds to a certain time of Earth's orbit around the sun. The longest and shortest days of the year, the summer and winter solstices, fall on Earth's axis at their respective distance from the sun. The summer solstice occurs around June 21. According to NOAA, this is the same day as the winter solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. Around December 21, which is the north's winter solstice, is when the south has its summer solstice. In both hemispheres, the summer solstice is recognized as the start of astronomical summer, while the winter solstice is viewed as the start of astronomical winter. Another important day in Earth's orbit around the sun is the equinox. The planet's axis is parallel to the sun during the equinoxes, which occur on March 20 and around September 20. This means that there is an equal amount of daylight and nighttime hours. In the southern hemisphere, the fall equinox occurs on March 20, while in the northern hemisphere, it coincides with the spring equinox, also known as the vernal equinox. On the other hand, the autumn equinox in the northern hemisphere, around September 20, coincides with the spring equinox in the southern hemisphere. A hemisphere's astronomical spring season begins on the vernal equinox, whereas fall officially begins on the autumnal equinox. 
However, these crucial moments frequently occur before theweather changes. The seasons are divided into three-month periods that best represent them. In the Northern Hemisphere, December and February are considered winter and summer, respectively. Depending on location, March, April, and May are either spring or autumn, while June through August is summer in the north and winter in the south. NOAA states that the cycle concludes with September, October, and November, when fall arrives in the north and spring in the south. For places that experience the seasons fully, the seasons may provide a great deal of variation to the year. People may be able to participate in sports that they cannot in certain places due to the weather, such as skiing in the winter and swimming in the summer. Every season has its unique potential risks and its distinct brand of beauty. Further ResourcesWith the help of this educational resource from Lumen Learning, examine the seasons in further depth. Read this NASA article to find out more about the seasons on planets other than Earth. With the help of this educational article from the National Weather Service, know what causes the seasons.
Next TopicSector Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










