Bandwidth DefinitionWhat is Bandwidth?The term "bandwidth" refers to the quantity of data that may be sent through a specific network connection or link in a particular time length. Ordinarily, it is expressed in bits per second (bps) or megabits per second (Mbps). A network connection's speed is determined by its Bandwidth, a fundamental idea in computer networking. A wired or wireless network's available capacity is gauged by its Bandwidth. It is the most data that can be moved through the web at a specific time. The faster a user can access and download data from the network, the higher the Bandwidth. 
Different Types of BandwidthUnderstanding the many kinds of Bandwidth that are accessible is crucial when discussing Bandwidth. Symmetric and Asymmetric Bandwidth are the two primary categories.
The two major forms of Bandwidth are not the only ones accessible. Some of them are Time-Division Multiplexing, Frequency-Division Multiplexing, and Wavelength-di Multiplexing.
What are the Bandwidth Requirements?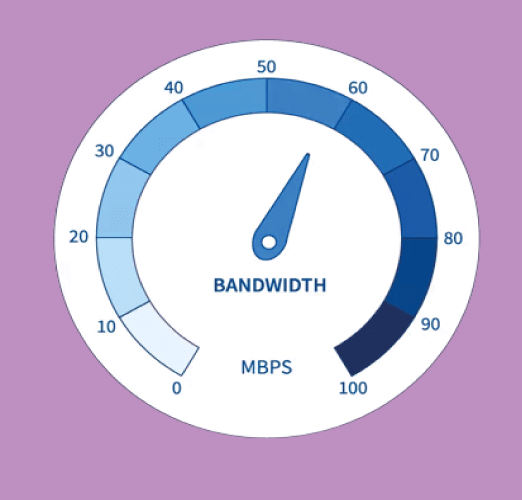
The volume of data that may be carried between two sites at a specific time is known as a network's bandwidth requirement. Bits per second (bps) or megabits per second are used to measure it. (Mbps). The speed, dependability, and quality of a network's services are all impacted by Bandwidth, which is a crucial component of network performance. The bandwidth needs of the various applications and services running on the network must be considered while constructing a network. For instance, in a home network, streaming music and video may use a lot of Bandwidth, but email and online surfing may use only a small amount. The Bandwidth needed for a corporate network might change based on the services and applications used. For instance, phone over IP (VoIP) or video conferencing could require a lot of Bandwidth, although online surfing and email might need a little.
The type of network architecture being used, the number of users on the network, the variety of devices connecting to the network, the type of applications and services running on the web, the data rate of those applications and services, and the number of users all affect the network's bandwidth requirements. As a result, it's crucial to consider each of these elements when figuring out how much Bandwidth a network needs. 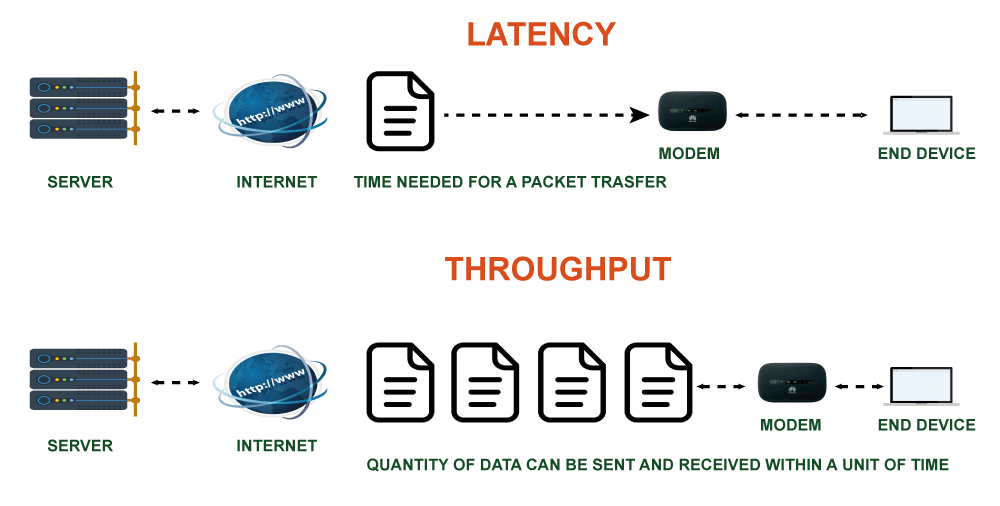
History of BandwidthThe ability of a network or a communications link to convey information or signals is referred to as Bandwidth. The term "bandwidth" first appeared in the late 19th century to define the frequencies a telegraph connection could transport. Since then, Bandwidth has gained significance in the world of technology, notably in computers and telecommunications. In general, Bandwidth is expressed in bits per second. (bps). Early telecommunications had a narrow range of frequencies that could only transmit a few hundred bits per second or bandwidths. However, bandwidths substantially expanded as technology developed, enabling far faster transmission speeds. The capacity of bandwidths to convey thousands of bits per second had been reached by the middle of the 20th century. This was particularly true in high-frequency and microwave transmissions used in military communications. The invention of coaxial cables in the 1950s allowed for the rapid transport of massive volumes of data. The contemporary digital subscriber line (DSL) connections were created when this technology was modified for usage in the telecommunications sector. 
The personal computer revolutionized how people utilized computers and the Internet in the 1970s. Computers needed more Bandwidth to run efficiently as their processing power increased. As a result, Ethernet networks were created, enabling data transfer rates of up to 10Mbps. The prior bandwidths, which could barely handle a few hundred bits per second, were greatly improved by this. The requirement for Bandwidth became even more as the Internet evolved in the 1990s. The need for Bandwidth increased dramatically with the web and streaming media development. Telecommunications firms started investing significantly in faster networks and more effective technology to accommodate this demand. By the turn of the twenty-first century, bandwidths had risen to the point that data transfer rates of up to 100Mbps were feasible. Today, as technology advances, bandwidths keep growing. Although Bandwidth has been a notion for over a century, its significance has never been higher. The demand for faster, more effective networks will only increase as the globe gets more connected. What is the Exact Meaning of Bandwidth?Usually, bandwidth measurement is done in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second (bps). (Bps). It is critical to understand how Bandwidth and data speed are different. The Bandwidth of a data link is the single measurement of its capability. Data speed is the speed at which information is sent via the network. Internet Service Providers (ISPs) frequently include Bandwidth in their subscription plans. The type of connection a user has and the program they have selected will determine how much Bandwidth is accessible to them. A user's relationship will generally be quicker with more available Bandwidth. This is so that more data may be transported at once using connections with more Bandwidth, which leads to speedier internet rates. Bandwidth is also used to refer to the amount of data that can be stored on a given device. For instance, the disk's Bandwidth may limit the greatest quantity of data that may be kept on a computer's hard drive. Typically, this is expressed in gigabytes (GB) or terabytes. (TB). Bandwidth may be used to define a connection's speed and measure data movement and storage capacity. It is essential to remember that data speeds and Bandwidth are different. Data speed is a measurement of the actual pace of data transport, whereas Bandwidth is a measure of capacity. In general, connections with more Bandwidth will deliver faster data rates. What is a Good Bandwidth?
The kind of connection, the volume of data being carried, and the volume of network traffic are only a few variables that affect a decent bandwidth. In general, a connection will perform better the more Bandwidth it has.
Getting the proper connection is crucial to guarantee a fair amount of Bandwidth. Cable or fiber-optic connections are typically the best option for residential customers. They provide quick speeds and reliable performance. The best choice for corporations is often dedicated leased lines because of their high reliability and speed. Regardless of the connection type you select, ensuring the network is set up and optimized is critical. This will guarantee the connection's effectiveness and dependability. It is also crucial to ensure the network is secure to prevent unauthorized access.
Next TopicLibrary Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










