IP Address DefinitionThe IP address normally showcases the location of a device on the network. This is a unique identifier for devices, in other terms it is a special address. The principles regulating the data structure sent over the Internet or a local network are known as "Internet Protocol," or IP. IP addresses, which contain geographical data and make devices reachable for communication, are essentially identifier that permits content to be transferred among devices on a network. There must be a means to distinguish computers, routers, and webpages online, and a method for achieving this is provided by IP addresses, which are crucial to internet operation. What is The IP Address?A series of integers divided by periods make up an IP address. Four digits represent IP addresses; 192.158.1.38 could represent one such address. The range of every single value in the set is 0 to 255. Therefore, the complete IP address range is 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. 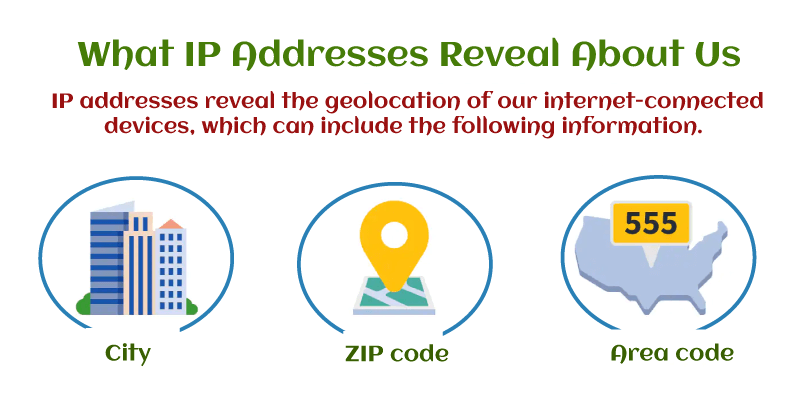
No two IP addresses are the same. The Internet Authority for Assigned Numbers (IANA), a branch of the Worldwide Organization for assigned numbers and Names (ICANN), generates and distributes them mathematically. To preserve the safety of the global web and make it accessible to everyone, ICANN was founded in the US in 1998. Every time someone acquires a website on the web, they use a domain name registry, which then pays ICANN a nominal fee. IPv4 and IPv6 are the two types of Internet Protocol (IP) addresses most often used on the Internet. An address using IPv4 is written as a string of four dots decimal digits, with a period separating each octet, like this: 192.168.35.4. While the remaining digits indicate the real host address in a particular network, which could be a personal computer or a server, the first octet's three digits identify a specific network on the Internet. Eight sets of four hexadecimal digits are represented by an IPv6 address, which looks like 2620:cc:8000:1c82:544c:cc2e:f2fa:5a9b. How Does IP Address Work?An IP address is a member of the TCP/IP family of protocols, and it operates in the background, facilitating internet connections between devices and websites. 
Computers can exchange information over the Internet with the help of an IP address. Most IP addresses are only numbers; however, as internet usage increases, some addresses now include letters. IP addresses come in four varieties: private, public, static, and dynamic. Static and dynamic signify permanence, whereas public and private indicate the precise position of the network (private is used inside the network, and the public is utilized outside the network). An IP address regarded as static was manually generated rather than assigned. A static IP address is also permanent, unlike a dynamic IP address given by a DHCP server, and is susceptible to change. The most typical kind of network protocol address is the dynamic IP address. Unlike static IP addresses, dynamic IP addresses have a limited lifespan and eventually expire. Either the computer instinctively asks for a new lease, or a new IP address might be assigned. Since each IP address is entirely peculiar to the computer systems or uses it has been assigned to, they can be compared to Social Security Numbers (SSNs). Routers can track where they are transferring data on the Internet thanks to generating these numbers. Additionally, they guarantee that the intended recipients' devices are receiving the messages. A device called a router requires an Internet Protocol (IP) address to connect to the desired web address, similar to how a delivery service needs a postal address to dispatch a parcel. An IP address has two main purposes:
According to one description of its function, "A name conveys what we want. An address identifies its location, and a path shows the destination. Each IP packet's header includes the IP addresses of the sending and receiving hosts. Importance of IP addressIP addresses are as significant as a person's identification number or card. It guarantees protection for your advantages and fosters your innovation in the subject matter or fields that interest you as a user. A separate IP address is crucial for any website that blogs or educates visitors by offering relevant content for college-bound youngsters. One can only envision the emergence of additional channels of an expanding network. To administer these systems to each last client, you require IP addresses, as technology is altering quicker than the human DNA itself. As a result, IP addresses are crucial since it would be challenging to access your network without them. What Distinguishes IPv4 from IPv6?IPv4, as well as IPv6, allow for the identification of networked devices. There are, however, a few minor variations in how they function. IPv4 restricted the accessibility of IP addresses; this led to the development of IPv6, a more recent IP version. A list of distinctions between IPv4 and IPv6 is provided below:
Type of IP address1. Private IP AddressA unique Internet Protocol (IP) address is assigned to each computer connected to a private or home network. Personal IP addresses are exclusively utilized on internal networks and are not accessible from the Internet. Machines, smartphones, tablets, Bluetooth devices, smart TVs, and printers are examples of devices that have private IP addresses. Secure IP addressing is projected to continue expanding as network of things products gain popularity. 2. Public IP AddressThese addresses are given by an ISP, allowing a router to connect to the World Wide Web or an external network. Since public IP addresses are available to everyone on the network, multiple devices using a single connection to the Internet will also share a single public IP address. 3. Changing or Dynamic IP AddressesEvery time a device connects to the Internet, an entirely novel IP address is given to it, and these IP numbers continually change. ISPs purchase immense pools of internet protocol addresses to automatically allocate to their clients. To save money and make network management simpler, they circulate and renew these addresses among several clients. Additionally, an IP address that changes has security advantages because it makes it more difficult for hackers to break into the network's interface. 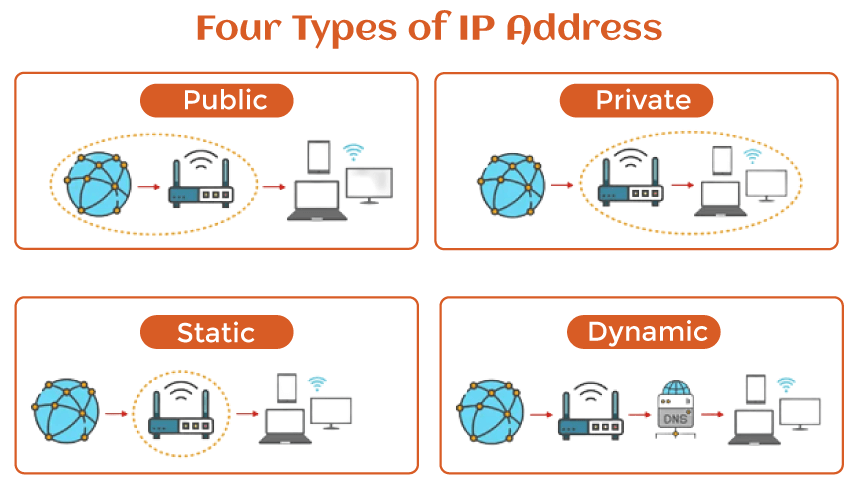
4. Permanent or Static IP AddressesOnce allocated by the network, static IP addresses are unchanging in contrast to dynamic IP addresses. Static IP addresses aren't necessary for most internet users and organizations but are for those interested in operating their own internet servers. Every website and email address connected to a specific web server will perpetually have a constant IP address that allows access via the Internet, thanks to a fixed IP address. Website IP addressThis includes IP addresses used for web developers who use a hosting provider rather than their servers to host their websites. There are two categories of website IP addresses:
IP Address SecurityCybercriminals can use an IP address in many ways. An IP address can be utilized for many harmful activities once made public. It's best to maintain it as confidential as you can because of this. Both were hiding the Internet Protocol (IP) address, using a private virtual network service to securely access the Internet, and hiding the IP location through a web proxy or browser that anonymizes online traffic, like Tor, are excellent options. Here are a few ways hackers can use a taken-away IP address. 1. Download Unlawful ContentCriminals frequently access and download unlawful content using hijacked and unsecured IP addresses. They can avoid being tracked in this way because the IP addresses can be linked to their owners. 2. Tracking A Person's LocationMost public locations, including their home city, can identify their precise location. Criminals can even trace the IP address owner's home address with a little research. 3. Attacks Known as Distributed Denial-Of-Service (Ddos)With an IP address, hackers can launch specific DDoS assaults against a system. To bring down a website during one of these assaults, enormous amounts of bogus traffic are typically sent there. 4. Spread SpamAdvertisers can add tracking software?which records IP addresses?to online activity and content. A guest browsing history targets advertising and creates spam using the stored IP addresses. Theft of identities is rising, and fraudsters are always searching for personally identifiable data (PII), such as mailing addresses or social security numbers. Even though an Internet Protocol (IP) address is not legally PII, it can still be used by cybercriminals to access other data. For instance, if a hacker has an individual's IP address, they can quickly find their ISP and try to mimic them through vishing attacks, which may prompt the ISP to provide sensitive information. ConclusionIP addresses are used when communicating among multiple distinct gadgets inside or outside of the network using the TCP/IP protocol. Internet Service Providers (ISP) are used to locate and manage devices. In today's environment, IP addresses are becoming more and more important. It enables you to find your devices and view any device that is connected to a network.
Next TopicLAN Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










