Motor DefinitionThe term "motor" can have various distinct meanings depending on the context. In general, a motor is a machine that transforms electrical or other energy sources into mechanical energy, which may subsequently be applied to execute tasks or create motion. 
Classification of MotorsMotors are often classified into two groups based on their functioning. AC motors and DC motors fall under these two groups. AC motors are well known for being adaptable regarding speed and for using much less power. DC motors are noted for their cost efficiency since they require far fewer units of electricity than AC motors. Another benefit of DC motors is that they are recognized for being simple to install. Types of Motor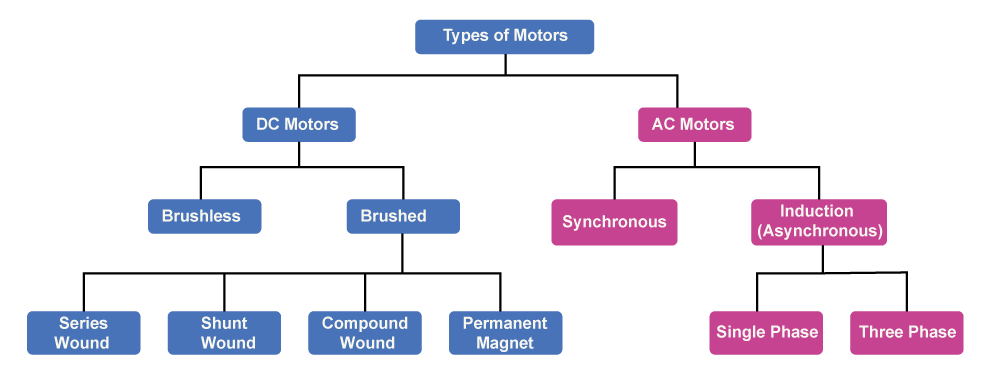
AC MotorThese motors are manufactured in such a way that the installed base is bigger than that of DC motors. This kind of engine offers a number of advantages. It is well known that these motors accelerate at a regulated rate. These motors have an adjustable torque limit and operating speed. It is also known that these motors lessen disruptions in electricity lines. These motors are further divided into two types.
DC MotorsDC motors are the most basic kinds of motors that are now in use. Compared to AC motors, these motors were more cost-effective, which is why they were used more frequently. A DC motor's speed can be adjusted by varying the voltage that is given to it. However, the most typical voltages that are typically provided to DC motors are 12 & 24V. These motors provide a number of benefits, including easy installation & a wide range of speed control options. It is known that these motors exhibit a speed-torque curve. DC motors are further classified into two types: Brushed and Brushless Motors. Brushed Motor- Brushed motors are electric motors that use brushes to deliver power to the revolving armature. The armature's commutator reverses the direction of current flow through the armature coil at the proper moment to achieve continuous spinning. These are the most common kind of DC motors used for relatively simple applications, and they operate with a much simpler control scheme. Due to their well-known high torque, these types of motors are used for lifting as well as in lifts and cranes. These motors are further classified into:
Brushless motors- An electric motor that doesn't need brushes to transmit power from the power supply to the spinning shaft is known as a brushless motor. The motor's direction and speed are instead controlled by electronic commutation. These motors are known for their straightforward construction; brushless motors produce excellent efficiency while requiring little maintenance. A brushless motor's functioning is based on the interaction of an electromagnet stator and a permanent magnet rotor. These are more efficient than brushed motors because they don't have brushes to wear out or produce friction. Additionally, they often emit less heat, noise, and electromagnetic interference. Electric cars, drones, computer fans, and industrial machinery are just a few areas where brushless motors are commonly used. They are also found in several home appliances, including air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines. Advantages of Motors
ConclusionIn short, a motor is a device that transforms one kind of energy into mechanical energy to cause motion or carry out work. Home appliances, industrial equipment, transportation, and construction are just a few of the uses and sectors that employ motors. Two of the most popular types of motors used today are AC and DC motors.
Next TopicAcid Definition Chemistry
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










