Pure Substance Definition
A pure substance is a material that comprises a solitary kind of molecule or atom. Pure substances can be isolated into two classes: Elements and Compounds. A elements is a substance comprised of a solitary atom, while a compound comprises at least two unique kinds of atoms fortified together.
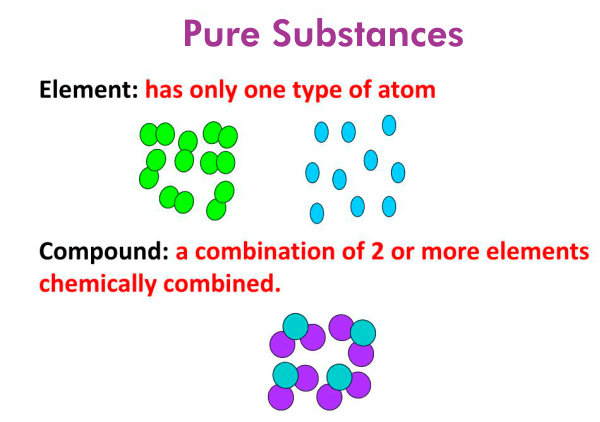
Properties of Pure Substances
Pure substances have several properties that distinguish them from mixtures. These properties include:
- Homogeneity: Pure substances are homogeneous, meaning they have uniform composition throughout.
- Definite Composition: Pure substances have a fixed chemical configuration. This means that they contain a specific ratio of atoms or molecules.
- Fixed Physical Properties: Pure substances have physical characteristics that cannot be changed, such as a constant melting point, boiling point, density, and degree of heat. These properties are independent of the sample size or shape.
- Invariable Chemical Properties: Pure substances have invariable chemical properties, which means that they react similarly under the same conditions.
Elements
One sort of atom makes up an element, a pure material. There are currently 118 identified elements, and each one has special characteristics of its individual. Elements are classified into two main categories: Metals and Nonmetals.
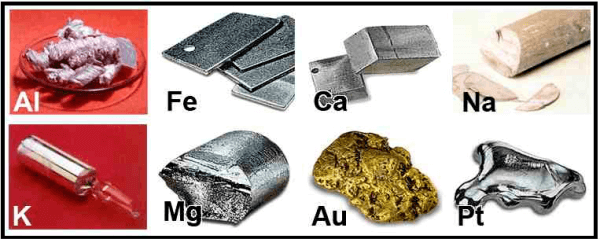
Metals are frequently lustrous, ductile, and effective heat- and electricity-conductors. They are also typically malleable, meaning they can be easily bent or shaped without breaking. Instances of metals include gold, silver, copper, iron, and aluminum.
Nonmetals are typically not shiny or brittle elements and are poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are typically not malleable, meaning they cannot be easily bent or shaped without breaking. Examples of nonmetals include carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur.

Compounds
A compound is a pure material consisting of chemical bonds between two or more atoms. Compounds have a definite chemical composition and can be represented by a chemical formula.
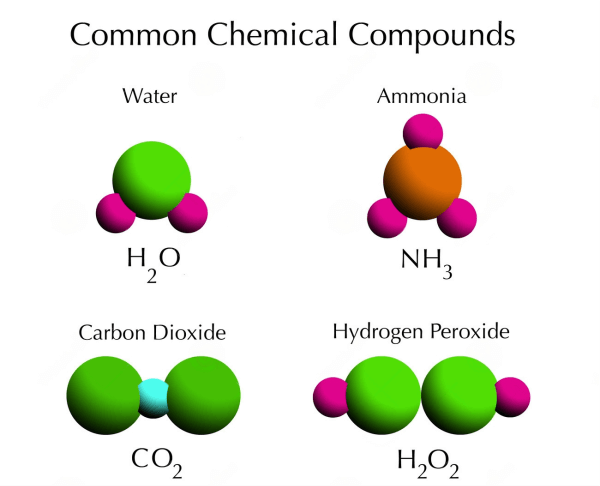
Properties of Compounds
Compounds have several properties that distinguish them from elements. These properties include:
- Melting and Boiling Points: Compounds have different melting and boiling points, unlike the elements that make them up.
- Solubility: Compared to the constituent components, compounds have varied solubility characteristics.
- Reactivity: In comparison to the constituent components, compounds exhibit varied reactivity characteristics.
- Electrical Conductivity: Most compounds are poor conductors of electricity, while some are good conductors.
- A Fixed Ratio of Elements: There is a set proportion of elements in compounds. For instance, two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom make up water at all times.
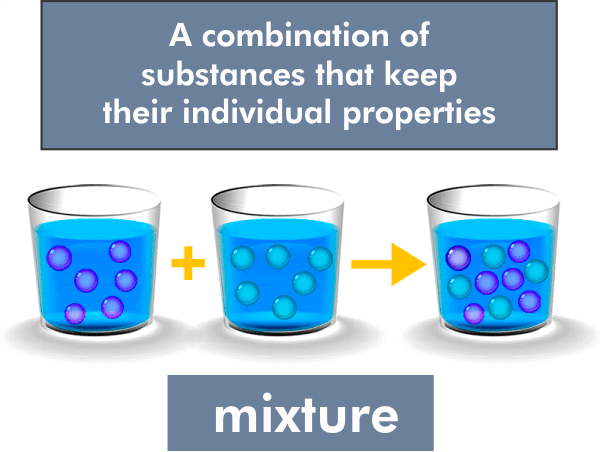
Mixtures
In chemistry, a mixture is a substance made up of two or more separate chemicals but not chemically connected to them. Mixtures can be composed of elements, compounds, or both, and they can have a variable composition, meaning that the amount of each substance in the Mixture can vary. Mixtures differ from pure substances, which are made up of only one molecule or atom and can't be physically divided into other substances.
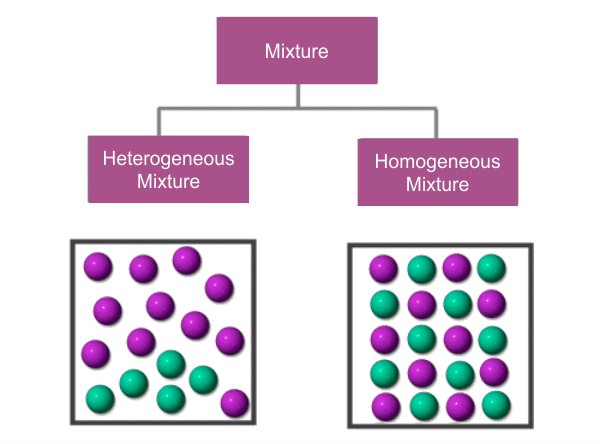
There are two categories of mixtures: Homogeneous and Heterogeneous. All parts of a homogeneous mixture have the same composition, and the combination as a whole has a consistent composition. For instance, a salt and water solution is a homogenous combination because the two ingredients are dispersed equally throughout the Mixture. On the other hand, heterogeneous mixes do not have a consistent composition throughout, i.e., various areas of the Mixture have varied compositions. Because the sand and gravel are not spread equally throughout the combination, a mixture of silt and gravel is an example of a heterogeneous mixture.
Mixtures can be physically separated into distinct components by physical methods like filtration, distillation, or chromatography. Via the passage of the combination through a filter, which lets the liquid or gas flow through while trapping the solid particles, solids are separated from liquids or gases infiltration. Distillation is a process that separates a mixture of liquids with different boiling points by heating the Mixture and collecting the vapors that are produced at different temperatures. Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures of substances depending on how well each one binds to a stationary and a mobile phase.
In outline, a mixture is a material that contains at least two substances that are not synthetically reinforced together. Mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous and can be isolated into their distinct parts through actual means. Compared to pure substances, which comprise only one type of atom or molecule and cannot be physically divided into other things, mixtures are distinct.
Differences Between Pure Substances and Mixtures
In the world, two types of material, i.e., Pure substance and Mixture, can be seen around us. While they may share some similarities, they differ fundamentally in several ways. Here are some of the key differences between pure substances and mixtures:
- Composition: Every sample of a pure material will have the same constituents since pure substances have a homogeneous composition. In contrast, mixtures have a variable composition, meaning that the composition of the Mixture can vary from sample to sample.
- Separation: Physical techniques such as distillation, filtration, or chromatography can separate mixtures, whereas pure substances cannot be physically separated into parts.
- Properties: Pure substances have well-defined physical and chemical properties characteristic of the substance, such as a specific melting point or boiling point. On the other hand, the characteristics of mixes are influenced by the characteristics of the individual components and the relative proportions of each component in the combination.
- Homogeneity: Pure substances are consistently homogenous, meaning their chemical makeup is constant throughout. Contingent upon whether the parts are consistently appropriated all through the Mixture, mixtures can be homogeneous or heterogeneous.
- Chemical Reactions: Pure substances have a definite chemical composition; their properties are determined by the atoms or molecules that make up the substance. In contrast, the properties of mixtures can be more difficult to predict because they are determined by the properties of the individual components, which can interact with each other in complex ways.
- Purity: Pure substances are, by definition, pure, meaning they do not contain any other substances. Conversely, mixtures can contain impurities or contaminants that may affect their properties or behavior.
- Energy Changes: Pure substances undergo phase changes or chemical reactions at well-defined temperatures or conditions involving specific energy changes. In contrast, mixtures can exhibit a range of behaviors depending on the properties of the components, and their behavior may not be as predictable or well-defined.
Pure substances and mixtures are fundamentally different materials with different compositions, properties, behavior, and separation methods. In different disciplines, like science, materials science, and designing, grasping these distinctions is essential.
Examples of Pure Substance
- Gold: Gold is a perceived component with the atomic number 79 and the chemical symbol Au. It is an uncommon, splendid yellow metal valued for its stylish allure. Since there is just one type of atom in gold and because it cannot be physically or chemically divided into other things, gold is a pure material. It has a well-defined melting point and boiling point and exhibits specific physical and chemical properties characteristic of the element.
- Water: Water is a compound with the chemical formula H2O. It is a colorless, odorless liquid essential for life on Earth. Since it just contains hydrogen and oxygen atoms and cannot be broken down into simpler compounds by physical or chemical processes, water is a pure material.
- Oxygen: The element of oxygen has the atomic number 8 and the chemical symbol O. It is a colorless, odorless gas essential for animal respiration and combustion in fuels. Since oxygen only contains one kind of atom and cannot be divided into smaller compounds by physical or chemical processes, it is a pure material.
- Diamond: Diamond is a form of carbon with a crystalline structure. It is a translucent, strong stone prized for its elegance and toughness. Because a diamond only contains one kind of atom (carbon), it is a pure material that cannot be divided into more basic components by physical or chemical processes.
- Sodium Chloride: A substance with the chemical formula NaCl is sodium chloride, usually called table salt. It is a white, crystalline solid that is essential for the human diet and has a variety of other uses. Since it contains sodium and chloride ions and cannot be physically or chemically broken down into other things, sodium chloride is a pure material.
- Helium: Helium is an element with the chemical symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless gas used in various applications, including balloons and as a cooling agent in nuclear reactors. Since it exclusively contains helium atoms and cannot be divided into other atom types by physical or chemical processes, helium is a pure material.
|







 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now











