Diabetes DefinitionDiabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects the way the body processes glucose, the main source of energy for the body's cells. Glucose comes from the food we eat and is carried by the bloodstream to the cells, where it is used as fuel. However, in order for the glucose to enter the cells, it needs the help of a hormone called insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas and acts as a key, allowing glucose to enter the cells and be used for energy. In people with diabetes, the pancreas either produces little or no insulin or the cells of the body are resistant to the insulin that is produced. 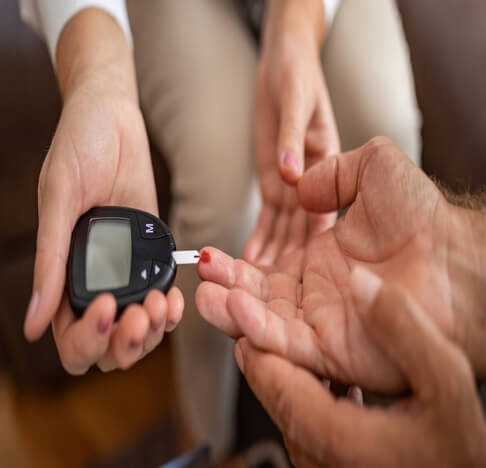
This leads to an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream, known as hyperglycaemia, which can cause a number of health problems over time. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can lead to a number of serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, kidney disease, blindness, and amputations. However, with proper treatment and management, people with diabetes can lead healthy, active lives. This typically involves a combination of medication, healthy eating, regular physical activity, and monitoring of blood sugar levels. Causes of DiabetesDiabetes is a complex disease that is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Although the exact cause of diabetes is unknown, there are several factors that can increase a person's risk of developing the disease which are given below:
In addition to these factors, certain medical conditions can also increase a person's risk of developing diabetes. For example, women who develop gestational diabetes during pregnancy are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. People with conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and certain forms of hepatitis are also at an increased risk. Symptoms of DiabetesDiabetes is a chronic disease that affects the way the body processes glucose, the main source of energy for the body's cells. The symptoms of diabetes can develop gradually over time, and some people may not even know they have the disease. However, there are several common signs and symptoms that can indicate the presence of diabetes. Following are some of the common and most popular symptoms of Diabetes:
Treatment of DiabetesTreatment for diabetes aims to keep blood sugar levels within a target range, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall health and quality of life. The specific treatment plan will depend on the type of diabetes and individual factors such as age, health status, and lifestyle. 1. Treatment for type 1 diabetes For people with type 1 diabetes, treatment typically involves daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump. The goal of insulin therapy is to provide the body with the insulin it needs to process glucose and keep blood sugar levels within a target range. People with type 1 diabetes will also need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and adjust their insulin doses as needed. 2. Treatment for type 2 diabetes For people with type 2 diabetes, treatment may initially involve lifestyle changes such as losing weight, increasing physical activity and making dietary changes. A diet that is low in processed foods and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity can also improve insulin sensitivity and help keep weight under control. In addition to lifestyle changes, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to take oral medications or insulin to help manage their blood sugar levels. These medications work by increasing insulin production, improving insulin sensitivity, or slowing the absorption of glucose from the gastrointestinal tract. The specific medication or combination of medications will depend on individual factors such as blood sugar levels, health status, and other health conditions. In some cases, people with type 2 diabetes may also need to undergo procedures such as bariatric surgery to help control their blood sugar levels. Bariatric surgery can help people with obesity and type 2 diabetes lose weight, improve insulin sensitivity, and lower their blood sugar levels. In addition to medications and lifestyle changes, people with diabetes will also need to receive regular medical care to monitor and prevent complications. This may include regular check-ups with a doctor, regular monitoring of blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and regular eye exams to monitor for diabetic retinopathy. People with diabetes will also need to receive regular foot exams to monitor for neuropathy and other foot problems. ConclusionDiabetes is a chronic disease that affects the way the body processes glucose, the main source of energy for the cells. It occurs when the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin, or the cells are resistant to the insulin that is produced, leading to an accumulation of glucose in the bloodstream. Proper treatment and management can help people with diabetes lead healthy lives and prevent the serious health problems that can arise as a result of the disease.
Next TopicDiabetes Mellitus Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









