Conservation DefinitionConservation is essential for maintaining pure resources and ensuring sustainable use. It includes careful upkeep to safeguard the depletion of finite sources such as soil, air, plants, water, animals and energy that are crucial for human survival and growth. Conservation measures safeguard valuable sources by decreasing waste and raising efficiency. For example, conserving water means using it wisely without pollution from harmful chemicals or unnecessary waste. Similarly, conserving soil involves promoting healthy crop growth while preventing erosion and nutrient depletion through proper practices. Conservation is a continuous effort that demands collaboration from people and groups to guarantee the sustainable utilization of Earth's limited resources for future generations. Conservation DefinitionConservation is a necessary practice that includes the safety and preservation of Earth's pure resources. Its goal is to keep the elegant balance between human practices and the environment, assuring that we do not consume or dismantle our planet's finite sources. 
Conservation plays a necessary role in protecting our planet for present and upcoming generations. Moreover, conservation accomplishments also assist in mitigating climate change by decreasing greenhouse gas excretion through sustainable procedures. Conservation is a significant aspect of environmental stewardship that needs collective action from people, communities, governments, and businesses globally. It is compulsory that we take responsibility for safeguarding Earth's pure resources by acquiring eco-friendly lifestyles and assisting initiatives aimed at saving our planet for upcoming generations. Types of ConservationThere are four types of conservation. 1. Environmental Conservation:This Conservation includes efforts to safeguard natural resources like air, soil, water and forests from pollution and degradation caused by human practices. It aims to promote sustainable development while lessening the effect on the environment. 2. Animal Conservation:This conservation gives priority to protecting endangered species from eradication due to habitat loss and hunting. This type of conservation is essential for maintaining biodiversity and promising that ecosystems will remain functional. 
3. Marine Conservation:This Conservation deals with preserving ocean habitats and marine life for future generations. It includes initiatives such as reducing plastic waste in oceans and protecting coral reefs from damage caused by fishing practices or climate change effects like warming waters. 4. Human Conservation:This conservation concerns itself with improving living conditions for people around the world. This type of preservation may involve providing access to clean drinking water or promoting education about health issues like HIV/AIDS prevention. Methods of ConservationThere are various methods for promoting conservation.
Conservation LawA conservation law is an elementary principle in physics that controls the behavior of physical systems. It justifies that a particular, measurable quantity, which can be supposed as a physical property, persists continually over time within an isolated system. Various types of conservation laws exist, such as those related to energy, momentum, angular momentum, mass and electric charge. These laws play an essential role in explaining how different phenomena occur in our world. For example, the law of Conservation of energy tells us that energy cannot be created nor destroyed, but it can only be transformed from one form to another. Essential Lines on Conservation of Natural Resources
Importance of Conservation
Conservation ChallengesThere are various challenges of conservation discussed below:
Conservation of Natural ResourcesConservation of natural resources like forests has been practiced in India for centuries through the use of sacred forests. These are areas dedicated to gods and ancestral spirits by tribal peoples, where human activity such as tree felling and hunting is restricted. This technique has led to the preservation of various plants and animals across different regions in India. 1. Soil ConservationSoil conservation involves preventing erosion and improving fertility through different methods.
2. Water ConservationWater conservation and management are crucial for the survival of humans, plants and animals. Achieving this involves various methods as follows:
3. Biodiversity ConservationThere are two main methods for saving biodiversity: In-situ conservation: It includes safeguarding plants and animals in their pure habitats or designated secured areas, like National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, and Biosphere Reserves. Ex-situ conservation: It represents the preservation of plants and animals in locations outside their pure habitats. This can be attained through numerous means like botanical gardens, gene banks, seed banks, zoos and tissue culture equipment. 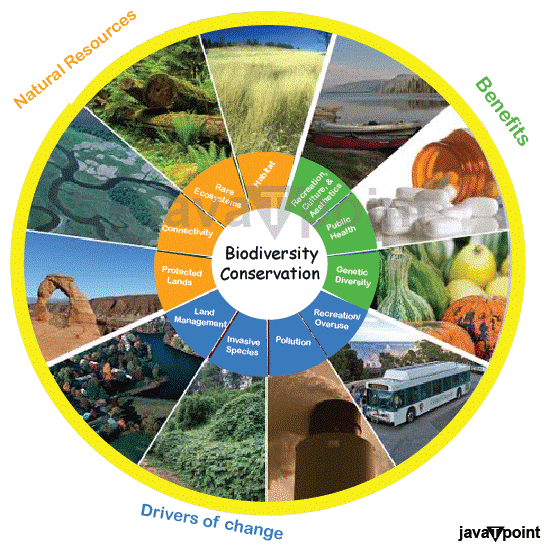
4. Energy Sources ConservationSeveral ways to conserve energy include:
Conservation LegislationThe Indian constitution has laws for conserving natural resources, including various acts and legislation.
ConclusionLastly, it is concluded that Conservation is the protection and preservation of natural resources like land, water, air, plants and animals. It aims to prevent their destruction or degradation for future generations while ensuring sustainable use. Conservation seeks to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance in nature while allowing human development. Conservation is a long-term process but not short-term, and it can assist many species for better and natural survival. FAQs1. What's a conservation intervention?A conservation action is any effort to manage, protect, enhance, or restore biodiversity or ecosystem services. 2. What are natural resource conservation and preservation?Conservation and preservation are two approaches to protecting different things. Conservation focuses on the responsible use of natural resources, while preservation aims to protect buildings, objects, and landscapes from any use. 3. What is the conservation treatment?Conservation treatment preserves records in their original format. Conservators examine and assess record conditions and materials, then recommend treatments to stop deterioration or improve the situation. 4. What is the individual's role in conserving natural resources?To prevent erosion in your garden and open spaces, plant various types of plants, herbs, trees, and grass. Use compost from kitchen waste for fertilization instead of chemical products. Avoid uprooting trees during construction whenever possible and use natural manure to nourish the plants. 5. How can students conserve natural resources?Students can conserve natural resources by eating organic food and conserve water by turning off taps when not in use and saving water at school and home. It also suggests pouring the remaining water into plants instead of draining it into sinks to avoid wasting it. 6. What are the goals of conserving natural resources?The primary goal of conservation is to keep ecological balance, make resources available for present and upcoming generations, preserve biodiversity, and make sure the survival of the human race.
Next TopicCyber Security Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










