Verb Ki DefinitionVerb is a tiny yet very powerful concept of English Grammar. Verbs are a crucial aspect of communication in the English language, and in any language for that matter, because they express what the subject is doing. It encompasses all acts, including those involving sentiments and emotions. Verbs come in a variety of sorts and forms, allowing them to differ significantly in order to offer comprehensive meaning. 
It is employed in a variety of circumstances and languages, and its meaning varies depending on the context. In this article, we will look at the various uses and definitions of verbs as well as provide examples and explanations to help you grasp their intricacies. In a statement, verbs are action words that express what the subject is doing. Verbs, like nouns, are a major section of the sentence or phrase, presenting a narrative about what is happening. In truth, complete concepts cannot be expressed without a verb, and even the simplest sentences, like 'Helen dances' have one. A verb can be a statement in and of itself, with the subjects, in most cases you, inferred, as in Dance! and Rush! While understanding grammatical rules, learners are often taught that verbs are 'doing' words, which means they present the portion of the phrase that defines the activity that is taking place: He bolted, she eats cheesecake on Saturdays, and the ponies galloped through the fields. Gallop, eats, and bolted are the actions in the sentences and thus they are the verbs. Nonetheless, it might be perplexing as not all verbs are clearly associated with action: I remember your name, John considered it, and we discussed numerous uses. These are non-action verbs, meaning they convey a state of being, emotions, ownership, sensation, or opinion rather than an action. Like, accept, feel, am, and have are some more non-action verbs. Before we go into the details of different sorts of verbs and verb forms, let's look at how different dictionaries define the term "verb." 
Definition Of Verb by Various Dictionaries
Thus, in a sentence, verbs are terms that show activity. They are one of the eight components of speech, much like nouns and adjectives. Verbs are also present:
Verbs in Sentences ExamplesVerbs form the initial part of a statement's predicate and are frequently the first word following a noun or pronoun. As an example:
How to Identify a VerbAs you can see from the examples above, the location of the verb in relation to the subject might help you identify it. Verbs are usually always followed by a noun or pronoun. The subject is made up of these nouns and pronouns. When the word thought follows the noun Robert, the action Robert (subject) was performing was walking (verb).
Various Verb CategoriesVerbs are classified into distinct groups based on how they behave in context. Let's have a look at the categories described below. Irregular Verbs vs. Regular VerbsAs you can see, verbs identify activities and may be employed in a variety of ways to express when the subject of a phrase is doing an activity. A regular verb can be conjugated to indicate whether the activity occurred in the past or is continuing. With normal verbs, the past form is usually created by adding a 'ed' to the base verb. Some verbs, on the other hand, do not adhere to this rule. These are known as irregular verbs. These verbs each have their own distinct form. If you're wondering how to master these irregular verbs, check out the page on irregular verbs. Examine the examples provided below.
The verb 'searched' is the past form of the regular verb 'search' by introducing a 'ed' to the ending of the root verb, and the verb form 'looking' is the constant form of the regular verb 'look' by introducing a 'ing' to the finish of the root verb.
The verb 'read' remains unchanged in its past form and as a past participle in the instances above. The past form of the root verb 'find' is 'found'. Intransitive And Transitive VerbsThe transitive and intransitive forms of verbs indicate how a verb behaves when employed with a direct and indirect object, respectively. Consider the following instances.
The verbs 'gave' and 'handed' in the first two phrases accept a direct and an indirect object, respectively, but the verbs 'ran' and 'walked' take no object in anyway. The verbs 'swept' and 'disliked' accept a direct object and no indirect object in the last two phrases. Transitive verbs are those that accept just a direct object, whereas intransitive verbs don't really take either a direct object or an indirect object. Another type of verb that accepts both the direct and indirect object is known as a ditransitive verb. 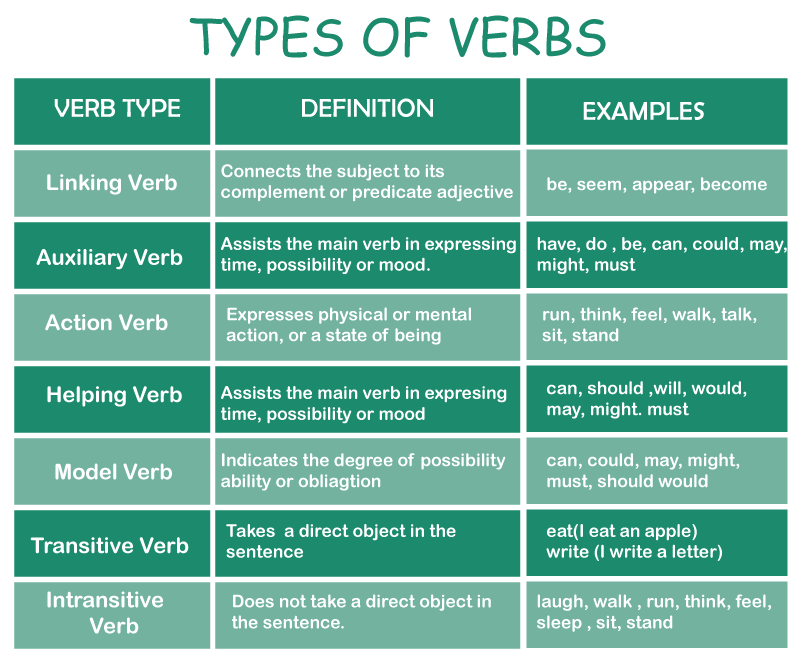
Examples of all the Different Types of VerbsVerbs are categorized into several different sorts based on their function or purpose in a phrase or environment. Let's look at the many sorts of verbs and some instances of each. Helpful Verbs/Auxiliary VerbsAuxiliary verbs, also known as assisting verbs, are verbs that are employed to make another verb seem more rational and understandable. It is used to modify the tense, mood, or voice of another verb. Hence, whenever an auxiliary verb is employed, there is always another word that serves as the primary verb in a phrase. Auxiliary verbs include the following:
One thing to remember when using auxiliary verbs is to form the auxiliary verb appropriately based on the tense form of the phrase. Another interesting point about auxiliary verbs is that they can also function as main verbs. There are also verbs known as modal verbs that can be employed as an assisting verb. Modal VerbsModal verbs are verbs that express the possibility, likelihood, capability, or requirement of something occurring. Unlike all other auxiliary verbs, modal verbs cannot be employed as the primary verb in a phrase. Examples of modal verbs are;
Phrasal VerbsThese are phrases made up of two or more parts of speech that serve the same purpose as a verb in a sentence. A phrasal verb is usually formed by combining a verb and a preposition. Here are some instances of phrasal verbs:
Check out the list of phrasal verbs and practice using them. Linking VerbsA linking verb, as the name implies, is a form of verb that's utilized to connect the subjects of a phrase to the other elements of the sentence in order for the statement to be intelligible. It links a subject to an object, an adjective, as well as a prepositional phrase. All verbs in the 'to be' form, as well as verbs like'seem' and 'become,' can function as connecting verbs. Look at the examples below to see how verbs play the role of a linking verb in sentences. Example 1: Linking Nouns to Other Nouns in a Statement Daniel is my sister. The word 'is' is employed in the preceding example to relate the subject 'Daniel' as the speaker's 'sister's'. The words 'Daniel' and 'sister' relate to the same individual in this phrase. Example 2: Linking a Noun to a Prepositional Phrase in a Statement The kids were in the playground. The verb 'were' is utilized to link the subject 'the kids' to the prepositional phrase 'in the playground' in Example 2. Example 3: Joining a Noun/Subject to an Adjective Your demonstration of the life span of the caterpillar was brilliant. The verb 'was' is used to connect the subject 'Your demonstration of the life span of the caterpillar' to the adjective 'brilliant' in the preceding example. Example 4: Linking the Subject/Noun to the Predicate using Seem/Become This novel on a grand adventure seems intriguing. The linking verb 'seem' connects the subject 'This novel on a grand adventure ' to the adjective 'intriguing' in this phrase. After 2 hours of non-stop instruction, the pupils started to get bored and weren't ready for another hour of instruction without a break. The linking word 'become' connects the subject 'The pupils' to the rest of the sentence in the preceding sentence. Types Of VerbsConsidering all of the jobs verbs have, it's hardly unexpected that there are several types. In reality, there are nine different sorts of verbs, and recognizing them can help you improve the quality of your writing. Let us have a look at types of verbs in English Grammar 1. Action VerbsAction verbs define things that people can do or show. The majority of verbs are action verbs. In most sentences, action verbs come after nouns or pronouns. Let us have a look at examples of Action Verb Action verbs include the following:
2. Stative VerbsStative verbs express a location or state of being that is not visible but exists nonetheless. While they don't accomplish anything observable, they are typically accompanied by a direct object.
3. Regular VerbsMost verbs are normal verbs, which add -d or -ed to their past tense form.
4. Irregular VerbsIrregular verbs are those that alter the form in the past tense.
5. Transitive VerbsTransitive verbs are action verbs that are accompanied by a direct object. Their activity is "transferred" to another noun (underlined). Several transitive verbs are meaningless without an object.
6. Intransitive VerbsIntransitive verbs convey an activity but do not have an object. They can, however, be accompanied by a phrase.
Depending on the context of the sentence, several verbs (such as wash or study) might have transitive or intransitive meanings. 7. Linking VerbsLinking verbs link the topic to specific details about the subject. Am, is, are, and were are all linking verbs that use various versions of the verb to be. These are some examples of connecting verbs:
8. Auxiliary VerbsAuxiliary verbs, also known as assisting verbs, broaden the meaning of the sentence's main verb (known as a participle). They can be found in verb phrases wherein a verb does not create a complete concept, as well as in perfect verb tenses.
Modal verbs are auxiliary verbs that indicate the potential or need of something. They are always used in conjunction with other action verbs.
9. Compound VerbsSimilar to how compound nouns combine two words to form a new noun, compound verbs combine two words to form a new verb. Compound verbs may be one or two words long or hyphenated. These have been highlighted for ease of recognition.
Phrasal verbs are a sort of compound verb that includes a preposition at the end. Since they are English idioms, they are frequently hard to immediately translate into other languages. (These have been highlighted for ease of recognition.)
Common Mistakes in Verb UsageVerb usage often can lead to some common mistakes. Here is the list of some common mistakes that learners can make;
Being aware of these frequent verbal errors can help you communicate more simply and efficiently. It's a good idea to practice appropriately employing verbs and to double-check your writing or speech for these types of problems. Verbal AgreementThe correspondence between the subject of a statement and the verb used is referred to as verb agreement. It is necessary for building grammatically correct phrases and correctly conveying meaning. Verb-subject agreementThe agreement between the subject of a phrase and the verb that relates to it in regard to number, persons, and gender is referred to as subject-verb agreement. ExamplesIn the statement "He strolls to the shop," for instance, the subject "He" is singular and necessitates the singular verb "walks." The sentence "They stroll to the shop," on the other hand, utilizes the plural subject "they" and demands the plural verb "stroll." Importance Of Verbs In English LanguageVerbs are an essential component of language, and their significance cannot be emphasized. A verb is a term that defines a specific action, event, or state of being. They are an important part of a sentence because they express the act or state to which the sentence refers. Sentences would be incoherent without verbs, and communication would be difficult. Verbs play a crucial role in creating a feeling of action and movement in language. Verbs define what people, animals, things, and ideas do and help to construct a picture of a certain scenario or occurrence. They provide language the ability to depict action, emotions, and movement, and they are necessary for narrative, persuasion, and description. Verbs are also important in grammar and sentence construction. They are used to produce tenses that represent the time period of an activity or state of being. Tenses enable speakers and writers to discuss events and situations that occurred in the past, present, or future, which is vital for successful communication. Furthermore, verbs aid in conveying emotion and tone in language. For example, powerful action verbs might convey a sense of excitement or urgency, whereas passive verbs can convey a more relaxed or thoughtful tone. The choice of verbs can also reveal the speaker's or writer's stance towards to the subject. Also, verbs are vital in producing meaning and clarity in language. Both speakers and writers can communicate unique meanings and details that might otherwise be lost by employing the proper verb tense, aspect, and voice. The usage of the present perfect tense, for example, can imply that an action was just done, but the use of the past perfect tense can suggest that an operation was completed before the other incident that occurred previously. Finally, verbs are a necessary component of language, and their significance cannot be emphasized. They are essential in communicating activity, producing meaning, and shaping tone and mood in language. Speakers and writers can communicate clearly and generate powerful and persuasive language by recognizing the value of verbs and perfecting their usage. Tips For Improving Verb Usage
ConclusionVerbs are an important aspect of language, and how they are used can have a considerable impact on the clarity and efficacy of communication. Both readers and writers can increase their capacity to present themselves with clarity and efficacy by studying the many forms and functions of verbs. Appropriate verb usage can boost the legitimacy and professionalism of written communication in corporate, academic, and personal situations. Proficiency of verb usage is essential for success in a variety of disciplines, including writing, teaching, public speaking, and leadership. As language users, it is our duty to make sure that our communication is clear, effective, and courteous. By committing to improve our verb usage, we may better communicate our ideas, viewpoints, and sentiments to our audiences. We encourage users to use the tips and tools provided to further their understanding of verb usage in their professional and private lives.
Next TopicVolcano Definition
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










