Stroke DefinitionA stroke often referred to as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), is a medical emergency that happens when blood flow is halted or diminished to a portion of the brain, resulting in brain cell damage or death. A stroke is a leading cause of disability and death globally and can have catastrophic, long-term effects. Ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes are the two primary types. Haemorrhagic strokes happen when a blood artery bursts, resulting in bleeding in the brain, while ischemic strokes happen when a blood clot blocks a blood vessel. 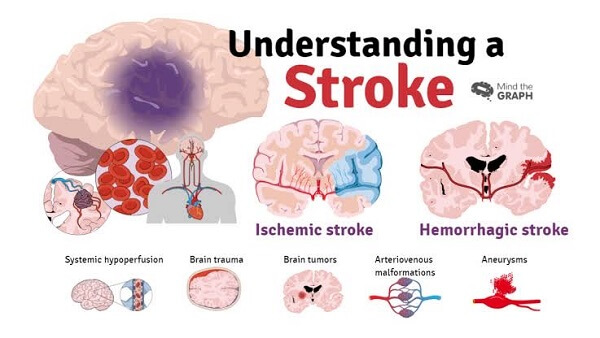
Around 80% of strokes are ischemic, making them more frequent. A blood clot may form and obstruct blood flow to the brain as a result of atherosclerosis, which is the hardening of the arteries, which can lead to their development. High cholesterol, diabetes, high blood pressure, and smoking are additional ischemic stroke risk factors. The severity of haemorrhagic strokes seems to be higher despite their rarity. These may be brought on by a head injury, excessive blood pressure, or an aneurysm (a weak point in a blood vessel that can blow out and explode). Blood clots in the brain from haemorrhagic strokes can create swelling and pressure that harm brain tissue and impair neurological function. Depending on the type of stroke and the area of the brain affected, the symptoms of a stroke might change. Some typical signs include:
If any of these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek medical assistance immediately because time is essential while treating a stroke. Early intervention can lessen brain damage and increase the likelihood of recovery. A physical examination, imaging tests like a CT scan or MRI, and blood tests to look for risk factors like high cholesterol or diabetes are frequently used to diagnose stroke. Depending on the nature and severity of the stroke, a doctor may recommend clot-busting medications or surgery to dissolve a blood clot or close a blood artery rupture. Stroke prevention entails controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol as well as altering one's lifestyle by giving up smoking, keeping a healthy weight, and exercising frequently. Also, it's critical to be knowledgeable about the warning signs and symptoms of a stroke and to seek medical help right away if any appear. A severe medical condition called a stroke can cause permanent disability or even death. Nevertheless, there are numerous methods to lower the risk of stroke and stop it from happening. Ways to Prevent StrokeThe following actions can be done to reduce the risk of stroke: 1. Reduce Blood Pressure: A stroke's main risk factor is high blood pressure. Because of this, it's crucial to frequently check blood pressure levels and act to lower them if they become too high. This can involve changing your food, getting regular exercise, quitting smoking, and taking your medications as directed by your doctor. 2. Maintain a Healthy Diet: By encouraging a healthy weight, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and lowering inflammation, a healthy diet can help lower the risk of stroke. Stroke risk can be lowered by eating a diet high in fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. 3. Exercise Regularly: Regular exercise can lower your chance of stroke by enhancing your cardiovascular health and blood circulation. Aim for 75 minutes of vigorous exercise or at least 150 minutes of mild exercise per week. 4. Stop Smoking: Smoking increases the chance of stroke. Stroke danger, among other health issues, can be decreased by giving up smoking. To help you stop smoking, look for assistance from medical professionals or smoking cessation groups. 5. Reduce Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol use can raise your chance of stroke. Men and women should each consume no more than two drinks per day, respectively, of alcohol. 6. Control Your Diabetes: Diabetes can raise your chance of having a stroke. As a result, it is crucial to control blood sugar levels, maintain a healthy diet, and exercise regularly. Take medication as directed by a doctor and go in for check-ups on a frequent basis. 7. Manage Stress: Stroke risk can rise with prolonged worry. Stroke risk can be decreased by finding healthy stress management methods, such as relaxing exercises or participating in enjoyable hobbies and activities. 8. Treat Atrial Fibrillation: Atrial fibrillation (AFib), a condition of the heart that raises the chance of stroke, should be treated. As a result, it is critical to manage AFib and take medicine as directed by a doctor. 9. Regular Check-Ups: Check-ups on a regular basis with a healthcare professional can help spot stroke risk factors and present chances for early intervention and treatment. Conclusion:A stroke is a medical emergency that happens when blood flow to a particular area of the brain is disrupted or diminished, resulting in brain cell damage or death. A stroke can cause sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, confusion, difficulty speaking or comprehending speech, difficulty seeing, difficulty walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, and an intense headache that appears out of the blue. Ischemic and haemorrhagic strokes are the two main forms, with ischemic strokes being more prevalent. Minimizing brain damage and boosting recovery chances depend on prompt stroke diagnosis and treatment. Managing risk factors and altering one's lifestyle are examples of preventative strategies.
Next TopicTime Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









