Computer DefinitionIntroductionIf you are a child of the modern period, you have probably used, seen, or heard about computers as they are so crucial to our daily life. Computers are widely available, making our duties more accessible and practical, whether at a school, bank, shop, railway station, hospital, or home. Given their importance to our lives, everyone needs to know what they signify and how they operate. 
In its purest form, a computer is nothing more than a calculator. But modern computers are much more than simply calculators. A computer is an electrical device that accepts input, stores it or processes it following user instructions, and then outputs the desired information in the appropriate format. What is a computer?The term "computer" is derived from the Latin word "computare," which indicates to calculate. A computer is an electronic programming device that processes raw data as input and outputs the result after processing it according to a set of commands (a program). After executing logical and mathematical processes, it renders output and saves it for further use. A computer's purpose is to run programs, and its combined hardware and software elements may be used to do several tasks. Programs are needed for it to function, and a series of binary digits are used to represent decimal values. It also has a memory for storing data, software, and processed information. Hardware describes the physical components of a computer, including its hard drives, transistors, and wires. Contrarily, software refers to data & algorithms. 
The Analytical Engine, created by Charles Babbage in 1837, is often regarded as the initial computer. Utilizing punch cards, read-only memory was implemented. "The father of the computer" is another name for Charles Babbage. A computer needs the following fundamental components to function:
Input-Process-Output ModelData is computer input, whereas information denotes the outcome of analyzing such data following user instructions. Unrefined data and numbers employed in logical and arithmetic operations to generate information are referred to as data. 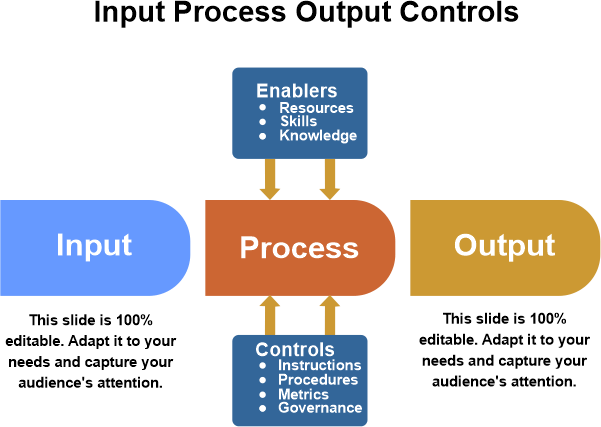
Two distinct types of methods can be used on data:
Essential Components of a Computer
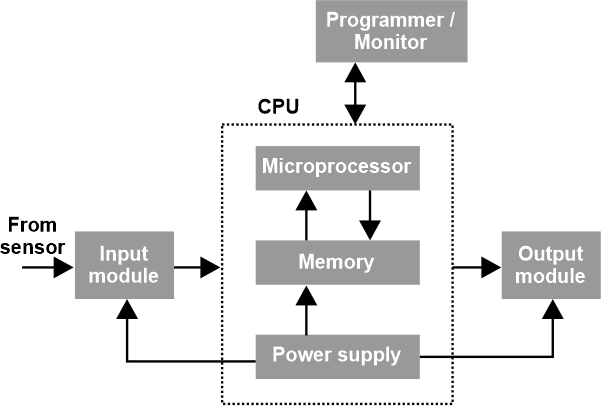
The central processing unit, or CPU, is the collective name for the control unit, arithmetic logic unit, and memory. The physical parts of a computer, such as a keyboard, mouse, printer, etc., are its hardware. Software is the set of programs or instructions that enable the computer to use specific hardware components. We can't see or interact with software. A computer can only function if it has the proper hardware and software. Software vs. HardwareThe computer system is divided into these main groups. We recognize that there exist two major categories of the computer while considering its definition. They are the computer's hardware and software. The hardware of a computer is what we can see, feel, and touch. Along with the CPU chip itself, they also consist of the output and input devices. In contrast, software refers to programs that carry out activities. For instance, the browser you use to see this application is software. Two forms of software exist the operating system, such as Windows or LINUX, and the application software, such as Microsoft Office, games, web browsers, etc. Without software, a computer is just a stupid piece of equipment, and computers are only helpful to humans thanks to their software. Hardware
Computer hardware refers to a computer device's essential hardware components. Hardware may be changed as needed or if it breaks. Hardware is frequently referred to as a computer device's mechanical or significant electronic components. These are utilized to assemble and prepare the computer for use. Monitors, the CPU, and other devices are some examples. Software
A computer system's software is a computer program run on a computing device to complete a task. It is a collection of applications and processes that can carry out specified duties. Most software is created or written in high-level programming languages, which both computer users and non-technical persons can understand. 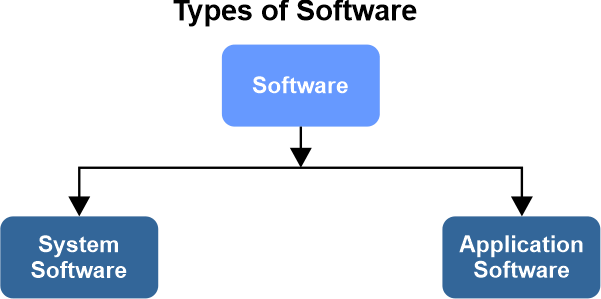
A computer's software is split into two sections. The list is as follows:
Types of ComputerYou should be aware that there are two different categories of computers. Computers can be classified according to their capacities for handling data or size. There are three different sorts of computers if data handling capabilities are considered. These three computer types are: 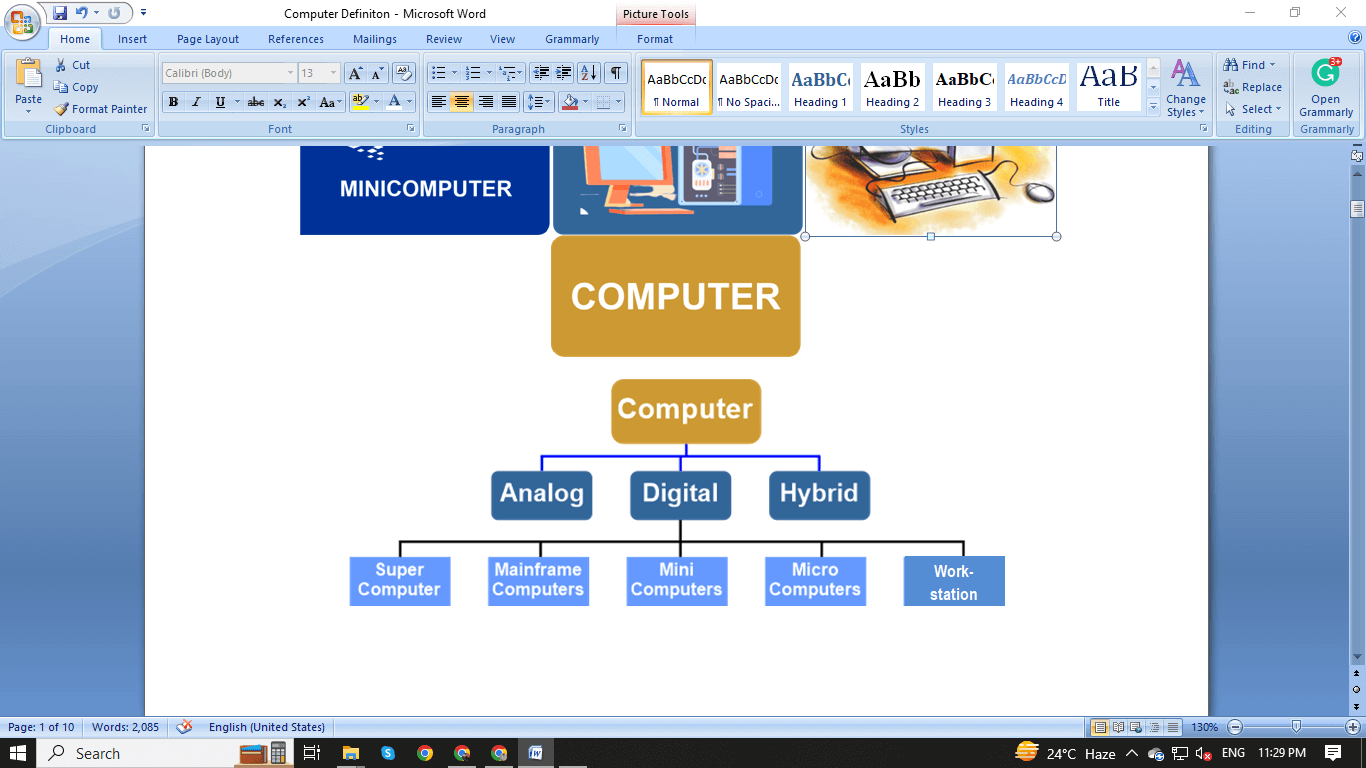
Computers may also be divided into groups according to processing speed and power. 1. Micro Computer
Microcomputers are often created and intended for everyday tasks like web surfing, information searching, MS Office, social networking, etc. It is a single-user computer that performs slower and has less storage space than other models, and its CPU is a microprocessor. With 8-bit microprocessor chips, the first microcomputer was constructed. Personal digital assistants (PDAs), laptops, desktop computers, tablets, and smartphones are typical microcomputers. 2. Mini Computer
Midrange Computers is another name for minicomputers. They are not made for a single person; they are multi-user systems built to accommodate several users simultaneously. As a result, small enterprises and firms typically employ them. Certain corporate divisions use these computers for their reasons. A minicomputer, for instance, can be used by the admissions office of a university to track the admissions process. 3. Mainframe Computer
The architecture of mainframe computers allows for simultaneous operation by thousands or millions of people. Additionally, it enables many running apps at once, and they can thus run several processes at once. Due to these features, the mainframe computer is perfect for large businesses processing much data, such as those in the banking and telecom industries. 4. Super Computer
The quickest and most costly types of computers are called supercomputers. Thanks to their fast processing and enormous store capabilities, they can process billions of instructions every second. Since they are task-specific, supercomputers are used for specialized tasks like significant mathematical problems in technical and scientific fields, including applications for electronics, petrochemical engineering, weather prediction, medicine, space exploration, and more. For example, NASA launches space satellites and manages and controls them for space research using supercomputers. 5. Work stations
It is a computer with only one user. It is similar to a personal computer, but unlike a microcomputer, it features a more powerful CPU and a better display. It is in the middle between a personal computer & a minicomputer in terms of performance and storage. Workstations are typically employed for specialized tasks like desktop publishing, software creation, and engineering designs. Benefits of computers

Drawbacks of Computer
Cloud computingThe term "cloud computing" describes the timely provision of various services through a device's connection to the Internet. One may use many tools and options in cloud computing to complete online tasks for work. Databases, servers, and data storage are some of the services provided by cloud computing. 
Instead of keeping documents on hard drives or other local storage devices, cloud computing allows you to store them in a remote database using a cloud-based storage service. The data and software saved in the cloud may be accessed by the specific electronic gadget so long as it has high-speed internet connectivity.
Next TopicRespiration Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









