Money Market - DefinitionThe trading of very short-term debt assets is referred to as the money market. It involves substantial exchanges between institutions and dealers at the wholesale level. At the retail level, it covers money market accounts created by bank clients as well as money market mutual funds purchased by individual investors. The money market entails the buying and selling of substantial quantities of extremely short-term debt instruments, including overnight reserves or commercial paper. 
Investments in the money market can be made by buying Treasury bonds, money market mutual funds, or by opening a money market account with a bank. Safe and liquid investments, with money market fund shares priced at $1, define money market investments. Compared to a standard savings account, money market accounts provide greater interest rates, but there are harsher withdrawal restrictions and account minimums. Knowing the Money MarketOne of the foundational elements of the world financial system is the money market. Large-scale money transfers between banks and the US government take place overnight in this transaction. Between financial institutions and businesses, wholesale transactions make up the majority of money market transactions. The US money market's assets increased to $4.77 trillion in 2020, illuminating the market's significant contribution to the preservation of economic liquidity. Short-term securities with high liquidity make up the trading instruments, together with open market funds. As a result, assets are easily convertible into cash. 
Furthermore, the duration of investments might be anything from a single day to a whole year, generally not longer than 365 days. The assets traded here have minimal risks and benefits given that investments having longer tenure provide superior returns. Money markets, which trade long-term assets and have higher rates, risks, and returns than capital markets, are so different from capital markets. Additionally, it is challenging for individual investors to provide funds due to the high-value transactions. The main market investors are, among others, banks, credit institutions, NBFCs, insurance firms, and governments. Retail investors have access to specialist banking accounts and mutual funds as a secondary means of investing their resources. The Reason Behind the Name "Money Market"The market for very secure, very liquid short-term debt securities is known as the money market. They are frequently regarded as quick-transferable cash equivalents because of these characteristics. A contemporary financial economy cannot run properly without a functional money market. By allocating capital to its most advantageous use, it enables savers to lend money to people in need of short-term loans. Governments, companies, and banks need these short-term loans to satisfy their immediate responsibilities or legal requirements. They are frequently provided overnight or for a few days or weeks. Those who have extra cash on hand might also earn interest thanks to it. Role of Central BankUsing the money market, central banks like the US Federal Reserve regulate the money supply and prevent inflation and deflation. The central bank purchases bonds and securities to combat deflation. As a result, the economy receives an increase in funding. Nominal interest rates decrease as the amount of money in circulation rises. The cost of borrowing money may be interpreted as the nominal interest rates. The central bank repurchases bonds and other securities during inflation. It thus decreases the amount of money available to the economy, increasing nominal interest rates. The aforementioned central bank behavior is shown on a money market graph. 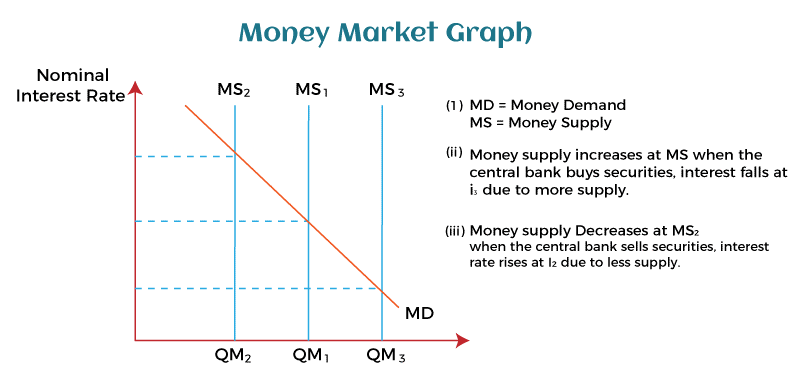
Functions of the Money MarketBy giving the government, commercial banks, as well as other major institutions access to short-term liquidity, the money market helps a nation's economy grow and remain stable. Money market investments allow investors to earn interest on extra funds they do not need. The money market serves the following primary purposes: 1. Financing TradeLocal and foreign merchants that want quick access to capital can get it through the money market. It offers a service for discounting bills of exchange, which enables quick financing for the purchase of goods and services. 
The discount marketplaces and acceptance houses are advantageous to international merchants. Other components of the economy, such agriculture and small-scale industry, can also access financing through the money market. 2. Central Bank PracticesA nation's central bank is in charge of formulating the monetary policy and taking action to maintain a sound financial system. The money market allows the central bank to effectively carry out its role in formulating policy. For instance, the short-term interest rates on the money market reflect the state of the banking industry and can help the central bank decide on an acceptable interest rate policy. Additionally, the central bank may influence the submarkets and carry out its monetary policy goals thanks to the linked money markets. 3. Growth of IndustriesBusinesses can easily fund their short-term lending needs for working capital through the money market. Businesses may have cash constraints linked to purchasing raw goods, paying staff, or covering other immediate expenditures as a result of the high frequency of transactions. 
They can simply take out a short-term loan using commercial paper and financing bills. Although long-term loans are not offered through money markets, they can have an impact on the capital market and can aid companies in securing long-term funding. The money market's current interest rate serves as the benchmark for the capital market's interest rates. 4. Commercial Banks' Self-SufficiencyCommercial banks have access to a ready market through the money market where they may invest their surplus reserves, earn interest, and yet preserve liquidity. Bills of exchange and other short-term investments can be quickly converted to cash to enable consumer withdrawals. Additionally, as an alternative to borrowing from the central bank when confronted with liquidity issues, they might borrow on the money market for a brief period of time. This has the benefit of allowing the money market to offer short-term loans at interest rates that are often lower than those set by the central bank. Types of InstrumentsFor short-term borrowing and lending in the money market, many financial instruments have been developed. They consist of: 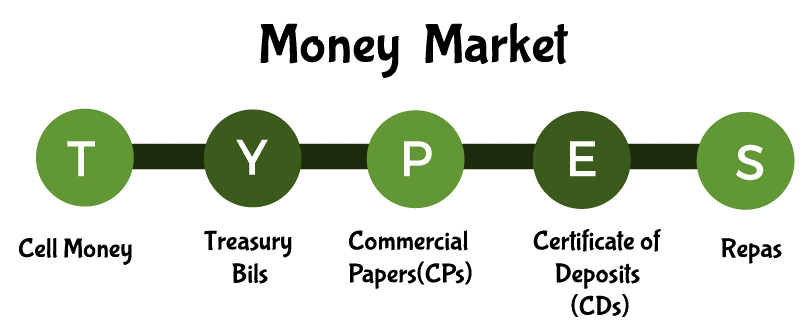
I. Treasury BillsSince the US government fully guarantees the issuance of Treasury notes, they are regarded as the safest financial instruments. The U.S. Treasury routinely issues them in order to refinance maturing Treasury bills and to cover deficit spending. They are available in one, three, six, or twelve month maturities. 
The interest rate is determined by the variation between the reduced purchase price of Treasury bills and their face value, which is the price at which they are offered for sale. They are bought by financial institutions including banks, broker-dealers, retail investors, pension funds, insurance corporations, and other sizable organizations. II. Certificate of Deposit (CD)A commercial bank will directly issue CDs, but investors can also buy them through brokerage houses. Any denomination may be issued, and the maturity date ranges from three months to five years. 
The majority of CDs have a set interest rate and maturity date, and there is a fee if you remove money before the CD is fully matured. A certificate of deposit is protected by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), much like a bank's checking account. III. Commercial PaperLarge organizations or businesses will issue commercial paper, an unsecured loan, to support short-term cash flow requirements like inventories and accounts payable. It is offered at a discount, with the investor earning a profit on the difference between the issue price and the commercial paper's face value. Since commercial paper may only be issued by organizations with strong credit ratings, it is seen as a secure investment. Commercial paper is only issued in amounts greater than $100,000. Through money market funds, individual investors can indirectly invest in the market for commercial paper. The maturation period for commercial paper ranges from one month to nine months. IV. Banker's AcceptanceA short-term debt instrument known as a banker's acceptance is one that is issued by a company but is guaranteed by a bank. It is issued by a drawer and gives the holder the right to the funds shown on the face at a given time. Because it benefits both the drawer and the carrier, it is frequently employed in international trade. 
Investors can make money from the short-term investment if the acceptance's owner decides to sell it on a secondary market. The maturity date typically occurs between one and six months after the date of issuance. V. Repurchase AgreementsIn a repurchase agreement (repo), which is a short-term type of borrowing, a security is sold with the promise to buy it at a better price in the future. Dealers in government securities sometimes utilize it when they sell Treasury notes to a lender with the understanding that they would subsequently buy them back at a predetermined price. Repurchase agreements are purchased by the Federal Reserve as a means of controlling bank reserves and the money supply. The maturity dates for the agreements range from immediately to more than 30 days. 
Benefits of the Money MarketThe following ways in which a nation's money market is established are advantageous to different economic sectors in that nation: 
Source of CapitalThe money market is able to provide short-term cash for commerce and industry using a variety of financial instruments, including treasury bills, commercial papers, certificates of deposits, etc. Perfect InvestmentFor its participants, the money market serves as a short-term investment destination. They have some extra money that they may invest in any money market instrument with. For achieving the regulatory reserve requirements for commercial banks, such products are also acceptable for investment. 
Effective Monetary ManagementA well-established and effective money market also serves as a vehicle for the successful implementation of the monetary policies of the nation's central bank, the RBI. Thus, it makes it easier to communicate the RBI's monetary management strategy for the entire nation. Economic DevelopmentA country's dominant monetary system must include the money market. It significantly contributes to a nation's overall economic development. Its effectiveness and the quick economic growth of the nation actually go hand in hand. 
Efficient Banking SystemThe efficiency and effectiveness of a nation's financial and banking institutions are greatly influenced by how the money market operates. The smooth operation of the financial and banking systems is ensured by a well-developed money market. Trade FacilitationThe following are some ways that the money market helps trade and industries:
Drawbacks of the Money MarketAlthough the Indian money market has the aforementioned benefits, it also has the following drawbacks: 
Limited TransactionsThere are some restrictions on how many transactions a market member may complete. Both withdrawals and deposits are subject to these limits; typically, each participant is only allowed to make three withdrawals and three deposits. This restriction prevents the growth of the money market. Potential Investment LossMoney market participants make their investments through banks. Investors run the risk of losing all or a portion of their investment if a bank is forced to close its doors due to unforeseeable events. The possibility of financial loss is constantly there in people's minds. Fluctuations in Interest RatesAnother danger that players in the money market are subject to is fluctuating interest rates. Interest rate changes can be favorable to investors or borrowers or unfavorable. Against the negative movement of interest rates, there is absolutely no protection. 
Simple AccessIronically, although it's true, having stress-free access to your money market account might really work against you. This is due to the fact that impulsive spending tends to be rather strong at times. Minimum Required BalancesMost banks require their customers to maintain a minimum amount in a money market account. There is a considerable likelihood of slipping below the needed balance, particularly when a money market account is connected to a checking account for overdraft protection. 
Money Market FundInvesting in highly liquid, short-term securities is the focus of money market funds, a type of mutual fund. Cash, cash equivalents, and debt-based securities with a short maturity that have a good credit rating are some examples of these instruments. U.S. Treasury bonds are another example. Money market funds aim to provide investors with great liquidity and very little risk. Mutual funds for money markets are another name for money market funds. 
Through money market funds, which are mutual funds with a portfolio of liquid assets, small-scale investors can acquire indirect access to this market. A variety of CDs, treasury notes, commercial paper, etc. are often included in the portfolio. It has a short maturity, great liquidity, and minimal risk. Through the mutual fund market, a division of the capital market, retail investors can purchase and sell mutual fund units at the current NAV. In light of the pandemic's exposure of many of this industry's weaknesses, regulators are working to create procedures to guarantee its resilience. ConclusionA contemporary financial economy cannot run properly without a functional money market. By allocating capital to its most advantageous use, it enables savers to lend money to people in need of short-term loans. These loans, which are frequently issued overnight or for a short period of days or weeks, are required by governments, businesses, and banks as a way to fulfill their immediate commitments or satisfy regulatory requirements. Additionally, it enables individuals who have extra money to earn interest. 
Money market investments have very low interest rates, frequently the risk-free rate of return, and are essentially risk-free. In contrast to risky assets like bonds or equities, they will not offer significant financial gains or investment growth. Additionally, some money market account types, such as certificate of deposits (CDs), allow investors to lock the funds away until the account matures, which might take months or years. One of the safest methods to invest money is in money market accounts and money market funds. In many cases, their returns are even lower than inflation and are far lower than those of alternative assets. Money markets are a popular short-term investment option for individuals and companies because of how minimal risk they are.
Next TopicNature Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










