Past Tense DefinitionThe past tense is a grammatical tense that is used to represent previous acts, occurrences, or conditions. It is an important component of English grammar, and learners must understand its usage and development in order to successfully express themselves in the language. 
We are aware of the three sorts of tenses employed in English grammar: Past Tense, Present Tense, and Future Tense. Each of these tenses is made up of verbs (including regular and irregular verbs) that are used to denote the happening of a situation or action at a specific moment. Let us study and understand more regarding the Past Tense and its various types today. Definition Of Past TenseThe past tense describes acts that occurred in the past. It's one of the three primary grammatical tenses, along with present and future. The past tense is used to show that an event has already occurred, but it can also represent a state of being. For example, something could have been done differently or in a distinct state in the past than it is now. It can be used to discuss what we have envisioned. Past Tense has been defined by experts as;

Types Of Past TensePast tense verbs, as the name suggests, are used to describe an action, occurrence, or condition that occurred in the past. Each tense contains four components that discuss the completeness of the event or action, and we have four sorts of past tense verbs depending on that:
Simple Past TenseThe simple past tense is utilized to express or describe an event or situation that occurred or existed in the past. The following situations or conditions call for the usage of the simple past tense:
Making a Simple Past Tense Verb We add '- ed' to produce the simple past tense verb. We add '-d' and to verbs concluding in 'e'. Nonetheless, several simple past tense verbs, such as cut, put, and set, stay the same in both the present and past tense. Here are several examples:
Examples of the Simple Past Tense
Regular Verbs
Irregular Verbs
2. Past Continuous TensePast Continuous Tense is kind of tense that is used to represent an ongoing action or event that occurred at some point in the past. It makes use of the auxiliary word was or were + present participle. Past Continuous Tense examples include:
As a result, you employ Past Continuous Tense to describe any previous occurrence or state that was ongoing at some point in the past. Past Continuous Tense Definition Past Continuous Tense is a tense often used express occurrences or circumstances that were happening at a certain point in the past but have now concluded. In other terms, the past continuous tense is employed to express or signify acts that started in the past and were still in progress when some other event occurred. It is vital to remember that two activities may have taken place simultaneously in the past, and one may have been interrupted by the occurrence of the other. As a result, both activities took place previously. It is sometimes referred to as the past progressive tense. Tense Structure The Past Continuous is used to indicate acts that started in the past and frequently continued for a small period after the action began. The Past Continuous Tense has the following structure: Was/were + V (Present Participle) Example: At four o'clock yesterday, I was exercising in the backyard. Was or were + present participle is used in this tense. We employ 'was' whenever the subject is single and 'were' whenever the subject is plural to create the past continuous tense. The present participle is produced by including the suffix -ing to the base of the verb. For instance, studying, reading, mingling, giggling, and so on. We indicate these by flipping the subject and was or were whilst framing the inquiries in the past continuous tense. We utilize not to create negative statements. The following are examples of when we utilize Past Continuous Tense with sentences: 1. For any disrupted action or situation in the past Sentence: For instance- While she was preparing dinner the telephone rang. That suggests that she was preparing food when the phone rang in the past. As a result, the first incident, cooking, was interrupted by the second event, the telephone ringing up. 2. Interruption at a given point in time Sentence: Yesterday at eight AM, I was drinking coffee. That is, at 8 a.m., I was in the stage of drinking the coffee. I had started drinking coffee before 8 a.m. 3. Describes concurrent actions or events Sentence: He was humming a tune while taking a stroll in the garden. That suggests that both humming a tune and strolling at the same time. 4. Sentence that Defines the Atmosphere Example Sentence: As I arrived to the shopping centre, many people were busy shopping for clothes, kids were enjoying in the entertainment zone, and others were eating great cuisine. It captures the atmosphere of a shopping complex from the past. Usage of the words 'always' and 'constantly' Sentence:
It suggests that his constant chatting annoyed me in the past. Past Continuous Tense Examples Let us have a look at past tense examples to better understand this.
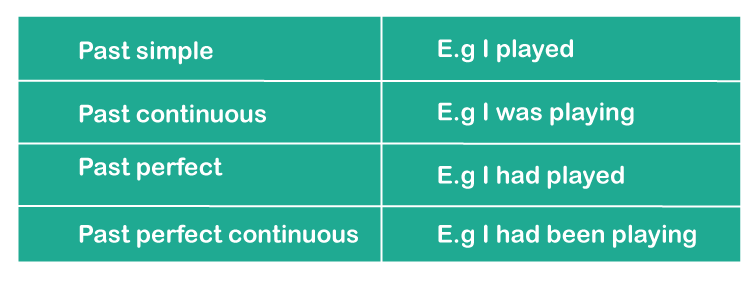
Past Perfect TensePast Perfect Tense is a tense used to represent acts that occurred before some period in the past. It employs the auxiliary verb had + past participle. The rule applies regardless of whether the topic is singular or plural. Past perfect tense examples include:
As a result, you employ the past perfect tense to describe any past event or state that occurred prior to some time point. Past Perfect Tense Definition The past perfect tense is utilized to represent actions that started and ended in the past prior to any other action occurred in the past. The past perfect tense, as the name implies, is a part of the perfect tense and so represents accomplished activities. In other words, it depicts the first finished activity, followed by another that occurred prior to the present moment. Definition and Formation
This tense incorporates had + past participle. We utilize 'had' in the past perfect tense regardless of whether the subject is singular or plural. The past participle is generated by appending the suffix -ed or -d to the root of the verb. For instance, pushed, skipped, mixed, cleaned, and so on. However, you may utilize verbs with irregular past participles like as woken, gone, done, won, eaten etc. Sentences in the Past Perfect Tense to describe: The following are examples of when we use Past Perfect Tense in conjunction with sentences: 1. Previous completed actions before starting another Sentence: Only after we'd reserved our seats, we were able to enter the movie theater hall. It indicates you reserved seats, which is the first completed activity, and you were permitted in the cinema hall, which is the second completed action. 2. Events that occurred before a certain event in the past Sentence: I had witnessed the films without ever having to purchase the bookings. It implies before you were permitted to view films without bookings but not anymore. 3. Conditional sentences Sentence: If I had bought cinema tickets, we could have seen the film. It indicates you had not acquired movie tickets and hence were unable to watch the film. 4. Reported Speech The guard inquired if we had purchased cinema tickets. It implies you had to present the guard the passes you purchased. 5. Demonstrate discontent with previous actions or circumstances. Sentence: I hoped I had bought the movie tickets ahead of time. It indicates you did not acquire cinema tickets and hence were unable to see the film. As a result, you feel disappointed with your previous actions. Important note: Do not use the Past perfect tense unless you are presenting a series of occurrences. So the listener or reader will be wondering what happened next in this scenario. There is a requirement for context in order to understand the past perfect tense. That makes no sense in the absence of context. With the past perfect, we frequently employ the adverbs already, still, just, ever, and never. Examples:
Past Perfect Tense Examples Here are some more sentences with the past perfect tense.
Past Perfect Continuous TenseIn our everyday lives, we frequently use the past perfect continuous tense. Nonetheless, we sometimes use it wrongly. This tense essentially expresses the "past in the past." As a result, you will learn about the construction and usage of the Past Perfect Continuous tense in this section. Past Perfect Continuous Tense The past perfect continuous tense is a verb tense used to represent an action that started in the past and continued until another point in the past. It's also known as the past perfect progressive. In general, the past perfect continuous tense is employed in a sentence to describe an action that began in the past and carried until a specified point in the past. It is also known as the past perfect progressive tense since it pertains to an action that continued until a specific point in the past. See the numerous meanings of the past perfect continuous tense presented by different dictionaries. Past Perfect Continuous Tense Definitions
Formation of Past Perfect Continuous Tense We create the past perfect continuous tense by using: had been + the verb's present participle (root + -ing) The past perfect continuous tense differs from the present perfect continuous tense in that it represents an action that began in the past and continued until the present. Conversely, the past perfect continuous tense refers to an action that began in the past, proceeded in the past, and finished in the past. Past Perfect Continuous Tense Forms We create the past perfect continuous tense by combining: Had +been +present participle We inverted the subject and had to indicate questions. We utilize not to create negatives. As an example: Statement: I had been standing there for more than 15 minutes when john finally showed up. Question: Had you been standing there for more than 15 minutes when he finally showed up? Negative: You hadn't been there for more than 15 minutes when he came. Past Perfect Continuous Uses To comprehend how to employ the past perfect continuous tense in our everyday lives, we must first study its functions. Duration Prior to Something in the Past The past perfect continuous tense is used to indicate that something started in the past and persisted until another point in the past. We may utilize the past perfect continuous with both "for 10 minutes" and "for 6 months." This is associated with the present perfect continuous, as you will see. But, the length will not remain till now; rather, it will end before another event occurs in the past. Examples:
Cause of an Event in the Past Another effective technique to express show and effect is to employ the past perfect continuous prior to another past action. Examples:
Past Perfect Continuous vs. Past ContinuousMost English speakers choose to use the past continuous rather than the past perfect continuous if we do not give a duration like "for 10 seconds," "for 3 months," or "since Wednesday." You must take great care because it may alter the meaning of the statement. Past continuous emphasizes intermittent acts, whereas past perfect continuous emphasizes a period of time preceding something in the past. The following examples will help you comprehend the distinction: Examples:
It highlights how weary she was because she had been practicing for a long time. It's also possible that she was still working out at the time OR that she had just completed. 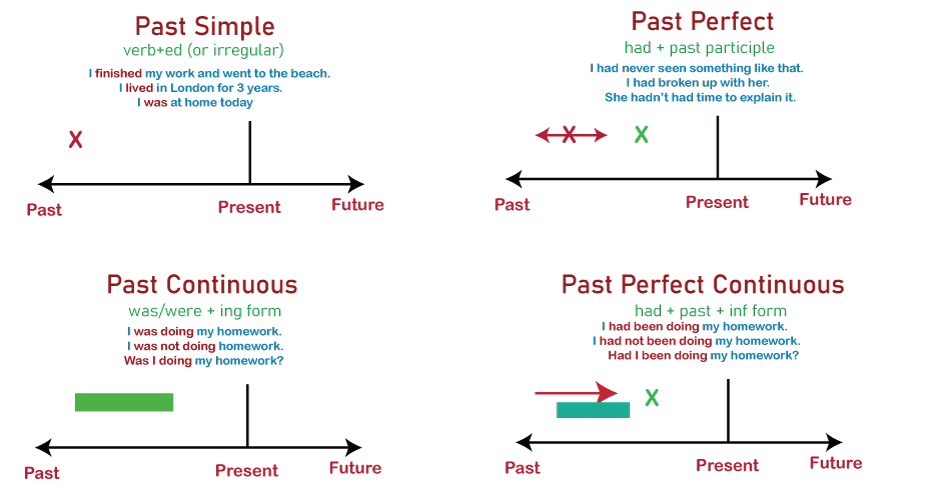
Tips for Usage and Application of Past TenseHere are some significant pointers on how to use and apply the past tense:
Practice using the past tense in varying situations to enhance your accuracy and effectiveness. Common Mistakes of Using Past Tense In some cases, using the past tense rather than the present perfect tense can make the statement sound odd or inaccurate. 1. When discussing a finished action or occurrence in the past, forgetting to use the past tense It is critical to utilize the past tense while describing a finished activity or occurrence in the past. "He walked to the mall," for instance, is correct, although "He walk to the mall" is incorrect. In certain cases, forgetting to utilize the past tense can make the phrase sound incomplete or inaccurate. 2. Using the past tense to express finished past actions or events The past tense is utilized to represent finished past actions or events, not current actions or events. "I was heading to the shop," for instance, is correct, however "I was liking that music" is incorrect. Employing the past tense to describe ongoing actions or events that happened can make the statement sound odd or inaccurate. 3. Employing the past tense whenever the present perfect tense is necessary for a past activity with a present result. As previously stated, the present perfect tense is employed to depict past activities with a current relevance or outcome. In some cases, using the past tense rather than the present perfect tense can make the statement sound odd or inaccurate. 4. Using the past tense to indicate a future event The past tense describes accomplished actions or events in the past, not future happenings. "I will go to the gathering," for instance, is correct, however "I will went to the event is incorrect. When used for a future event, the past tense might make the statement sound odd or inaccurate. 5. Employing the past tense whenever the past participle form is needed in a passive construction. The past participle variant of a verb, not the past tense, is employed in passive compositions. For instance, "The bike was broken" is right, whereas "The bike was broke" is incorrect.In passive compositions, employing the past tense rather than the past participle form might make the statement sound odd or inaccurate. 6. Irregular verbs with similar-sounding past tense forms. Certain irregular verbs include similar-sounding past tense forms, that can cause misunderstanding. In the past tense, the words "drink" (drank) and "sink" (sank) sound alike. Confusion might occur when irregular verbs that sound alike in their past tense form are used incorrectly. Thus, it is vital to be mindful of these typical mistakes while using the past tense in order to avoid misunderstanding and enhance your ability to use it correctly. ConclusionFinally, the past tense is a grammatical form that is used to represent previous acts, occurrences, or moods. It is used to transmit information about finished actions as well as to build a sequential relationship between various events. Based on the verb, the past tense can be formed in an array of ways, and irregular verbs may also have distinctive past tense forms which must be memorized. To avoid confusion and communicate properly, it is critical to employ the past tense correctly.
Next TopicPatent Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









