Forecast DefinitionForecasting is the practice of creating predictions based on previous and present facts. These can afterward be compared (resolved) against what happens. For example, a corporation might forecast its sales for the coming year and then compare it to the actual results. Prediction is a similar but more generic term. 
Forecasting can refer to specific formal statistical approaches that use time series, cross-sectional, or longitudinal data, or it can refer to less formal judgmental procedures or the process of prediction and resolution itself. Usage can differ depending on the application. For example, in hydrology, the phrases "forecast" and "forecasting" may be reserved for estimates of values at specific future periods. Still, "prediction" is used for more general estimations such as the number of times floods will occur over a long period. Risk and uncertainty are central to Forecasting and prediction. It is generally accepted that indicating the degree of uncertainty attached to projections is a good practice. In any type of case, the data must be up to the date if the forecast needs to be as accurate as possible. In some circumstances, the data used for predicting the variable of interest is forecast itself. Applications of ForecastingForecasting has many uses in sectors where estimations of future conditions are relevant. The accuracy varies significantly depending on the field. It is likely that the final value will be close to the forecast if the factors that connect to what is being predicted are well known and understood and there is a significant quantity of data that can be utilised. If this is not the case, or if the forecasts alter the actual outcome, the forecast's reliability can be considerably reduced. Building Egain Forecasting has become popular due to climate change and rising energy prices. This tries to reduce the energy required to heat the building, lowering greenhouse gas emissions. 
Forecasting is utilized in the customer demand planning in manufacturing and distribution businesses daily. While the accuracy of projections for actual stock returns is contested by the efficient-market hypothesis, forecasting of broad economic trends is common. Both non-profit and for-profit private entities provide such analysis. Foreign exchange movements are often forecasted using a chart and fundamental research. The primary distinction between chart analysis and fundamental economic analysis is that chartists investigate merely the price activity of a market. In contrast, fundamentalists strive to understand the underlying causes of the action. Financial institutions combine evidence from fundamental and chartist researchers into a single note to make a final forecast on the currency in question. Forecasting has also been used to predict how conflict situations may develop. Forecasters do empirical studies to assess the effectiveness of various forecasting models. However, research has shown little difference in the accuracy of projections made by specialists with an understanding of the conflict scenario and those made by persons with far less information. Similarly, other researchers claim that role thinking putting oneself in the shoes of others to foresee their decisions does not improve forecast accuracy. 
The link between forecasting and planning is crucial. Forecasting is the prediction of what the future will look like whereas planning is the prediction of what the future should look like. There are many correct forecasting methods. Your approach should be based on your objectives and circumstances (data, for example). A selection tree is an excellent place to look for a method. The applicability of Forecasting will be as follows Customer Demand Planning and Supply Chain ManagementForecasting can be used in supply chain management to ensure the correct product is at the right place and time. Accurate Forecasting will assist merchants in reducing surplus inventory and because of increasing profit margins. Forecasting accurately will also assist them in meeting consumer demand. Demand planning often known as supply chain forecasting, incorporates statistical Forecasting and a consensus procedure. According to studies, extrapolations are the least accurate but firm earnings estimates are the most dependable. Demand planning is a supply chain management method that allows a company to forecast future demand and successfully adapt company output whether products or services are reliable. Economic ForecastingThe process of producing economic predictions is known as Economic Forecasting. Forecasts can be made at a high level of aggregation, such as GDP, inflation, unemployment, or the fiscal deficit, or at a lower level such as for specific sectors of the economy or even specific enterprises. 
Economic Forecasting is the primary activity in economic analysis and is a measure to determine the future prosperity of an investment pattern. National governments, banks, central banks, consultants, and private sector groups such as think-tanks, enterprises, and international organizations like the International Monetary Fund, World Bank, and the OECD all engage in economic Forecasting. "Consensus Economics" collects and compiles a wide range of forecasts. Some forecasts are prepared every year, but many are altered more frequently. Egain ForecastingEgain Forecasting is a procedure of controlling building heating that involves calculating the amount of heating energy that should be provided to the building in each time unit. Combining structural physics and meteorology, building attributes, weather factors such as outdoor temperature, wind power and direction, and solar radiation will all be considered. 
In the case of conventional heating regulation, only the current outdoor temperature is considered. The ENLOSS mathematical energy balance model developed by Prof. Roger Taesler from Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute in association with Thorbj�rn Geiser (member of the board) and Stefan Berglund who are both currently employed at Egain Sweden AB, served as the foundation for developing the Egain forecasting method. Energy ForecastingDemand (load) and price forecasting for electricity, fossil fuels (natural gas, oil, coal), and renewable energy sources (RES; hydro, wind, solar) are all part of energy forecasting. Forecasting can take two forms predicted price value forecasting and probabilistic Forecasting. When the electrical sector was regulated, utility monopolies utilized short-term load forecasts to maintain supply dependability and long-term demand estimates to plan and invest in new capacity. Land-use ForecastingThe method of predicting and projecting the probable future allocation as well as distribution of land uses within a certain geographic area is known as land use forecasting. It entails analysing present land use patterns, demographic trends, economic considerations, and other relevant information in order to forecast how land will be used in the future. 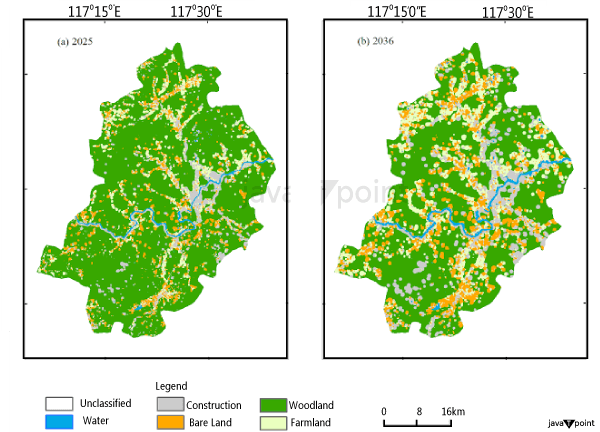
In practice, land-use models are demand-driven with aggregate information on growth provided by an aggregate economic forecasting activity serving as inputs. Estimates of land-use are used in transportation planning process. Political ForecastingThe objective of political Forecasting is to predict the consequences of political events. Political events can include prudent decisions, actions by political leaders, and other issues involving politicians and political institutions. 
Political Forecasting for elections is quite popular, particularly among mass market audiences. Political forecasting methods frequently use mathematics, statistics, and data science. Political Forecasting about elections is connected to psephology. Product ForecastingProduct forecasting is the science of estimating a new product's success in the market. The forecasting model must consider product awareness, distribution, price, meeting unmet demands, and competitive alternatives to do this. Trend analysis, market research, and statistical models are some of the methodologies utilized for product forecasting. 
Examining past data to uncover patterns and trends that may be utilized to forecast future demand can be stated as trend analysis. Gathering information on consumer preferences, shopping patterns, and market trends to evaluate future demand for a product can be stated as research analysis. Statistical models, such as regression and time series analysis use mathematical algorithms to forecast future demand based on existing data. By meeting client demand, effective product forecasting can help firms reduce inventory costs, enhance production efficiency, and maximize profits. Sales ForecastingForecasting future sales based on historical data, market trends, and other pertinent factors is known as sales forecasting. It is a must-have tool for organizations of all sizes, allowing them to make informed decisions regarding inventory, staffing, and other resources. 
Various methodologies such as regression analysis, time series analysis, and machine learning algorithms can be used to generate sales forecasting. These procedures enable firms to find patterns in historical data and utilize them to forecast future sales. Businesses can avoid stockouts, decrease waste, and increase profitability by precisely forecasting sales. Examining and adjusting sales projections frequently is crucial to account for changes in market circumstances and other factors which may affect sales. Technology ForecastingTechnology forecasting aims to predict the characteristics of relevant technical machines, procedures, or approaches in the future. Technology forecasting are developed by researchers based on experience and current technological advances. Technology forecasting like other forecasts can assist public and private organizations in making smart decisions. 
Forecasters can improve decisions by analysing future opportunities and hazards to maximize benefits. Today, most countries are undergoing massive social and economic changes which are strongly reliant on technological advancement. Government and economic institutions can plan for the future by analysing these changes. However, not all historical data can be utilized for technology forecasting, forecasters must also use modern technology and quantitative modelling based on expert researching and conclusions. Telecommunication ForecastingAll telecommunications service providers perform forecasting calculations to support in network planning. Accurate Forecasting permits operators to make crucial investment decisions such as product development and introduction, advertising, pricing etc., well before product launch, ensuring that the company will profit from a new initiative and that capital is used correctly. Weather ForecastingWeather forecasting uses science and technology to predict atmospheric conditions for a particular area and time. Weather forecasting has been attempted informally by the people for millennia and formal forecasting has be started since the 19th century. Weather predictions are created by gathering quantitative data about the current state of the atmosphere, land, and ocean and then using meteorology to project how the atmosphere will change at a specific location. 
Weather forecasting was previously computed manually based primarily on changes in barometric pressure, present weather conditions, and sky conditions or cloud cover, now relies on computer-based models that consider many atmospheric aspects. The chaotic nature of the atmosphere causes forecasting inaccuracy, the enormous computational power is required to solve the equations that describe the atmosphere, land, and ocean, the error involved incomplete recognition of atmospheric and related processes. As a result, forecasts become less accurate as the difference between current time and the time where the forecast is being made (the forecast range) increases. Using ensemble and model consensus helps reduce error and provide the forecast confidence. Importance of ForecastingForecasting is the practice of estimating future events or outcomes using data from the past and present. It is an essential decision-making tool in many industries, including business, finance, economics, and government. Here are some of the reasons Forecasting is important Expanding into New MarketsForecasting is essential when entering new markets or establishing subsidiaries in new areas. Expanding into new markets, particularly foreign markets, entails numerous risks and uncertainties. Forecasting, on the other hand, allows you to figure out your odds of success in the target market, determine your prospective customers, and estimate the level of competition you're going to face. Investing Money WiselyThe lifeblood of business is an ongoing supply of cash. As a result, you must invest in regions that have the potential to provide high profits. Forecasting is the greatest way to identify these locations. Every firm has profitable areas worth investing in, whether it's financing a coming product launch, bringing on new talent, investing in the growth of existing employees, or improving your digital marketing approach. Setting Measurable Short- and Long-term ObjectivesGoals provide a clear picture of what the organisation is attempting to accomplish. Creating short-term goals to achieve long-term goals is a critical component of any successful organisation. Forecasting supports you in setting both short-term and long-term objectives. Forecasting can be done several ways, depending on the nature and scope of your organisation. Take Advantage of Real-time DataReal-time consumer data is obtained by modern enterprises from a variety of sources. By integrating real-time consumer data, sales forecasting models allow you to easily anticipate future demand for a certain product or service. Sales representatives, internet surveys, and market tests are some of the sources of customer data. Promotes Collaboration and CoordinationForecasting is not the responsibility of a single person. Rather, it requires the participation and coordination of all team leaders. Engaging all individuals involved in the process of forecasting future events implies collaboration and coordination. It also ensures adaptation to rapidly changing environments. Plan FormulationForecasting is a crucial component of planning because the premises of planning are predictions. In fact, forecasting serves as a basis for planning. Under all circumstances and in all cases, planning involves a significant amount of future prediction in regard to present circumstances and the environment. ConclusionForecasting provides data visibility, allowing organisations and individualsto change and adapt to future predictions by maximising resources. There are a variety of tools available to help businesses acquire information and gain an overview of how operations, processes, budgets, and other aspects have evolved and what should be influenced andimproved. Overall forecasting is an important tool in many sectors, including economics, finance, business, and urban planning. While forecasting can never be completely precise, it can provide useful insights and assistance for planning and decision-making processes. Forecasting is an important aspect of modern civilization since it allows us to plan for the future and improve our chances of success.
Next TopicIsotonic Solution Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










