Morphology definition

The word morphology, pronounced as "mawr-fol-uh-jee," is used in different branches of learning and study. This noun is used in biology and linguistics, such as:
In biology: The word morphology in biology is considered as its branch that studies the forms of things or deals with the form of a living organism and the relationship between their structure.
In linguistics: In language study, it is considered the study of the forms of words.
History: The word morphology is a Greek work made with a combination of two words, "morph"( means shape) + "ology"( study of the topic). This term was discovered by August Schleicher in 1859.
Morphology definition in linguist
In language, words play an important role therefore, their study is mandatory. The study of words is termed morphology, which includes the formation of words and their relationship with other words in the same language. It details the structure of words (root words, suffixes, prefixes, stems, and parts of words). It is a part of linguistic (word) semantics and makes you investigate the construction of words in the language.
In English, a single letter can alter one-word pronunciation and meaning. For example: accept, accept, and expect. Sometimes, only pronunciation remains the same, and one letter difference changes the meaning. Children start learning with the smallest sound, called "phonemes," and the smallest written sound, called "graphemes," but in reality, they start understanding words with morphemes (smallest unit of meaning like root word, an affix, one part of a compound word and so on). "Morphemes" is the minimal unit of words whose meaning cannot be subdivided further, and the study of these words is called "morphology."
"In language, the study of the smallest segment of language having some meaning called as morphology (deal with words and their makeup)."
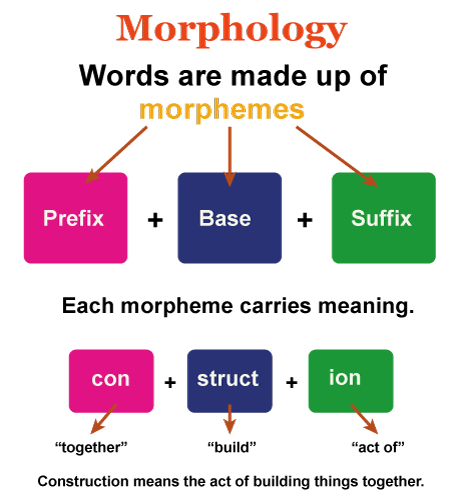
Kinds of morphemes:
a. Free morphemes - These words occur alone, like "bad" words occur alone-other examples like picture, father, adverse, gentle, gem, worse, etc.
b. Bound morphemes - These words occur with another morpheme like "ly," which is a bound morpheme that has its meaning but can't stand alone. It always attaches as a suffix to other morpheme and gives it a meaning.
Free morpheme +Bound morpheme = Word
Bad + ly = Badly
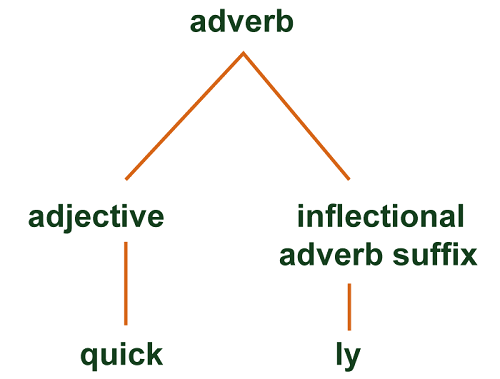
Bound morphemes have two categories: derivational morpheme and inflectional morpheme.
- Derivational morphemes: These are morphemes that can change the grammatical category of the root word. For example: adverse + ly = adversely.
- Inflectional morpheme: They can alter the word but don't change the root word's grammatical category. For example: Cat + s = ca
Words are divided into function words (grammatical) and lexical words (content).
- Lexical words include verbs, nouns, adverbs, and adjectives and are called open-class words. These carry the content or meaning of a message. For example: deliver, meet, stand, compact, tree, excess, blanket, etc. Lexical words or morphemes are important to the sentence as after their deletion, the sentence loose it's meaning.
- Function words (functional morphemes) are considered articles, prepositions, conjunctions, and pronouns and are known as closed-class words because no new word is hardly or is rarely added to this class. They don't carry the content of a message but are more functional and meaning full or coordinate the meaningful words. For example: there, we, and, so, if, with, etc.
- Prefix, suffix, infix, and circumfix are added to morphemes like re, or, um, gr, or t that adds meaning to a word.
Purpose of morphology
The main aim of morphology is the deep understanding of morphemes in teaching and learning because these are important for phonics (reading and spelling), vocabulary, and comprehension.
Morphology definition in biology

The word morphology has a different meaning in biology that stands for studying the shape and structure of living organisms. Biology is the branch of science that deals with the detailed study of living beings, and morphology is the study of the internal and external structures of the organism.
The word "morphology" came from the two words "morph" & "logos"(Ancient Greek words), which means "shape" & "study."Therefore in biology, morphology is " the investigation or study of size, shape, and form of animals, plants, humans or microbes with the interactions of their parts (with all structural elements)."
Morphological characteristics
An organism can be defined by its different attributes, and these attributes are defined as numerous types of traits, like behavioral traits. Organism morphology is described on the morphological characteristics considered as traits that can be broad or narrow. These characteristics include (in animal or living organisms):
- Body size
- Fin shape and size
- Number of flower or petal arrangements
- Scale size or scale shape
- Organ shapes and sizes
Division of morphology
In biology, the morphology is of these types:
- Cellular morphology: It is the detailed study of cells. Depending on the organism, cells may vary in size and form. There are different types of cells present in the body that is epithelial cells ( these cells create cell walls that prevent the free flow of objects from one side to another), fat storage cells ( these are spherical and broad), and nerve cells (these are long and thin cells).
- Tissue morphology: Organism tissues are studied under tissue morphology because tissues have different functional morphologies.
- Skeletal muscles cells (they create lengthy twisted bundles)
- Epithelial tissue (found in lungs like grape-like sacs of cells responsible for the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
- Cartilage (this tissue absorbs trauma from running and walking)
- Organ morphology: It is the study of body organisms that follow a similar pattern of function and shape as if the heart consists of four chambers and ventricles walls are thicker than the atria to pump blood to other body parts.
- The whole organism: It's the highest level of morphology, having different examples of morphology. Here the whole organism is a detailed study and categorized differently.
Types of morphology
The study of morphology is divided into several subfields, which are interested in the shape of organisms and approaches. The types of morphology are functional, structural, and experimental.
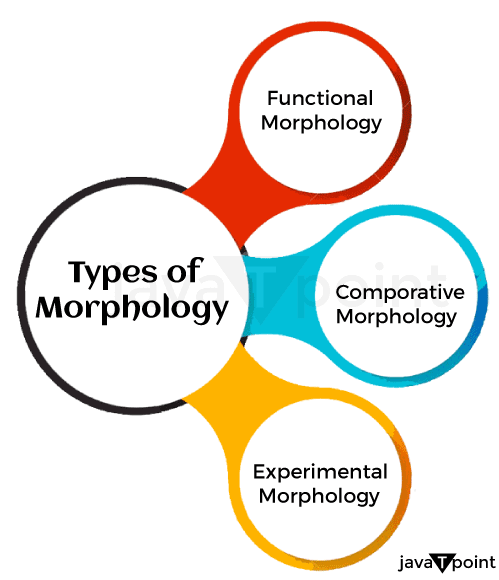
| Functional morphology |
It is the study of the relationship between form and the function of organism structure. An organism's shape tells about how its body functions as this study from insights that heavily depend on the comparative morphology.
For example, Birds' feathers are an appropriate example for studying or understanding functional morphology. Every kind of bird has different feathers. Some are sleek, soft, downy, sturdy, small & large. Sleek and sturdy feathers support the study of flight as they are more aerodynamic and withstand the rigorous demands of flying. But soft downy feather morphology concluded that they don't serve the same function. Excellent insulation provided in a case when the soft fibers of a down feather are pressed against the body. It also help in generating the fight and the feather shape and structure indicate its purpose itself. |
| Comparative morphology |
The comparative morphology is the study of two homologous structures (two different groups of organisms have a structure in common) vary across the different organisms. The organism's structure can be the same but takes different forms. For instance, the bones that make up a bird's wing and the bones that make up a human arm are alike. As a result, comparative morphologists are interested in figuring out how these similar structures change throughout the life tree. |
| Experimental morphology |
Apart from functional and comparative morphology, and experimental morphology, the morphologists take insight from the comparative morphology and speculations from functional morphology, which are investigated through physical experiments. Experiments are carried out on the species in a controlled environment where the functions of two species are compared to a special trait.
For example, Two swimming fishes are compared in a stimulated flow tank having drastically different tail fins that are observed to understand how the tail shape alters swimming kinematics.
Morphologists also create artificial structures to observe the organism and test its limits deeply. |
Conclusion:
In linguistics, morphology is the deep study of words, and in biology, it deals with the form of living organisms, including plants, animals, and human beings. Some of the terms related to morphology are:
- Study plants' physical form and an external structure called phytomorphology or plant morphology.
- The study of internal plant structure is called plant anatomy.
- Study fruit in detail, including its structure, called fruit morphology or anatomy.
|





 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










