Fertile Definition
It is an adjective that shows the ability of soil, land, or environment to support in growth and reproduction of animals, plants, or other organisms. The fertile word is used to denote a conducive environment for the production of crops, the survival of living beings, and the expansion of vegetation. The fertile term is also used in the Human Reproduction Process. The fertile word refers to a person's capacity to conceive a child, particularly a woman.

Causes of Soil Infertility
- Diminishing of Nutrients: Excessive or continuous cultivation of crops without suitable nutrient management practices that includes crop rotation, balanced fertilization, and cover cropping can lead to emptying nutrient in the soil. When crops consume nutrients from the soil without sufficient replenishment, soil fertility can diminish, leading to a decline in crop yields and lower agricultural productivity.
- Erosion of the Soil: Soil erosion happens due to wind, water, or other factors that can remove the top layer of the soil, which is rich in organic content, beneficial microorganism, and nutrients. Erosion occurs due to insufficient soil cover, deforestation, overgrazing, improper agricultural practices, and deforestation leading to the removal of fertile topsoil and diminishing soil fertility.
- Alkalinization or Acidification of the soil: Soil PH is an important measure of Acidification, or Alkalinization can impact the availability of nutrients for plant consumption. Consistent use of alkaline or acidic fertilizer, irrigation with lack of poor quality, or other important
- Salinization of the Soil: This condition occurs when soluble salts assemble. Some reasons for the condition are substandard water quality, imperfect drainage, and high irrigation. Salts will impact plant growth and will have a negative influence on the fertility of the soil by hampering the water and nutrients of the soil.
- Climate Change, Deforestation, and Degradation of the Land: Climate change has an immense influence on the fertility of the soil via variations in the precipitation patterns, temperature, and severe weather patterns, which can impact soil health, nutrient cycle, and organic content of the soil. Deforestation refers to the mass-scale cutting down of trees. The roots of trees hold the soil tightly, thus reducing the chance of soil erosion. Some factors that lead to land degradation include improper land management practices, land degradation, and clearin Land degradation will cause the removal of the topsoil, decreased soil fertility, shortening of forest cover, and disruption in the hydrological process.
- Unsustainable Agricultural Methods: Unbridled or unlimited use of chemicals such as pesticides, chemicals, and herbicides without proper administration would lead to diminished soil fertility and degrading of the soil. Insufficient irrigation practices, poor agricultural methods, and improper tillage will contribute to fertility loss.
Methods to Improve Land Fertility

- Usage of Green Manure: Plantation of cover crops such as grasses or legumes as green manure during fallow periods or between cash crops can help improve India's soil fertility.
- Addition of Organic Matter: Using organic matter such as manure, compost, and other types of organic items helps increase soil fertility as it increases organic content in the soil. Organic matter also assists in retaining moisture and offers crucial nutrients to plants, and endorses the growth of beneficial soil organisms.
- Drainage and Irrigation Management: Proper drainage and irrigation management help administer optimal soil moisture levels, optimize nutrient availability for plant consumption, and prevent water logging or drought stress. All of this helps to increase soil fertility.
- Testing and Analysis of the Soil: Undertaking soil tests for the determination of
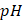 level, organic content, and other characteristics can help recognize imbalances and deficiencies that can impact soil fertility. Depending upon the test results, suitable fertilizers and soil amendments can be added to fix the nutrient deficiencies and lower the level, organic content, and other characteristics can help recognize imbalances and deficiencies that can impact soil fertility. Depending upon the test results, suitable fertilizers and soil amendments can be added to fix the nutrient deficiencies and lower the
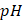 level to construct conducive conditions for plant growth. level to construct conducive conditions for plant growth.
- Crop Rotation Process: Crop rotation in the field helps to maintain or increase the soil fertility of the land. Different crops require different nutrient requirements, and crop rotation helps stop nutrient depletion and lower the pest menace and disease that may be particular to certain crops.
- Controlling Soil Erosion: Adoption of soil erosion control methods such as contour farming, erosion control structures, mulching, and terracing can help in preventing or lowering the process of soil erosion; it will help in soil preservation and protecting the topsoil.
- PH Management of the Soil: The soil Ph helps control soil acidification and alkalinity, an important indicator for nutrient availability. Using lime or other items helps to adjust Soil Ph to a suitable range for particular crops and improves soil fertility.
- Integrated Pest Management: Adoption of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) practices such as judicious use of pesticides, biological control agents, pest-resistant crop varieties, and crop rotation helps in managing pests and diseases in an appropriate manner which can ultimately help in improving soil fertility by minimizing crop losses and reducing the use of chemical that may impact the fertility of the soil negatively.
- Conservation Tillage: Soil fertility can improve by eliminating, reducing, or using minimum practices, fostering deposition of organic content, reducing soil erosion, and improving water filtration. Minimum tillage practices assist soil structure preservation and reduce disturbance to the soil organism, boosting soil fertility.
Fertile Term in Human Reproduction System
The fertile term is also used in the process of Human reproduction. It is used to denote the ability to conceive and generate progeny. In the female, the term fertility refers to the ability of females to produce ova and have a regular menstrual cycle and the presence of a healthy reproductive system that will endorse pregnancy. In males, fertility refers to the ability to generate and deliver sperms that can fertilize the eggs.
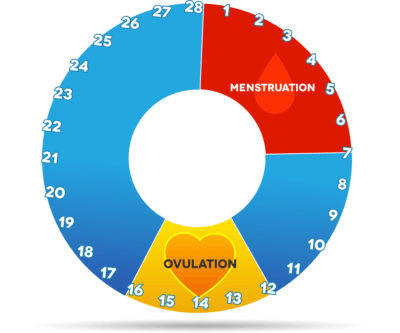
The menstrual cycle refers to the normal process when the female body gets readied for possible pregnancies. It is subject to change from person to person. The fertile window refers to the period when women have a high possibility of getting pregnant if she engages in sexual intercourse.
Important Factors that Determine the Fertility Rate
The Fertility Rate is the number of children born alive to women of that age during the year as a proportion of the average annual population of women of the same age. Several factors influence the fertility rate, and it includes:
- Application of Contraceptive Methods: Fertility rates can be affected by the uses, accessibility, and availability of contraceptives. High contraceptive use can reduce the fertility rate by allowing a person to control the timing and number of children they are having.
- Age of a Female: The fertility rate is profoundly influenced by the age of women having children and the duration between pregnancies. It has been observed that females that have early offspring bearing and reduced birth spacing have a high fertility rate.
- Cultural and Religious Practices: The fertility rate is impacted by cultural and religious practices and beliefs. Some cultures and religious beliefs stress that having bigger families would increase fertility, while others fostering smaller families would decrease fertility.
- State Interventions and Policies: Policies of the state, such as incentives or disincentives for offspring bearing, child and maternal health programs, and family planning programs, influence the fertility rate. For example, programs that endorse reproductive health and family planning may reduce fertility rates.
- Accessibility to Healthcare and Reproductive Health Services: The presence of quality healthcare that includes accessibility to reproductive healthcare can influence the fertility rate. The fertility rate is profoundly impacted by preconception care, access to family planning, skilled birth attendance, and parental care by offering services and information to assist people in making informed decisions regarding their reproductive health.
- Infertility and Reproductive Disorders: The fertility rate is also affected by infertility or reproductive disorders.
Biological Factors Affecting Fertility
The term biological means that it is the ability of the individual, generally a sexually reproductive species, to generate offspring. It includes the generation of gametes (ova and sperms), successful process fertilization, pregnancy, and offspring birth.
Some of the biological factors that affect fertility in humans are:
- Reproductive Physiology and Anatomy: Specialized organs in the male and female reproductive systems play an important role in fertility. The presence of hormones also regulates this process. In males, the production of sperms in the testes, its movement through the reproductive tract, and its discharge. In females, it includes the monthly ejection of mature eggs from the ovaries. The process is called ovulation and the movement of the eggs via the fallopian tube and readying of the uterus to successfully implant the fertilized eggs.
- Quality and Production of Gamete: Generating good and healthy sperms in the male and healthy sperms in the female individual is crucial for reproduction. Some elements that influence gamete production are lifestyle preferences, genetics, holistic health and well-being, and environmental components.
- Well-Being and Health: Well-being and the couple's health become determinant factors in fertility. Components such as lifestyle preferences, present medical conditions, stress, exposure to a toxic environment, and dietary choices (Consumption of drugs, smoking, healthy diet, exercise, and alcohol)
- Process of Implantation: After fertilization, the zygote must implant and develop as a uterus for a successful pregnancy. Elements that influence the implantation process and successful pregnancy are the holistic health of the mother, good hormonal balance, and uterine health.
- Successful Fertilization: It happens when sperm enters and fertilizes an egg, which is crucial for achieving pregnancy. Several elements, such as the interaction between sperms and ova and the quality of sperms and eggs, can impact fertilization.
Conclusion
The term "Fertile" is used in varied aspects. But the primary usage of this term has been stated above. In the larger sense, the term fertile can also be understood as creativity, capacity, or potential for creativity, growth, or development. This can be explained: a fertile brain can produce innovative ideas and imaginative stories. A fertile period was also treated as a breakthrough advancement in technology and innovation. The debate was fertile, with ideas, opinions, and perspectives. Some fertile word has different connotations.
|




 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now





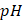 level, organic content, and other characteristics can help recognize imbalances and deficiencies that can impact soil fertility. Depending upon the test results, suitable fertilizers and soil amendments can be added to fix the nutrient deficiencies and lower the
level, organic content, and other characteristics can help recognize imbalances and deficiencies that can impact soil fertility. Depending upon the test results, suitable fertilizers and soil amendments can be added to fix the nutrient deficiencies and lower the





