Congestive heart failure definition
Heart failure
Heart failure is a biological condition in the human body when the heart muscle doesn't pump blood properly as it should always. Humans feel shortness of breath or difficulty doing regular work in this condition because the heart can't pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. It happens suddenly, but we can observe the situation in the long term, and many different heart problems can cause it.
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is another name for heart failure when a human feels pain in the chest when the heart can't pump blood according to the body's needs. "Congestive" is a condition build-up of fluid in the ankles, feet, lungs, feet, and other organs.
Millions of people have gone through heart failure, and in medical terms, it is a coronary artery disease that happens due to various reasons:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Being overweight or obese
- Stress or tension
- A sedentary lifestyle
- High level of cholesterol/triglyceride in the blood
- Poor diet
- Swollen feet and ankles
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Faintness
- Swollen abdomens or liver
- Irregular or fast pulse rate, palpitations (sensation of feeling heartbeat)
Symptoms of heart failure
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Having a problem with the heart's rhythm, known as arrhythmias
- Edema (fluid build-up) in the legs
- Some of the diseases that can cause heart failure are:
- Underactive thyroid
- Amyloidosis
- Overactive thyroid
- Severe anemia
- Sarcoidosis
- Emphysema
- Too much iron in the body (hereditary hemochromatosis)
It can result in death but can be curable with proper treatment, including medications, heart surgery, or transplantation.
In heart failure conditions, heart muscles cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's need for blood and oxygen. The heart tries its best to make up for the body by enlarging itself, pumping fast, and developing muscle mass, and it stretches itself to contract more strongly and pump more blood. This enlarges the heart and increases muscle mass. Initially, the heart pumps more strongly and fastly, increasing the heart's output.
The heart's body also compensates as blood vessels narrow and keep blood pressure up to estimate the heart's loss of power. The kidney also retains more water and salt, except it excretes through urine, which increases blood pressure volume, so the heart pumps more strongly. But access to this condition leads to heart failure at its worse.
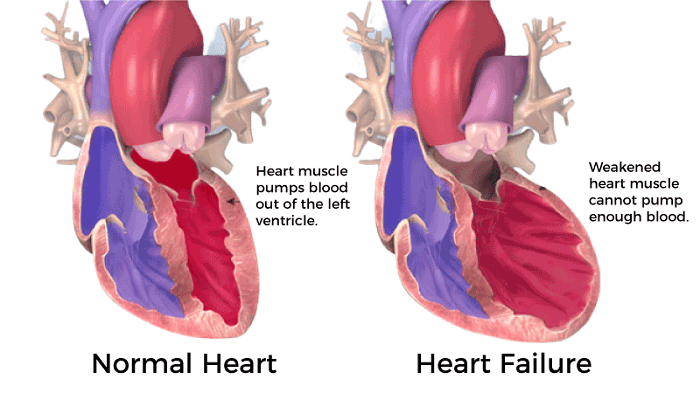
Detail explanation of the cause of heart failure
There are multiple reasons for failure, weakened, damaged, or stiff heart in which the heart chamber may stretch and get bigger, or ventricles get stiff due to which the soul can't fulfill the need for blood to the body enough blood between beats. This condition arises when the heart muscle is damaged by different reasons (alcohol consumption, smoking, drug use, and some chemotherapy medicines), and genes are also responsible. There are some other reasons following:
- High blood pressure: High blood pressure (hypertension) makes the heart work harder from the regular pumping of blood, and with time, this extra work causes the heart muscles to be stiff or weak to pump blood properly.
- Hereditary heart problem and heart problem by birth (congenital heart defect): It is detected that the heart and its chambers or valves aren't formed properly, making it difficult to pump blood, leading to heart failure.
- Arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms): In some cases, heart rhythms are irregular (heart beat fast and slow), which may lead to heart failure. But treating irregular heart rhythms can help reverse heart failure in some people.
- Myocarditis (Inflammation of heart muscles): This condition arises due to a virus, including COVID-19, that leads to-sided heart failure.
- Heart valve disease: When the heart valve doesn't work properly and weakens the heart over time leads to heart failure at some point. It is a curable condition that can reverse heart failure.
- Other diseases: Chronic heart failure is contributed by other long-term or short-term diseases such as HIV infection, diabetes, underactive or overactive thyroid, or a build-up of iron or protein.
Congestive heart failure types
- Left-side heart failure: In this lower left heart chamber, known as the left ventricle affected in which, fluid back up in the lungs and causes shortness of breath
- Right-side heart failure: In this, the lower right heart chamber, known as the right ventricle affects, and fluid gets back up in the belly, feet, and legs that, causes swelling too
- Systolic heart failure: The whole left side heart fails because the left ventricle can't squeeze as strongly as it should. Enough blood can't be pumped to the body by the heart.
- Diastolic heart failure: This left ventricle can't fill or relax, so the left side heart fails. The heart couldn't be able to fill the blood properly.
Risk factors for congestive heart failure
- Age factor ( Congestive heart failure risk increases after 50 years of age)
- Already having heart attack issue (mild or major attack)
- Blood pressure issue
- Family history of congestive heart failure
- Drinking habit
- The habit of cocaine or alcohol and tobacco products
- Having coronary artery disease
- Due to an inactive lifestyle
Stages of congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure is a chronic medical condition; if not cured instantly, it worsens with time. This condition has four stages ranging from high risk to advance heart failure. These stages (A, B, C, and C) are as follows:
Stage A: Considered a primary stage that shows the symptoms of heart failure, it is called pre-heart failure. It is 70% active in families having a history of congestive heart failure or one or more similar medical conditions like these: coronary artery disease, hypertension, history of rheumatic, history of an alcohol use disorder, diabetes, family history of cardiomyopathy, metabolism syndrome, consuming drug history, cancer history or other medical problem.
Stage B: The heart's left ventricle doesn't work properly or is structurally abnormal. But here, there weren't any symptoms of heart failure.
Stage C: At this stage, heart failure symptoms are diagnosed as they may previously have signs or symptoms.
Stage D and reduced EF (ejection fraction): The final stage of heart failure. It shows the advanced symptoms that become worse without treatment. Finally, proper treatment and medication are required.
Congestive heart failure stages treatment.
Conditions and symptoms of heart failure are curable after treatment, and the treatment depends on the type of heart failure. Treatment plans include medications and lifestyle changes that help cure the primary symptoms, but proper heart failure is not curable. When the heart muscle pumps less blood to the body organ takes you to the next stage of heart failure. Different backgrounds can be cured with various treatments that restrict you from moving forward to other locations and slow down your heart failure progression. These are the treatment for each stage:
| Stage |
Treatment |
| Stage A |
- Treatment for high blood pressure and cholesterol
- No tobacco products, no alcohol or recreational drugs
- Recommendation of regular exercise
- In coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, or other cardiac or vascular condition, ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker) and ACE-1 (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ) are used.
|
| Stage B |
- All the stage A treatment
- If the EF is 40% or lower, ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker) and ACE-1 (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor )are used.
- In a case when you have already suffered a heart attack or have a 40% or lower EF, a beta blocker is used
- In the case of heart attack or EF 35% or less, an Aldosterone antagonistis used
- Surgery is also suggested in critical cases (valve repair or replacement)
|
| Stage C |
- All the treatments of stages A and B
- Beta-blocker
- Possible fluid restriction
- Aldosterone antagonist
- Removal or restriction of salt (sodium) in the diet
- ICD - Implantable Cardiac Defibrillator therapy
- Biventricular pacemaker (Cardiac resynchronization therapy)
- Regular exercise with the motive of losing and maintaining weight
- Mediations to slower down the heart rate
- A water pill (diuretic) is used if the same symptoms continue
|
| Stage D |
- Include treatment of all the above stages and evaluation of more advanced treatment options like heart surgery, heart transplant, ventricular assist devices, palliative or hospice care, and the continued infusion of inotropic drugs.
|
| Stage C and D with preserved EF |
- Include all the treatments for stages A and B
- To reduce or relieve symptoms water pill (diuretic is used)
- Medications for all heart failure-causing symptoms like high cholesterol, kidney disease, obesity, coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, asthma, thyroid disease, anemia, chronic lung disease, atrial fibrillation, and kidney disease
|
Diagnose of congestive heart failure.
Here are some of the tests conducted to diagnose congestive heart failure:
- Blood tests
- Genetic testing
- Chest X-ray
- Cardiac catheterization
- Stress test
- Echocardiogram
- Heart MRI
- CT (Cardiac computed tomography)
- ECG or EKG (electrocardiogram)
- MUGA scan (multi-gated acquisition scan)
Prevention from congestive heart failure
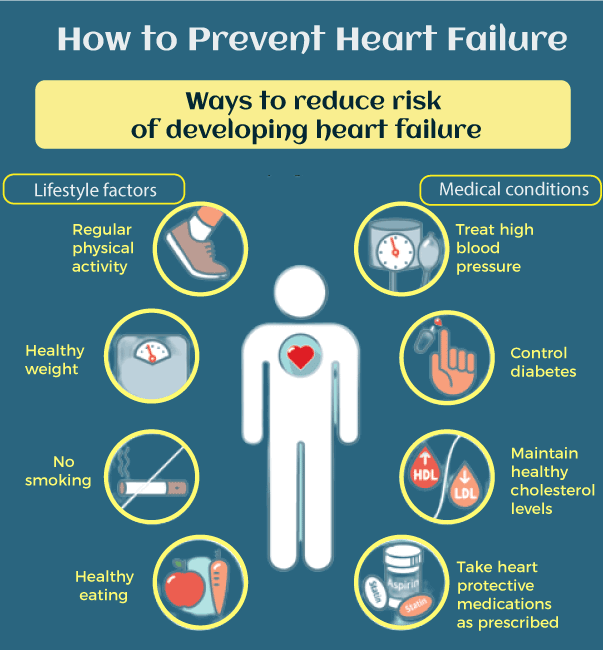
- Healthy eating: In our era, nothing is natural; even our food is artificially grown. Therefore we should eat as much healthily as possible, especially food rich in omega-3 fatty acids and low in sodium, for the betterment of the heart. Eating fresh fruits and vegetables regularly regulates the healthy blood flow in arteries.
- Weight loss: Being overweight is also a major reason for heart failure; therefore, it is mandatory to lose extra weight to make the body or heart function properly. By consulting doctors, healthy eating, meditation, medicine, and proper exercise, we can take control of our weight. Not even heart disease being overweight can give rise to other conditions in the body.
- Stay away from smoking and drinking: In this hectic world, tension is a permanent partner of human beings, and to reduce this, they opt for smoking and drinking rather moderate alcohol intake (1 drink per day) is beneficial, but the access it leads to various heart problems. It can damage the brain and liver too.
- Regular exercise: Half an hour is mandatory for everyone to be safe and healthy. Regular physical activity less than or equal to 5 days a week help in maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Reduce hypertension: For the development of heart failure, high blood pressure or hypertension is one of the major issues. High and low blood pressure in individuals at increased risk for heart disease to an optimal 120/80mm Hg level reduces this risk. Hypertension can be effectively reduced by specific medicines, which are also effective in lowering heart failure risk. This includes angiotensin receptor blockers, diuretics, and angiotensin-converting enzymes.
- Regular monitoring of heart disease: By monitoring and controlling the blood sugar: High blood sugar or diabetes is one the reason for the development of heart failure. It is common in today's lifestyle but can be treated easily with proper exercise, diet, and antidiabetic medications under the guidance of a physician, which can lower the risk.
Recommended surgeries and devices for heart failure patients:
- Heart valve surgery: The heart has four damaged chambers or valves and requires heart valve surgery in which valves are repaired (at least one of the four chambers). These valves are named the pulmonary, mitral, aortic, and tricuspid valves. The surgeon replaces or repairs the damaged and diseased heart valve or valves in this surgery.
- CABG (Coronary bypass surgery) or angioplasty is an emergency step doctors take to deal with a heart attack. In bypass surgery, the blocked coronary arteries (coronary artery disease) are opened by surgeons to restore the heart muscle without open heart surgery.
- Pacemaker: It is used for the weak heart that helps treat slow heart rate. It supports both sides of the heart contract at the same time.
- Defibrillator: A device sends an electric pulse into the heart to stop life-threatening abnormal heart rhythms.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










