Biodegradable DefinitionIn recent years, biodegradability has become an increasingly important concept, especially as concerns about the environment continue to grow. Biodegradable materials are ones that can be transformed into less complex, non-toxic chemicals by natural processes. The potential to lessen the quantity of garbage that enters landfills and the environment makes biodegradability important. This article aims to explore the meaning and importance of biodegradability, including its various definitions, types, and applications. 
Definition of BiodegradableThe capacity of a substance to be broken down chemically into simpler molecules by the activity of microbes is referred to as "biodegradable."Biodegradation is the main method used to recycle organic waste since it is a natural process that takes place in the environment. In simple terms, biodegradability is the ability of a substance to be transformed into natural components by the action of living organisms. 
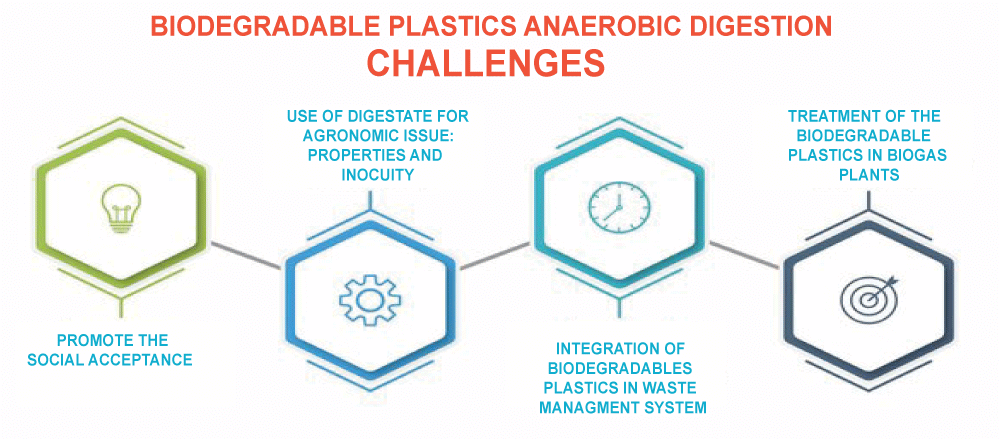
Types of BiodegradabilityThere are two major type of biodegradation, including aerobic and anaerobic. Anaerobic biodegradation takes place when oxygen is not present, whereas aerobic biodegradation takes place in the presence of oxygen. Both forms of biodegradation rely on the activity of microorganisms to convert organic matter into more basic substances. However, aerobic biodegradation is generally faster and more complete than anaerobic biodegradation. Another type of biodegradability is photodegradation, which occurs when a substance is broken down by exposure to sunlight. This process is often used to break down plastics and other synthetic materials, which do not readily biodegrade in the environment. Applications of BiodegradabilityBiodegradability has numerous applications in various industries, including agriculture, food production, and manufacturing. For instance, biodegradable plastics are gaining popularity as an alternative to conventional plastics made of petroleum.These polymers may be degraded by environmental microbes since they are derived from renewable materials, including maize starch. This lessens the quantity of plastic garbage that pollutes the environment and landfills. In the food industry, biodegradable packaging is becoming more common. The quantity of waste produced by the food business is decreased by the use of these packaging materials, which can be degraded by microorganisms. Biodegradable mulch films are used in agriculture to suppress weeds and keep moisture in the soil. These films are made from natural materials, such as starch and cellulose, and can be broken down by microorganisms in the soil. 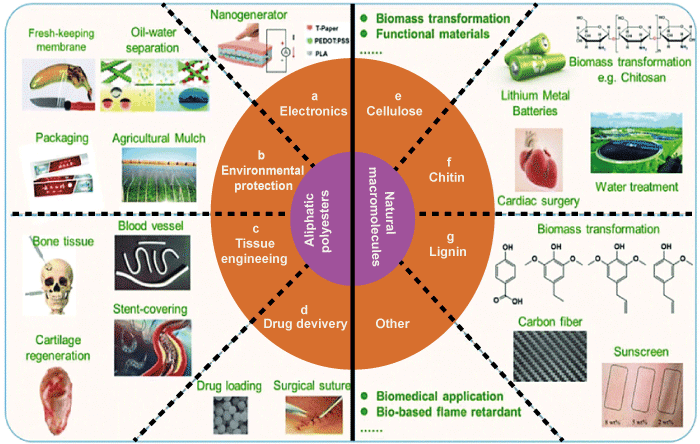
Benefits of BiodegradabilityThe benefits of biodegradability are numerous and significant. The potential to lessen the quantity of garbage that pollutes the environment and landfills is its most significant advantage. Biodegradable materials may degrade naturally; therefore, unlike conventional plastics and other synthetic materials, they do not build up in the environment. Biodegradability also has environmental benefits. The production of biodegradable materials often requires less energy and resources than the production of traditional plastics and other synthetic materials. This helps to conserve natural resources and lowers the carbon impact of these items. Biodegradability also has economic benefits. The use of biodegradable materials can lead to cost savings for businesses and municipalities. For instance, using biodegradable plastics can cut the quantity of the garbage that gets up in landfills, hence lowering the cost of waste disposal. Issues with BiodegradabilityAlthough biodegradability offers many advantages, there are a number of difficulties that come with using it. Making sure biodegradable waste is disposed of appropriately is one of the main problems. Although these materials can be broken down by environmental microbes, if they are not exposed to the proper circumstances, they cannot degrade. This means that biodegradable materials may still end up in landfills and the environment if they are not properly disposed of. The absence of standards in biodegradability testing and labeling is another problem. There isn't yet a test or labeling procedure that is recognized worldwide for biodegradable materials. This makes it difficult for consumers and businesses to determine the biodegradability of a product, which can lead to confusion and misinformation. There is also a concern that the increased use of biodegradable materials may lead to an increase in land use for agricultural production. This is because many biodegradable materials are made from crops such as corn and sugarcane, which require large amounts of land to grow. Lastly, the production of biodegradable materials may require the use of chemicals and other additives, which can have negative environmental impacts. For example, some biodegradable plastics require the use of chemical additives to enhance their biodegradability. If these compounds are not handled properly, they may have detrimental effects on the quality of the soil and water. Biodegradability vs CompostabilityBiodegradability and compostability are two related but distinct concepts that are often confused. While both refer to the ability of a material to break down into simpler compounds, there are important differences between the two. 
The term "biodegradability" describes a substance's capacity to decompose into simpler molecules under the influence of microbes. This can occur in various environments, such as in soil, water, or even in the human body. Both aerobic and anaerobic conditions can lead to biodegradation. Contrarily, compostability refers to a substance's capacity to decompose into compost, a nutrient-rich substance that may be added to the soil.Composting is a specific process that involves the controlled breakdown of organic materials under aerobic conditions. Certain microbes must be present for composting to occur, and the compost pile's nitrogen and carbon levels must be balanced properly. All materials that can be composted are biodegradable. However, not all biodegradable materials can be composted. For example, some plastics are biodegradable but cannot be composted, as they do not break down into compost. These materials may break down into simpler compounds, but they may still leave behind harmful residues in the soil. Composting is a more specific process that requires certain conditions to be met, such as the presence of specific microorganisms and the right balance of carbon and nitrogen. Composting can only occur under aerobic conditions, which means that materials that are compostable must be able to break down in the presence of oxygen. Composting has several benefits, including the production of nutrient-rich compost that can be used to improve soil quality and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers. Reducing the quantity of organic waste dumped in landfills, where it can produce methane gas and worsen climate change, can also assist with composting. In conclusion, biodegradability and compostability are related but distinct concepts. Compostability refers to a material's capacity to decompose into compost under specified circumstances, whereas biodegradability refers to a material's capacity to decompose into simpler compounds by the activity of microbes. Composting is a specific process that involves the controlled breakdown of organic materials under aerobic conditions, and it has several environmental benefits. We may choose the materials we use and the methods of disposal more wisely if we are aware of the distinctions between biodegradability and compostability. 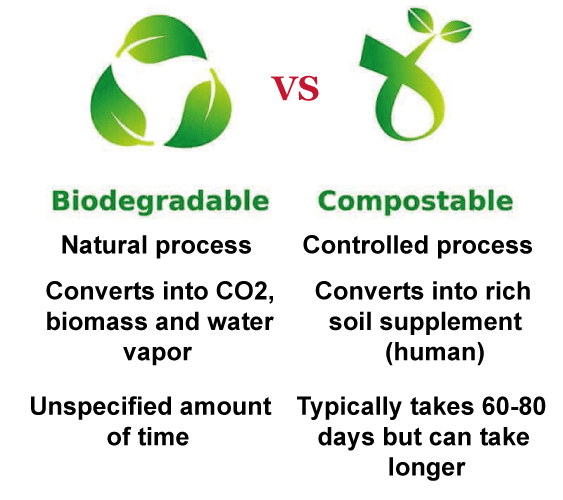
Types of Biodegradable MaterialsThere are many different types of biodegradable materials, each with its own unique properties and applications. Some common types of biodegradable materials include:

Overall, there are several kinds of biodegradable materials that may be applied in a variety of various situations. We may work towards a more sustainable future by using biodegradable products and reducing the quantity of the garbage that is dumped in landfills and the environment. Standards and CertificationsAs biodegradable materials become more popular, there are various standards and certifications that have been developed to ensure that products labeled as "biodegradable" meet certain criteria. Here are some of the most common standards and certifications:
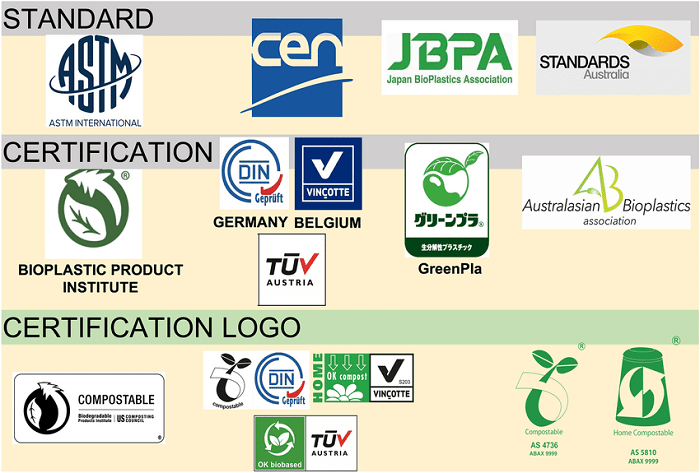
Overall, standards and certifications play an important role in ensuring that products labeled as "biodegradable" or "compostable" meet certain criteria for environmental sustainability. By looking for products with these certifications, consumers can make more informed choices and support more sustainable practices. ConclusionBiodegradability is an important concept that has significant implications for the environment, the economy, and society as a whole. The ability of a substance to be broken down by natural processes into simpler compounds is critical for reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and the environment. Biodegradable materials have numerous applications in various industries, including agriculture, food production, and manufacturing. The utilization of biodegradable materials is not without its difficulties, though. Ensuring proper disposal and lack of standardization in testing and labeling are just a few of the issues that need to be addressed. We can build a more sustainable future for present and future generations by solving these issues and encouraging the use of biodegradable materials.
Next TopicBiogas Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share