Chemical Reaction DefinitionIt breaks bonds within the reactant molecules, and new products develop within product molecules to form a new substance. 
We observe and feel chemical reactions in our daily life-for Example, metabolic activity in our body and transmission of light directly from the sun. There are two types of changes that happen in the environment, and they are Physical and Chemical Changes. 
For Example, if a candle melts to wax and cuts the supply of Oxygen, the lit candle will be extinguished. Chemical change - Burning of the candle Physical Change - Changing of the candle to wax In physical change activity, only the state of the substance changes. In case of Chemical change, new development or formation takes place in that process either energy is absorbed or given off. So, we can say that chemical changes coincide with some physical changes. Simple Concepts of Chemical Reactions
Chemical Equations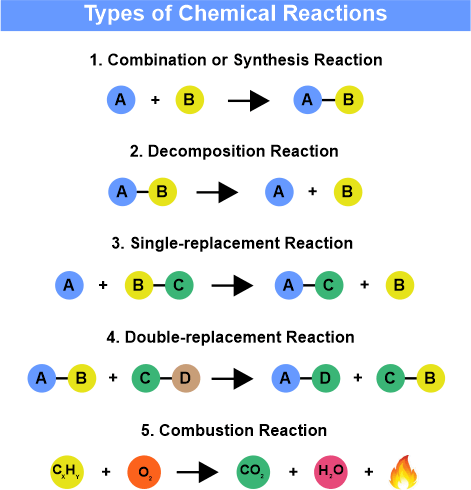
Since a vast quantity of chemical reactions takes place in our environment, scientists felt the need for the method to simplify how we show the chemical reaction in the form of a Chemical equation. A chemical equation is a mathematical statement that shows the product formation developed from the reactants and also stated the condition of how the reaction has been performed. Reactants are written on the left-hand side, and products that have been formed are written on the right-hand side of the reaction. Two-headed or one-headed arrows link reactants and products. For Example, X + Y → Z + W Here, X and Y are reactants that react to give rise to the product. In a real Chemical reaction, reactants are represented by their natural Chemical formula. All chemical reaction has to abide by the law of conservation of mass, for that Chemical equation must be written in the balanced form. For Example, the number of ions and atoms on both sides (reactants and products) has to be equal. This is known to be as balancing of the equation. Let us understand the Example given of Methane (CH4) and Oxygen (O2) CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2 O The number of each atom present on the LHS (left-hand side) and RHS (right-hand side) is balanced. This equation follows the law of conservation of mass. Different Forms of Chemical ReactionsDifferent forms of a chemical reaction are determined by the changes in the product formation, the reactants' involvement, and so on. Different forms of chemical reactions are
1. Combustion ReactionIt is a simple reaction involving combustible material with an oxidizer to give an oxidized product. An oxidizer is a chemical fuel that is needed to burn like Oxygen. Example of the combustion reaction includes 2Mg2 + O2 → 2MgO + Heat In the above equation, it can be stated as two magnesium atoms react with a molecule of Oxygen, generating two molecules of the compound magnesium oxide and liberating heat in the process. 2. Neutralisation ReactionA neutralization reaction takes place between acid and base and gives rise to salt and water as their product. The water molecule is developed by the interaction of H+ + and OH- Ions. When a strong acid and base go under neutralization reaction, the overall Ph of the product comes out to be 7. Let us understand this reaction with the help of the neutralization reaction that takes place between Hydrochloric Acid and Sodium hydroxide to produce Sodium chloride and water. Hcl + NaOH → NaCl + H2O Here is a strong acid, and NaOH is a strong base. Here, they both react with each other and give Sodium Chloride (Common Salt) and water. 3. Decomposition ReactionIt is a reaction in which the component break downs to give multiple products. Some alterations must be made in the environment, like heat, electricity, and light, to overcome the forces of attraction between the bonds. Let us understand with the help of an example: Decomposition reaction between Calcium Carbonate producing Calcium Oxide. It is also known as Quick Lime and is used in cement production. CaCO3 (s) → CaO (S) + CO2 (g) When Calcium carbonate is heated, it splits into Calcium oxide and Carbon dioxide. 4. Redox ReactionIt is a reduction-oxidation reaction, and the transfer of electrons between two species takes place. Let us understand with the help of a suitable Example: The reaction between Zinc and Hydrogen. Zn + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2 Zinc reacts with two positive ions of hydrogen, to which electrons get to move from the Zinc atom, and hydrogen becomes a stable molecule and Zinc ion in the product. 5. Double Displacement Reaction or Precipitation ReactionIt is another form of displacement reaction in which two compounds react, and as a result, the anions and cations shift their position and produce two new products. Let us understand with some examples between Silver Nitrate and Sodium chloride. The product formed is Silver chloride and sodium nitrate after a double displacement reaction. AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3 Here, Silver Nitrate and Sodium Chloride come under the double displacement reaction in which Silver replaces Sodium in Sodium chloride, and sodium unites with Nitrate forming Sodium Nitrate along with the silver Chloride as the product. 6. Synthesis ReactionIt is one of the simplest reactions in which the compounds integrate under some physical influence producing a complex product. Let us understand the Synthesis reaction with the help of an example that takes place between Sodium (S) and Chloride (g), giving rise to Sodium chloride 2Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → 2NaCl (s) In the above reaction, two atoms of Solid sodium react with Chlorine gas, producing Sodium Chloride. Important Points
Frequently Asked QuestionsQuestion: What do you mean by Chemical Reaction? Answer: It is defined as when two or more molecules combine to give rise to a new product is called a Chemical reaction. The process can vice versa; a component can split itself to produce two new products. Question: Give one Example of
Answer: Redox Reaction PbO (S) + H2 (g) → Pb (S) + H2 O (l) In this reaction, the Lead oxide is reduced to Lead, and hydrogen is oxidized to water Double Displacement Reaction It is also referred to as a Precipitation reaction. AgNO3 (s) + HCl (l) →/← AgCl (S) + HNO3 (l) Displacement Reaction Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu Here, Iron replaces Copper as Iron is more reactive than copper.
Next TopicChromatography Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










