Skeleton DefinitionThe skeleton is the structure made of cartilage and bones that protects and supports the body's internal organs and soft tissues. It is the supporting structure that holds together the body of most humans/animals. 
Human skeletonThe internal framework for support of the human body is the skeleton. At birth, it has around 270 bones; by adulthood, part of them have fused, leaving it with about 206 bones. The bone mass in the skeleton accounts for around 14% of total body weight (roughly 10-11 kg for the normal person) and achieves its maximum mass around the ages of 25 and 30. 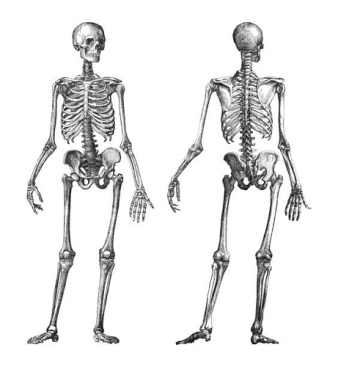
The human skeleton isn't as sexually dimorphic as numerous other primates. Still, slight variations exist between genders in the shape and structure of the skull, dentition, elongated bones, and pelvis. Female skeletal elements frequently have less robust and smaller physical features than corresponding male components within a particular population. The human female pelvis differs from men's to make childbirth easier. In contrast to most primates, male humans don't have penile bones. Animal SkeletonAlong with supporting the body, the animal skeletal system also aids in movement, defense, and sensory functions. In many protozoans, the body is supported by a simple pellicle, a hard, translucent, and nonliving envelope. It is accomplished by dead internal and external structures that support axes in the colonies of non-moving coelenterates (a group of aquatic or marine organisms) like coral, whose colonies expand to huge sizes. For the many types of creatures that can move, either internal or external structures known as endoskeletons or exoskeletons are used to accomplish movement. 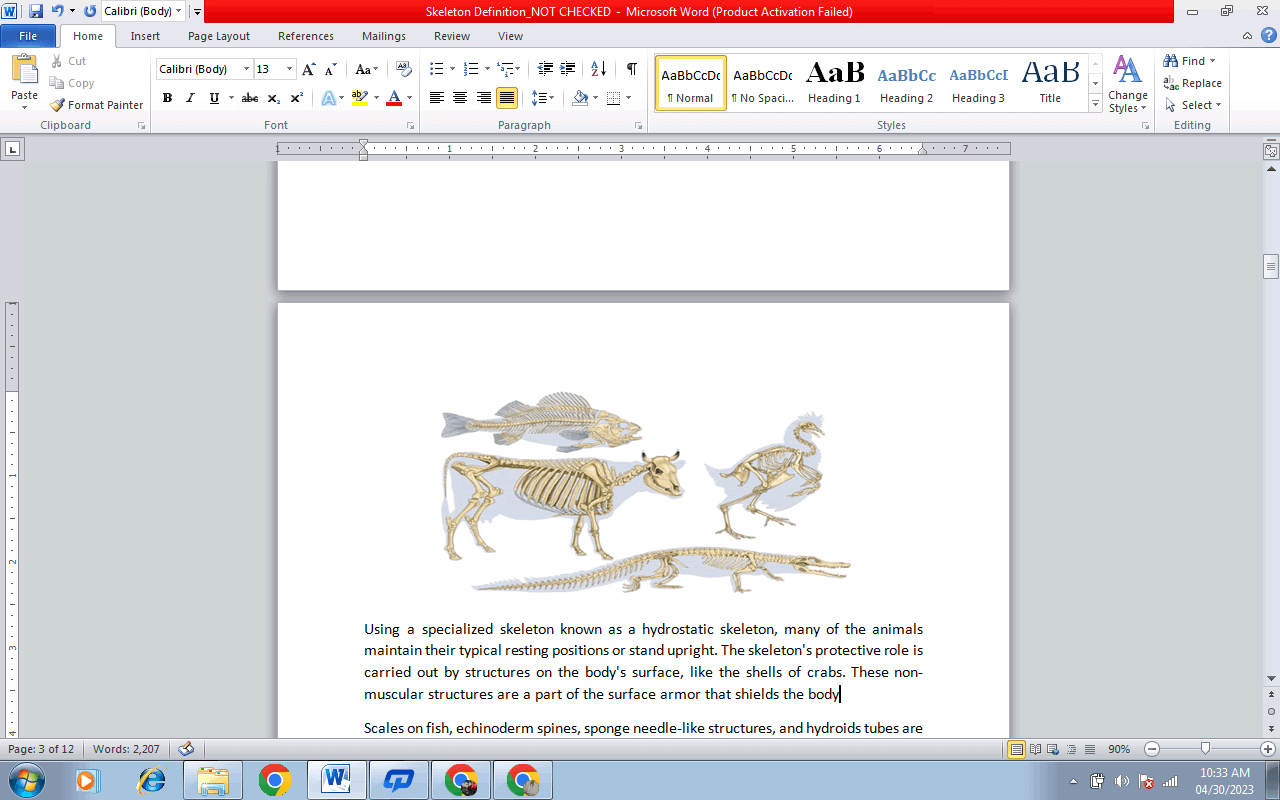
Many of the animals maintain their typical resting positions or stand upright using a specialized skeleton known as a hydrostatic skeleton. The skeleton's protective role is carried out by structures on the body's surface, like the shells of crabs. These non-muscular structures are a part of the surface armor that shields the body Scales on fish, echinoderm spines, sponge needle-like structures, and hydroids tubes are examples of similar features which help in protection. The skull of the vertebrate contains bones that help in protecting the brain. Numerous skeletal components in most vertebrates and invertebrates offer protection and a rigid base for the insertion of muscles. Skeletal SystemYour body's skeletal system serves as a structural support system. It gives the body its structure, allows movement, produces blood cells, safeguards organs, and stores minerals. The skeletal system is also referred to as the "musculoskeletal system". The main structural element of the body is the skeleton. Along with bones, it comprises connective tissue such as tendons, ligaments, and cartilage. It is also referred to as the musculoskeletal system. The axial and appendicular skeletons are the two main parts of the human skeleton. The axial skeleton, designed for placement around the body's central axis, includes the head, spine, and ribs. Major sense organs, including the eyes, ears, nose, and tongue, are also protected, along with the brain, spinal cord, heart, lungs, and esophagus. The bones in the arms, legs, shoulder, hip girdles, and other parts of the appendicular skeleton are connected to the limbs. 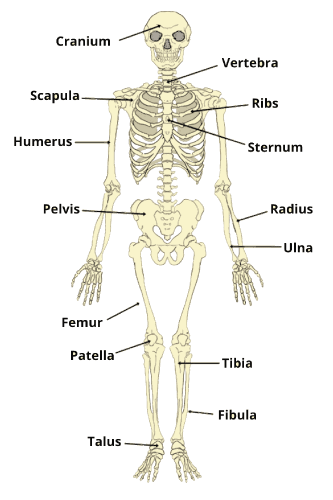
Parts of the skeletal systemThe skeletal system is a network of several components that all work together to help in movement. The primary component of your skeletal system is made up of your bones, which are solid objects that form the skeleton (the framework of your body). An adult human skeleton has 206 bones. The three primary layers of each bone are:
The other parts of theskeletal system are as follows:
FunctionsThe skeleton performs six important functions: support, movement, protection, blood cell production, mineral storage, and endocrine regulation. SupportThe skeleton's primary purpose is to provide an animal's body shape. Some aquatic species, like the octopus, don't have skeletons. This is feasible because tissues are partly supported by the fluid surrounding them, which is much bigger than air and enables some animal body structures to float. For land animals, it is necessary to have a skeleton that battles the pull of gravity, which could otherwise hinder movement and even destroy organs. Therefore, all animals that move about on land have either an exoskeleton, such asthose of insects and spiders, or an internal skeleton, such asthose of human beings and other vertebrates. MovementThe joints connecting the bones allow for movement, with some allowing for a broader range of movement than others. For example, the neck's ball and socket joint allows for a greater range of motion than the pivot joint. Skeletal muscles supply the force for movement and are attached to the skeleton at various locations on bones. The primary components of movement are muscles, bones, and joints, and the nervous system regulates each. According to some theories, primitive humans' ability to move with speed and delicacy was reduced by decreased bone density. Human bone density has drastically decreased due to the transition from hunting to agriculture. ProtectionThe skeleton helps to prevent damage to numerous important internal organs:
Blood cell productionIn the skeleton, a process known as hematopoiesis causes bone marrow to produce new blood cells. In early childhood, hematopoiesis mostly occurs in the marrow of long bones, including the femur and tibia. It primarily affects the sternum, vertebrae, pelvis, and skull in adults. StorageMinerals and calorie-rich fat that other bodily tissues may need can be stored in bones. The dense portion of bone tissue is rich in calcium, which the body can release from the bones for various purposes. The fat-rich yellow bone marrow tissue can store calories and nutrients since it mostly comprises fat. Iron is abundant in red bone marrow tissue, a component of red blood cells. Anaemia is when there is insufficient formation of red blood cells, which can cause weakness, tiredness, dizziness, and even fainting. Iron deficiency is a common cause of anemia. Endocrine regulationThe hormone osteocalcin, released by bone cells, affects male sex hormones, blood sugar, and fat storage. The pancreas produces more insulin in response to the production of osteocalcin by bone cells, which lowers blood sugar levels and increases cellular sugar uptake. Additionally, it triggers the release of the hormone adiponectin from fat cells, which encourages the breakdown of fat for energy. Osteocalcin is supposed to encourage the body to manufacture more bone cells and guide the male testicles to produce more testosterone. It isn't easy to understand how hormones interact in the human body. In this instance, it is possible that by triggering the release of insulin and the decomposition of fats for energy, it could free up more energy that the body can utilize to increase the number of bone cells. Besides these six functions, the skeletal system performs various tasks. It:
Skeletal System StructureThe skeletal system is generally designed to support an animal against gravity and protects its internal organs. Although this article focuses on the skeletal system of humans, most animals have some form of skeleton. Some species, such as sponges, can have a basic structural skeleton of calcium deposits. Others, such as the turtle, have significantly changed their skeletal structure to offer additional protection. Although this article focuses on an endoskeleton, many animals also have an exoskeleton that serves the same functions. The bones, protecting plates, or chitinous skeleton surround the muscles rather than being on the inside. The system's structure may appear completely different, but it is comparable. The only distinction is that tendons and muscles attach to the system's inner surface instead of the bones' surface. An animal's skeletal system's design reflects its evolutionary history and survival requirements. For example, humans have a tailbone. This is a developing relic from when our ancestors had a tail and were swinging from the trees. Our need for a tail diminished as we evolved into bipedalism, and it was eventually reduced to a single non-functional bone. As humans and other animals developed, animals constantly changed and adapted their skeletal systems. What are Some Typical Conditions That May Impact the Skeletal System?Various diseases and disorders can affect the tissues, joints, and bones that make up the skeletal system. Some occur due to illness or harm; others appear due to aging-related wear and tear. The skeletal system may be affected by several conditions:
How Can One Maintain The Health Of Their Skeletal System?To maintain the wellness and power of your skeleton, you are supposed to:
What Occurs When a Bone is Broken?Your physician will categorize the fracture based on how the bone breaks. Various fracture types include:
If you fracture a bone, your doctor will need to perform an imaging procedure called an X-ray to determine the type of fracture. You will need to rest it (keep it from moving) in a steady or cast for three to eight weeks, depending on the seriousness of the break. It may take several months for broken bones to fully recover. Interesting Facts
Next TopicSolution Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










