Echo DefinitionDefinitionEcho reflects sound waves created when sound is reflected off a solid surface. It is a phenomenon that occurs when a sound wave is bounced off of a surface, like a wall or another object, and then returns to the source. The Echo is used for various purposes, including communication, entertainment, and measurement. An echo is an acoustic phenomenon whereby sound waves are reflected or bounced off a surface, typically in a continuous sequence. It creates an echo effect, with the reflected sound heard several times before dissipating. Echoes can be used to locate objects in the environment and measure the distance and size of objects. 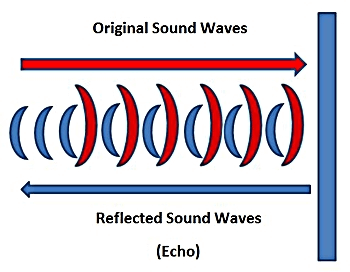
HistoryThe concept of the Echo has been around since ancient times. The Greek philosopher Aristotle first describes the phenomenon in his book, "On the Heavens." He observed that when a clap is made in a cave, the reverberation will return multiple times before fading away. The term "echo" was first used in English in the early 16th century. Echoes have been known since antiquity and were used by the ancient Greeks to locate objects and measure distances. The Greek philosopher Aristotle was the first to describe the phenomenon in detail, around 330 BCE. He used the term ??? (?ch?) to describe the repeated reflection of sound, which he observed in a cave. The term "echo" is derived from the Greek word ??? (?ch?). It was later taken up in Latin as eco and eventually passed into English. Types of EchoSeveral types of Echo can occur depending on the type of sound waves bouncing off a surface. These include:
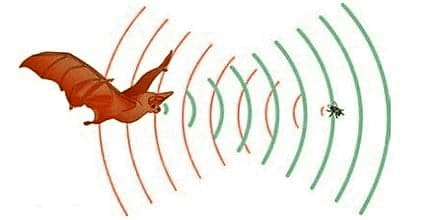
UsesEcho has many practical applications in both science and technology. It is used for communication, entertainment, and measurement. Communication: Echo has been used for communication for centuries. In ancient times, it was used by sailors and others to send messages over long distances. It is still used today for communication, such as underwater communication systems. Entertainment: The Echo is also used in entertainment, such as music. By using Echo, musicians can create unique acoustic effects and change the sound of their music. Measurement: The Echo is also used for measurement. In engineering, Echo is used to measure distances and other physical properties. In medicine, Echo measures the size and shape of organs, such as the heart. Echoes main typesThere are two main types of Echo: natural and artificial. Natural Echo results from sound waves being reflected off of a surface back to the observer. This type of Echo is common in large, enclosed spaces such as auditoriums and canyons. Natural Echo is often used to create a sense of spaciousness in these spaces. Artificial Echo is created using electronic devices to amplify a sound or signal and then reflect it to the listener. This type of Echo can be used to create a sense of depth in music and other audio recordings. Effects of EchoEcho has a variety of effects on sound, both natural and artificial. Natural Echo Natural Echo can have various effects on sound, depending on the size and shape of the reflecting surface, as well as the distance between the observer and the reflecting surface. Natural Echo can create a sense of spaciousness in large, enclosed spaces such as auditoriums and canyons. Natural Echo can also enhance or distort the sound of music or other audio recordings, depending on the size and shape of the reflecting surface. Artificial Echo Artificial Echo can be used to create a variety of effects on sound. For example, an artificial Echo can be used to create a sense of depth in music and other audio recordings. Artificial Echo can also be used to enhance the clarity of ultrasound images. Physics of EchoThe physics of Echo involves the reflection of sound waves between two or more surfaces. When a sound wave is generated, it will travel in a straight line until it strikes an obstacle, at which point the wave will be reflected. The reflected wave will then travel in a straight line until it strikes another obstacle, at which point it will be reflected again. This process is repeated until the wave is completely absorbed by its environment. The distance between the source of the sound and the reflecting surface, as well as the nature of the reflecting surface, will affect the characteristics of the Echo. For example, a long distance between the sound source and the reflective surface can result in a longer echo. A hard surface such as a wall will reflect the sound more efficiently, resulting in a clearer echo than a softer surface such as a carpet. 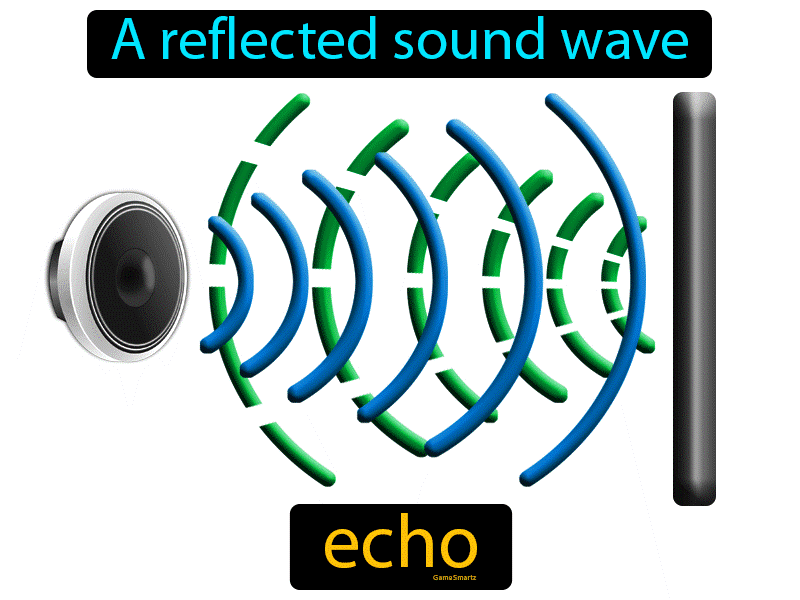
Connotation of EchoThe connotation of Echo varies depending on its context. In literature, it is often used to emphasize a point or to create a certain atmosphere. Music is used to add depth and texture, and in modern-day technology, it is used to aid in navigation. In general, Echo is associated with a sense of mystery and intrigue. It can be seen as an indication of something hidden or unknown and can be used to create an atmosphere of suspense. It is also commonly used in horror films and stories, as the reverberating sound of an echo often adds an air of fear and tension. ApplicationsEchoes are used in various applications, such as sonar, radar, and medical imaging. Sonar and radar use echoes to detect objects and measure distances. Medical imaging, such as ultrasound, uses echoes to create images of the inside of the body. Echoes are also used in music to create effects such as reverb and delay. Physical ExplanationAn echo occurs when sound waves travel from a source, reflect off an object, and return to the source. The time it takes for the sound wave to travel from the source to the object and back is called the echo time. When the sound wave reflects off the object, it changes direction and speed. The reflected wave is called an echo and is a distinct sound. The sound wave continues reflecting off the object multiple times, creating echoes. The strength of the Echo depends on the material of the reflecting surface. Hard surfaces like walls and rocks will produce stronger echoes than soft surfaces, such as cloth or carpet. ConclusionEcho is an acoustic phenomenon in which sound is reflected off a surface, resulting in the sound being heard again as an echo. It is created by reflecting sound waves between two or more surfaces. Echoes are used in various applications, such as sonar and radar, medical imaging, and music. Echo reflects sound waves created when sound is reflected off a solid surface. It is a phenomenon that occurs when a sound wave is bounced off of a surface, like a wall or another object, and then returns to the source. There are several types of Echo, including direct Echo, reflected Echo, reverberation, diffraction, refraction, and resonance. Echo has many practical applications in science and technology, including communication, entertainment, and measurement. Echo has a variety of uses, both natural and artificial. Natural Echo creates a sense of spaciousness in large, enclosed spaces. In contrast, the artificial Echo is used to create various effects on sound, such as creating a sense of depth in music and other audio recordings. Echo has a variety of effects on sound, both natural and artificial. Natural Echo can create a sense of spaciousness in large, enclosed spaces, while artificial Echo can create various effects on sound.
Next TopicEfficient Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










