Phone Definition
Introduction
Mobile phones are the devices used to send and receive calls over a radio frequency available to a particular area. This radio connectivity links the sender and receiver with a channel that supports duplex transmission.
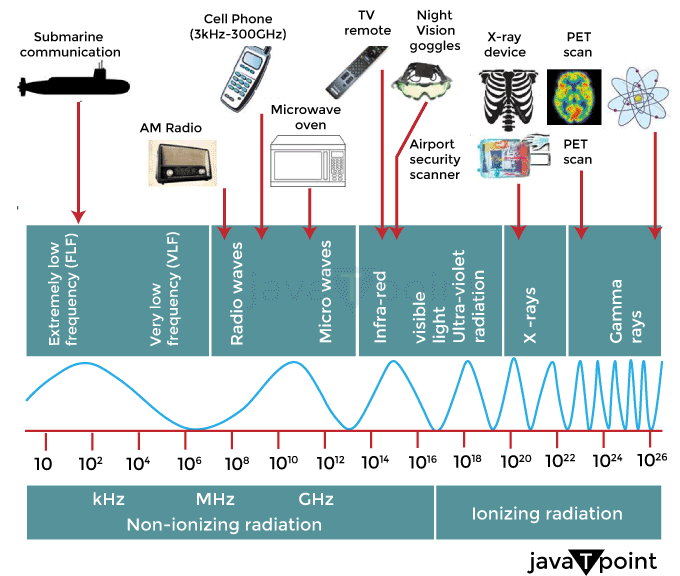
The radio frequency link creates a connection with a mobile phone operator's switching infrastructure, granting access to the public switched telephone network. In North America, mobile phones are referred to as cell phones (or "cell phones") since modern mobile telephone services utilize a cellular network design. Digital mobile phones are capable of a wide range of other services in addition to voice calling, including multimedia messaging, text messaging, email, short-range wireless communications (infrared, Bluetooth), Internet access, satellite access (navigation, messaging connectivity), business applications, video games, and digital photography. Smartphones are mobile phones with significantly more advanced processing capabilities than feature phones, which only have rudimentary computing capabilities.
Note: - Duplex transmission - It is a type of data transmission in which the sender and receiver can send and receive messages simultaneously in both directions.
Evolution of the Mobile Phone

On April 3, 1973, Motorola's Martin Cooper gave a demonstration of the first portable mobile phone in New York City, utilizing a 2-kilogram handset. The earliest cellular network in the world was introduced in Japan by Nippon Telegraph & Telephone in 1979. The DynaTAC 8000x was the first portable mobile phone to be made available for purchase in 1983. Between 1983 and 2014, the number of global mobile phone subscribers increased by seven billion, or one for every person on Earth. The top three smartphone manufacturers in the world in the first quarter of 2016 were Samsung, Apple, and Huawei, and 78% of all mobile phone sales were made up of smartphones. As of 2016, Samsung, Nokia, and Alcatel were the top-selling brands of feature phones (sometimes known as "dumbphones").
Main Components of a Mobile Phone
All phones share the following parts:
- An International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) number is used to individually identify each GSM, WCDMA, IDEN, and some satellite phone device.
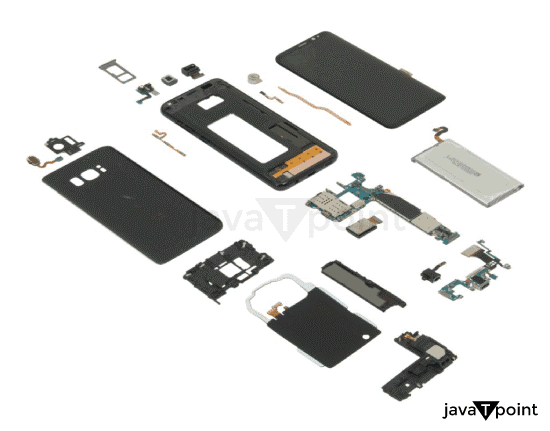
- Users of mobile phones can make calls and send texts using the most basic services.
- An input device that enables user interaction with the phone. A keypad is the most typical type of input device, but touch screens can also be found in smartphones.
- A battery that serves as the power supply for the phone's functionality, often a lithium-ion battery.
- Every GSM phone uses a SIM card to enable account switching between gadgets. A comparable card known as an R-UIM is also seen in some CDMA devices.
Different Categories of Mobile Phones
This classification is based on the capabilities of mobile phones. There are three main categories of mobile phones: 1) Basic phones, 2) Feature phones 3) Smartphones.
1) Basic Phones
A basic phone serves the most fundamental function, which is making and receiving calls. Consider the outdated Nokia smartphone, which was mainly used to play the game Snake. Any phone that doesn't have any mind-blowing technical extras is considered a basic phone in today's society. Users of the entry-level phone can communicate via voice calls, text messages, basic internet browsing, and more. Additionally, these phones may include monophonic ringtones, games, a lamp, a simple camera, etc. The idea behind a budget phone is to avoid having to pay for data plans that nobody uses. Simple phones just charge for the minutes or texts that are used or sent. Therefore, they are quite inexpensive.
2) Feature Phones
A feature phone is a subcategory of a mobile phone that offers more functions than a typical mobile but is not a substitute for a smartphone. Text messaging, calls, and some of the more sophisticated functionality available on smartphones may all be done on feature phones. This category of phones has the ability to access the Internet, cameras, and more storage compared to the basic phone. Feature phones often include a keypad with numbers. The main target market for feature phones is users who desire a versatile mobile phone but are unwilling to pay the additional costs associated with genuine smartphones.
Although there are no inherent distinctions between feature phones and smartphones, most feature phones do not accept third-party applications. Additionally, it could not have modern multimedia and Internet connectivity features and limited processor power and storage space.
3) Smartphones
A smartphone is a cellular phone with an integrated computer and additional features such as an operating system (OS), web browsing, and the capacity to run software applications that were not previously found in phones. These phones support 3G (third generation) and Wi-Fi (wireless fidelity) and often have a QWERTY keypad.
Consumers and those who use smartphones for work or business both utilize them. They give users access to a wide range of computing and mobile apps, and they are now necessary for modern daily life.
Difference between a Telephone, a Mobile Phone and a Cell Phone?
You may be heard some people call the telephone a mobile phone or a cell phone and also sometimes they just call it a phone, so all the terms have the same meaning or not.
1. Telephone
The telephone allows two or more users to communicate when they are far away to hear each other clearly or directly. A telephone transforms sound typically and most effectively the human voice into electronic signals that are sent through wires and other communication channels to a different telephone, which reproduces the sound for the user on the receiving end.
2. Mobile Phone
A mobile phone is a portable hand-held communication tool that enables call-making and receiving. Compared to earlier models, which could only make and receive calls, present mobile phones are significantly more versatile. These days, they can support cameras, web browsers, video players, and navigational systems. The main objective behind the invention of the mobile phone is to make it portable because earlier landline phones use wires for telecommunication.
3. Cell Phone
It is a type of mobile phone that operates on a battery or a cell hence it is called a cell phone. They both share the same features and services. Nowadays cell phone has developed into smartphone.
Who Invented Telephones?
Alexander Graham Bell is recognized as the creator of the telephone since his invention and demonstration of a device intended for "transmitting vocal or other sounds telegraphic causing electrical undulations" was successful. The invention of the telephone has created a great deal of mystery and debate. The theme has given rise to books, essays, and court cases. Naturally, Alexander Graham Bell is credited with the invention of the telephone. Even though his invention was the first to be protected by a patent, he was not the first person to come up with the concept of a talking telegraph.
In 1849, Italian immigrant Antonio Meucci started working on the idea of a talking telephone. For his idea of a talking telegraph, he submitted a caveat in 1871. Meucci had difficulties and was unable to extend his caveat. Up until the United States House of Representatives issued a Resolution on June 11, 2002, honoring Meucci's accomplishments and work, his part in the creation of the telephone went unrecognized.
Some historians contend that Elisha Grey, a professor at Oberlin College, submitted an application on the same day for a caveat of the telephone. Alexander Graham Bell submitted his application for a patent on the telephone. These gentlemen didn't physically visit the Patent Office; rather, their solicitors did so on their behalf. Bell's lawyer was the first to appear at the patent office, said Travis Brown's History First Patents: The Very First United States Copyright for Many Everyday Things. It was Thursday, February 14, 1876. He was that day's fifth entry, while Gray's attorney was the 39th.
Invention of Smart Phones

Our technology developed from a black-and-white television, a printed newspaper, and a landline phone to an online movie streaming service and a tiny touchscreen smartphone. An example of a portable computer that combines processing capability and mobile phone features is a smartphone. They differ in terms of old feature phones in that they have more powerful hardware capabilities and complete mobile operating systems. These features enable wider software, internet access (including surfing on the web using cellular data), and multimedia functionality (including video, gaming music, and), in addition to basic phone features like voice calls and text messaging.
There are several unique characteristics of smartphones. The International Telecommunication Union counts people who have active mobile broadband subscriptions, which include tablets and other devices with Internet access. In developed nations, smartphone adoption has now surpassed that of earlier mobile technology. However, they make up around fifty percent of mobile telecommunications in the underdeveloped world.
Benefits/Advantages of Smart Phones
There are various benefits of a smartphone.
- Communication
- Social networking sites
- Keeping Life Intact, More Organized!
- Photos and Video
- Calendars and Organization
- Maps, Navigation, and Travel
- Video in Real Time
- Entertainment
- Notes and Reminders Maps, Navigation, and Travel
- Online Banking and Finance
- Contacts
- Watches and Alarm Clocks
- Emergencies
- Remote Working
- Flashlight/Torch
- Learning and Research
Some of the main advantages are described here:-
1. Communication:
Originally, mobile phones were just mobile phones. Before examining mobile phones as tools for accessing the Internet, taking pictures, or making payments, we must first examine their main purpose: communication. A mobile phone's main function is to facilitate communication, whether it be through voice calls or text messages. Mobile messaging apps employ either short message service (SMS) or multimedia message service (MMS) to send text messages as well as audio, graphics, photographs, and videos.
Instant communication is possible with co-workers, family, friends, and the majority of the world's population, thanks to mobile phones. You can always remain in contact thanks to countless social networking services like Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook. Smartphones evolved from the first communication tools. Therefore, enhancing interpersonal communication was the major objective of its creation. Modern communications have been made possible by smartphone technological advancement. They can be used everywhere there is a signal, unlike earlier communication devices, and are always with the caller.
2. Social Networking Sites
Smartphones made easy use of social networking sites. They have browsers, internet, etc., all that is required to use these sites. This has increased the use and success of social sites.
3. Keeping Life Intact, More Organized
It offers a lot of features to live your life correctly and keep it organized. It has all things you need such as a digital book reader, a camera, an MP3 player, a GPS gadget, and more.
4. Photos and Videos
Nowadays, many individuals don't even possess cameras because their phones already have all the photo and video capture features they need. When the media has been captured and recorded, it may be quickly uploaded to the Internet or distributed to others by Bluetooth, email, or message. Numerous phones also come with added features, such as picture editing.
5. Calendars and Organization
Mobile phones are amazing organizational tools, and using their calendars is a terrific way to keep track of a hectic schedule. Whenever you have an appointment with the doctor, someone special's birthday, or just need help planning your daily responsibilities for work and personal time; your phone will let you know.
6. Navigation, Maps, and Travel
Since our phones began using GPS to guide us to our destinations, navigating has never been simpler. We can receive real-time updates on our position, accidents, roadworks, and other reasons for sluggish traffic, as well as details about local amenities like petrol stations, restaurants, and hotels, whether we are walking, cycling, or driving. You can use your phone to look up schedules, buy, and show your ticket when taking a plane or train.
7. Online Banking and Finance
Your funds can be well-organized with mobile devices. With only a few clicks, you may check the balances of your accounts, transfer funds, and pay invoices. In many cases, it's far handier than utilizing your home computer or coming into your branch. There are also applications that provide you with information about the economy, equities and shares, and your credit score.
8. Contacts
Having all the important contact information for co-workers, friends, and family in one convenient location is made possible by phones. There is no excuse for misplacing or losing anyone's address, email address, or phone number.
Different Brands and their Country of Origin

There are many brands which belong to other countries but their mobile phones are very popular in different countries.
According to the most recent information on the best smartphone companies listed by the volume of shipments, Samsung sold 64.3 million smartphone devices in the third quarter of 2022. It shipped 7.2% fewer phones overall in Q3 2022 than it did in Q3 2021. It accounts for 21% of the market share for shipments of smartphones worldwide. In other words, Samsung produced at least one out of every five smartphones supplied in Q3 2022. With the launching of new 5G devices, the business hopes to increase its market share. As the impacts of the epidemic fade, the company is seeking to capitalize on the flood of demand from customers who are now prepared to update their outdated technology.
Apple, a competing brand, came in second place with 49.2 million smartphones shipped in Q3 2022, a 2.5% annual decline and a 16% market share. With a combined market share of 37% for global smartphone shipments, Samsung and Apple were responsible for approximately 1/3 third of all smartphones shipped in Q3 2022.
Xiaomi, whose shipment reached over 40.5 million smartphones in Q3 2022, is ranked third place on this list of the top smartphone manufacturers (by shipment). This reflects a drop of 8.8% from the previous year. In fact, the business recently recorded record sales growth of 64% in the second half of last year, outpacing Apple to take up the position of second-largest smartphone producer.
Oppo came in at number four, shipping 29.5 million phones in the third quarter of 2022. In comparison to the previous year's figures, this is a considerable yearly decline of 22.6%. Vivo, which delivered 26 million handsets, a 22.8% yearly decline, rounds out the top smartphone brand list.
Apple is the only exclusive phone brand that has increased mobile shipment volume year over year, outpacing even the market. Approximately 301.9 million smartphones overall, from all brands, were supplied in Q3 2022 with a decline of 11.7% annually.
What is GSM (Global System for Mobile)?
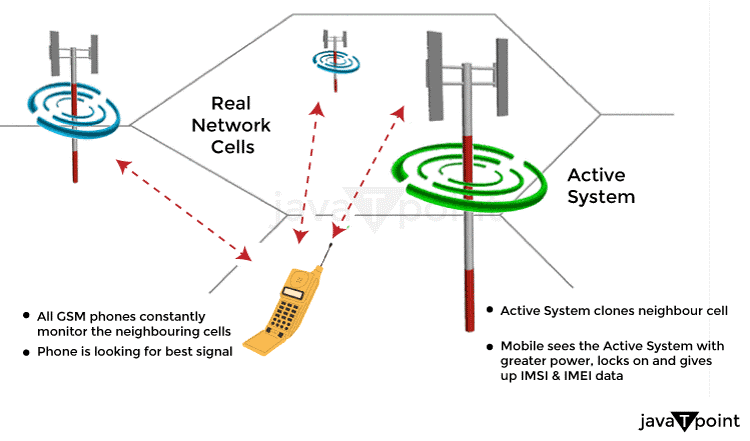
GSM offers a range of phone and data services, including roaming. Roaming is the practice of using your GSM phone number on a GSM network that is not your own. The GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) digital mobile network is used by a large number of mobile phone users, mainly in India. The most popular of the three major digital wireless telephony technologies GSM, code-division multiple access (CDMA), and TDMA, GSM makes use of a version of TDMA.
The development of wireless mobile telecommunications, which also includes Enhanced Data GSM Environment (EDGE), High-Speed Circuit-Switched Data (HSCSD), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), and Universal Mobile Telecommunications Service (UMTS), includes GSM as one of its technologies.
Working of GSM
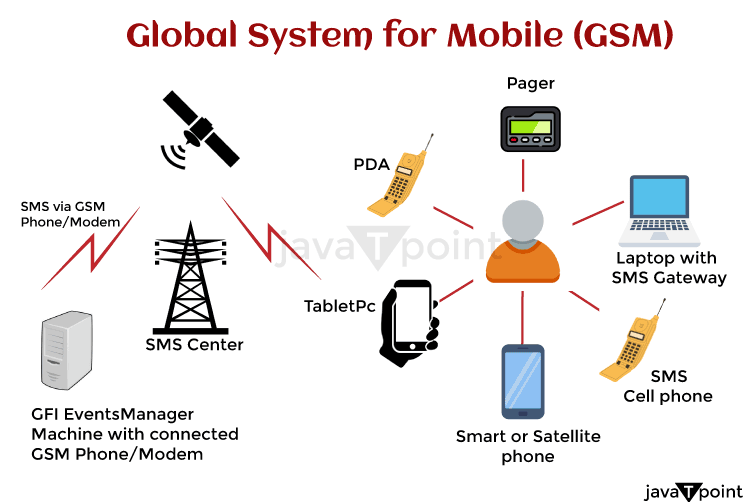
GSM transforms information into an electronic format, compresses it, and sends it together with two more streams of user information over a channel, both in their own time slot. It works with either the 900 MHz or 1,800 MHz frequency band. With the use of roaming agreements with foreign businesses, several GSM network providers enable their customers to use their phones when on the go internationally. GSM network consists of four-part or component that is used by GSM to provide its services.
These four components are:
- The Base Station Subsystem (BSS).
- The Network Switching Subsystem (NSS).
- The Operation.
- Mobile Device.
Mobile devices are connected to the network via hardware. The SIM card provides the network with identification information about the mobile user. Between the mobile and the NSS, traffic is managed by the BSS. The base transceiver station (BTS) and base station controller (BSC) are its two primary parts.
The radio transmitters, receivers, and antennas used to communicate with mobile phones are mostly found in the BTS, whereas the brains that control it are found in the BSC. A number of base transceiver stations are under the supervision and communication of the BSC.
The NSS element of GSM, which is known as the core of the network, keeps tracking the location of the caller to provide delivery of cellular services. Home Location Register (HLR) and the Mobile Switching Center (MSC) are the two main components of NSS. These parts carry out a variety of tasks, including call routing and short message service (SMS), as well as SIM card-based caller account authentication and storage.
Limitation of Global System for Mobile
The favored technology for today's telecommunication networks is GSM. However, it has drawbacks as well. Some of the limitations of GSM are:
1. Lag in bandwidth: Multiple users share the same bandwidth using GSM technologies, which can occasionally cause significant latency as additional users join the network.
2. Electronic interference: The pulse-transmission method used by GSM is known to create interference with electrical devices like hearing aids. Mobile phones must be turned off in some locations, including airports, petrol stations, and hospitals, due to electromagnetic interference.
3. Data transfer rate: GSM has a somewhat slow data transfer rate. To receive greater data rates, a user must switch to a device with more recent GSM forms.
4. Repeaters: Carriers must set up repeaters for GSM technology in order to expand coverage.
NOTE: - Repeaters are the devices used to retransmit the data after increasing their strength to travel long distances.
Role of Mobile Phones in E-waste
E-waste, also known as electronic garbage, is anything that has wires, connectors, or other electrical components. When these goods aren't properly disposed of, they might release poisonous substances into the atmosphere because they typically contain hazardous ingredients. Given the growing severity of the present global trash situation, this is (clearly) not good for the environment.
The Garbage Electronic and Electrical Equipment (WEEE) conference stated an expected 57.4 million tonnes of electronic garbage worldwide in 2021, which is more than the Great Wall of China's weight. It is obvious that there is a rising e-waste problem in the world.
Recycling e-waste is the reuse of electronic garbage, giving electronic components a second chance at life. The majority of electronic components, including batteries, circuit boards, and plastic or metal casings, may be recycled. However, only 20% of electrical goods are really recycled effectively.
6.64 billion people worldwide, according to Statistics, own a smartphone. That represents 83% of the human population, a rise of 34.32% from 2016. Many of the primary elements needed to make these mobile phones will run out within the next century if only 20% of them are recycled. The ongoing semiconductor scarcity, which has recently had an impact on both vehicle and smartphone makers, will be quickly made worse by this.
The market is now dependent on the speedy replacement of outmoded technology due to the rapid growth of mobile technology. Throughout their lifetimes, mobile devices have a variety of negative environmental effects, but by implementing circular economy principles, such as production control, device reuse, remanufacture, and recycling, as well as improved standardization, circular design involving component material selection, and modularization for easier disassembly, according to the Global E-waste Monitor, these effects can be minimized and spread over a longer period.
Conclusion
The mobile phone has transformed our world. People now use them for work, play, school, and a number of other things. Cell phones and smartphones have evolved with time. Nowadays, the majority of individuals have cell phones, and they depend on them more than ever. The cell phone is an amazing innovation that has permanently changed our way of life.
|

 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
















