Homeostasis DefinitionHomeostasis is a fundamental concept in physiology, medicine, and biology. The word "homeostasis" refers to the equilibrium inside an organism's body. It maintains a controlled internal environment in reaction to alterations in the external world. The main purpose of Homeostasis is to keep the body's internal environment in equilibrium so it can continue to function properly. A complex network of feedback loops achieves Homeostasis. 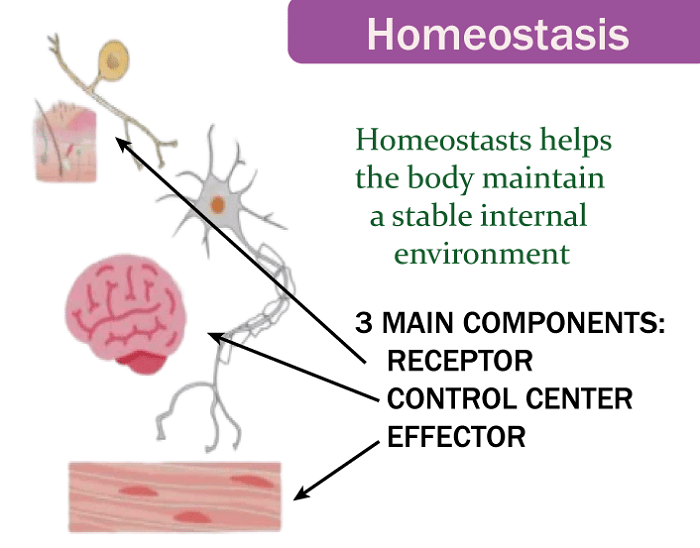
The body's physiological processes are regulated by hormones and other substances the endocrine system releases. These hormones and other substances act as messengers that travel throughout the body and stimulate specific cells or organs to respond to environmental changes. The body's ability to recognize and adapt to environmental changes helps it balance the environment inside. How to Maintain Homeostasis?To maintain Homeostasis, the body must be able to detect changes in its environment. It does this through a variety of sensory systems, such as the nervous system, the muscular system, and the endocrine system. All across the body, sensory organs pick up on environmental changes and send this information to the brain. The brain then sends signals to the appropriate organs and tissues to adjust the body's internal processes. Important of HomeostasisHomeostasis is important for an organism's health, as it helps the body maintain a steady internal balance state. The body could not survive in the face of environmental changes without Homeostasis. For example, if the body's temperature were to drop suddenly, the body would be unable to respond to the change quickly enough and could become dangerously cold. The body has to be able to quickly recognize and react to any environmental changes if we want to avoid this. How does Homeostasis Work?The body can maintain Homeostasis by using both positive and negative feedback loops. Positive feedback loops cause the environment to alter, which further prompts the same behaviour. For instance, the body's temperature will decrease when exposed to cold conditions. This will trigger a response from the body's thermoregulatory system, which will cause the body to shiver to generate heat. This shivering stimulates the body's thermoregulatory system, resulting in an even greater response. Negative feedback loops, on the other hand, result in a change in the environment that counteracts the initial response. For instance, the body's temperature will decrease when exposed to cold conditions. The body's thermoregulatory system will then respond by activating sweating to cool the body down. This sweating will then counteract the initial drop in temperature, resulting in a return to the body's normal temperature. Homeostasis is a complex process involving the coordination of many systems and processes. It is essential for an organism's survival, as it helps the body maintain a steady balance in response to external environmental changes. Without Homeostasis, the body would not be able to survive in the face of environmental changes. Homeostasis is an important concept in physiology, medicine, and biology. Examples of Homeostasis
Facts About Homeostasis
Next TopicHuman Resource Management Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









