Computer Hardware DefinitionComputer hardware refers to a system's physical components, including the processor, memory, storage, input/output, and other peripherals. The purpose of computer hardware is to provide a platform for running software applications that allow users to perform various tasks efficiently. 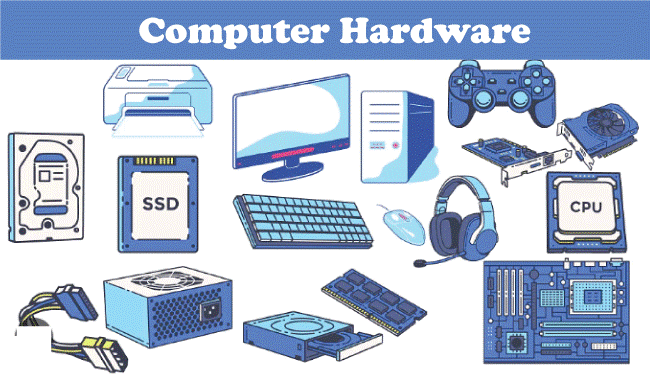
In other words, those parts of a computer system that we can see and touch are usually called computer hardware. Common examples of computer software include the processor, memory, storage, and connected input and output devices. The brain of the computer is the processor, the Central Processing Unit (CPU). It processes data and an instruction received from software applications and other hardware components and performs arithmetic and logical operations on the data to provide meaningful information. Memory, such as RAM and ROM, allows the computer to store data and instructions for the CPU to access quickly. The more RAM a computer has, the more applications and data it can handle simultaneously. RAM is a volatile memory that typically stores data temporarily. Storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs), are used to store data and applications permanently. These devices have much larger storage capacities than RAM but are slower to access. Input devices like keyboards, mice, and scanners allow users to input data and commands into the computer. Output devices, such as monitors, printers, and speakers, allow users to receive information and results from the computer. Other peripherals, such as network adapters and sound cards, enable the computer to connect to other devices and networks and provide additional functionality. These peripherals are also referred to as computer hardware. History of the Computer HardwareThe history of computer hardware dates back to the early 1800s with the invention of the mechanical calculator, an early version of the computer that performed basic mathematical calculations. However, it was only in the middle of the 20th century that the modern computer as we know it today was developed. In the 1940s, electronic computers were first created using vacuum tubes, which were large, fragile, and required much power. These early computers were used mainly by the military and scientific researchers for complex calculations. In the 1950s, the development of the transistor revolutionized computer technology, making it possible to create smaller, more reliable, and less power-hungry machines. This led to the development of the first commercially available computer, the UNIVAC, used for business applications such as payroll and inventory management. In the 1960s, the integrated circuit was invented, allowing even more complex and powerful computers to be built in smaller packages. This led to the development of the mainframe computer, which was used primarily by large businesses and government agencies. In the 1970s, the personal computer was invented, starting with the Altair 8800, followed by the Apple II and the IBM PC. This marked the beginning of the computer revolution, as computers became more affordable and accessible to the general public. Since then, computer hardware has continued to evolve rapidly, with advances in microprocessors, storage devices, and graphics technology, enabling computers to become more powerful and versatile. Today, computers are an integral part of modern society, used for everything from communication and entertainment to scientific research and business management. PurposeThe purpose of computer hardware is to provide a reliable and efficient platform for running software applications that allow users to perform various tasks. Without computer hardware, software applications would have no platform to run on, and users would be unable to use computers to perform tasks such as word processing, data analysis, multimedia editing, and gaming. Computer hardware also plays a critical role in the performance and efficiency of computer systems. The faster and more powerful the hardware components are, the more efficient the computer system will be in performing tasks. For instance, hardware upgrades, such as upgrading RAM or replacing an old hard drive with a faster SSD, can greatly improve a computer system's performance. Types of Computer HardwareThere are several types of computer hardware, each with its specific function in a computer system. Here are some of the most common types: Input DevicesInput devices are used to provide data and instructions to the computer. Examples of input devices include keyboards, mice, scanners, and microphones, and these devices convert the physical input into digital signals that the computer can understand. Output DevicesOutput devices are used to display or retrieve output data from the computer. Examples of output devices include monitors, printers, and speakers, which convert digital signals into a form that humans can understand. Central Processing UnitThe CPU is the computer's brain and is responsible for executing instructions. It is a small chip that fits into a socket on the motherboard. The CPU receives instructions from the computer's memory and performs calculations and logical operations. The speed at which the CPU can execute instructions is measured in gigahertz (GHz). A faster CPU can perform more instructions in a given amount of time, making it more powerful. MemoryMemory helps to store the data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. The two types of memory in a computer system are random access memory (RAM) and read-only memory (ROM). RAM is volatile memory, meaning its contents are lost when the computer is turned off. On the other hand, ROM is non-volatile memory, meaning its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off. However, it should be noted that ROM is different from storage devices such as HDD or SSD. Communication DevicesCommunication devices are used to connect the computer to other devices or networks. Examples of communication devices include modems, routers, and network interface cards (NICs). These devices allow the computer to communicate with other devices over a network or the internet. MotherboardThe motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer system, and it connects all the other components and provides the pathways for data and instructions to flow between them. The CPU and memory are connected directly to the motherboard, while other components are connected through ports and slots. Power Supply UnitThe power supply unit is responsible for providing power to all the components in the computer system. It converts the AC power from the wall outlet into DC power that the components can use. Difference between Computer Hardware and SoftwareComputer hardware refers to the physical components of a computer system, such as the central processing unit (CPU), motherboard, memory, storage devices, input/output devices, and other peripherals. These components work together to process data and perform tasks. On the other hand, computer software refers to the programs, applications, and instructions that run on a computer system. Software is intangible and exists as code, typically written in a programming language, executed by computer hardware. Examples of software include operating systems, productivity tools, games, web browsers, and mobile apps. In essence, hardware is a computer system's physical, tangible component, while software is the intangible, logical component that instructs and controls the hardware to perform specific tasks. Hardware and software are interdependent, with hardware providing the platform on which software can run and software providing the instructions that allow hardware to perform specific functions.
Next TopicConcave Mirror Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










