How to fix a general protection faultGeneral Protection Fault errors generally occur when software tries to access and use a section of memory that is being utilized by another process or program. These errors are specific to Windows computers. In other words, the error shows that a certain amount of RAM is not available for the running program. 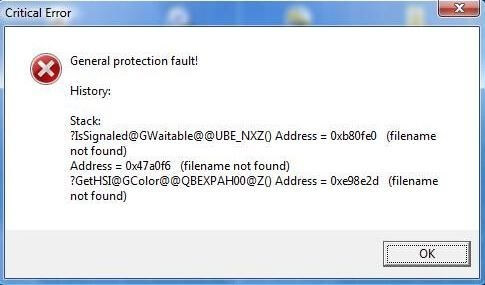
General Protection Fault errors may also show that the memory is not authorized to access the program which is trying to access it. You are experiencing a memory violation issue, to put it simply. Users typically receive a warning informing them that this is taking place, but it is not enough you can do about it aside from restarting the program and hoping it will function properly the following time. Unfortunately, these problems frequently cause the system to freeze. Users are thus forced to restart their computers as they have no other choice. It seems that when you play a game, GPF issues happen frequently. Apparently, some games, like the Harry Potter game series, are more likely to cause GPF issues as compared to others. When you are using beta test versions of software, the chances of occurring a general protection fault are high. However, even seasoned systems can also result in a general protection fault when a user quickly presses a number of keys that the programmer is not able to easily predict them. Also, this error can occur as a result of an incorrect system setup. You can record the information (you are typically given a string of digits that pinpoints precisely where in storage the mistake is occurring) and contact the firm that makes the software that appears to be the cause to show this message if you are continuously receiving the same general protection fault message. While running any application on your computer, if you are facing GPF (general protection fault) errors, the suggestions below may help you resolve the issue. Remove all TSRsBefore running the application that generates the GPF, disable or unload any TSRs or programs that are already running. Delete all program temporary filesWhen you run the applications on your computer, they generate the temporary files that are stored on the hard drive, which may cause GPF errors by forcing programs to access other memory portions. You are required to remove all these temporary files left over from programs that have been operating recently or that are still present on the hard disk. After deleting temporary files, check to see if the error persists. Running Disk Cleanup is the simplest way to do so.
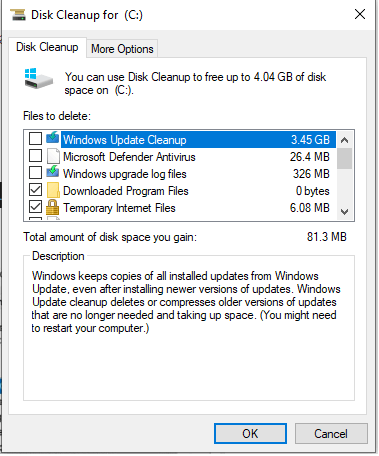
Run ScanDisk and DefragYou should run the ScanDisk and Defrag on the hard disk so that you can be sure the hard drive doesn't have a problem that could make the swap file or data files invalid or corrupt. Verify your computer has more than 200 MB availableYour computer's Windows swap file cannot grow in size when required if your system does not have sufficient storage space. Programs may be switched between memory and the hard disk more frequently as a result of this condition, which increases the number of GPFs. Recently installed software or hardwareSometimes, installing new software or hardware on the computer may cause the GPF errors. Therefore, if you have just installed any latest hardware or software, uninstall or reinstall that application or hardware to be sure it isn't the root of your problem. Disable external cacheIn order to verify an external cache is not the source of your GPF problem messages, you should temporarily disable this cable if your CPU uses it. If this option is present, it can be disabled via the CMOS setup procedure. If this fixes the problem, we advise you to get more advice by getting in touch with the makers of your computer's motherboard, CPU, or CPU for additional recommendations. Tip In rare instances, a BIOS update made to address this issue can also overcome cache- related problems. Disable Power Management and screen saversTo be sure that Power Management and screen savers are not the roots of the problem, disable them if you are experiencing GPF messages after prolonged periods of inactivity on the computer. Operating system issueA generic protection issue can be caused by files related to Windows. A general protection fault, for instance, with KRNL386.EXE and Explorer. In this situation, you can reinstall Windows to solve the problem with Windows-related files. Minimize the load on your systemIt's time to reduce the load on your system if you know exactly what happened to cause the error but have not been able to fix it. Press Ctr+ Alt+Delete to get started. A list of all application running will be displayed on the screen. Steal this list. Next, categorize the programs on the list into essential and optional ones. Nearly all of the programs will not be necessary unless you are doing something extremely important. To close this window, click Cancel or press the Esc key on the keyboard. Cleaning up the registryIt's time to examine the registry now that the fundamental system configuration has been taken care of. Once more, use extreme caution when you are working with the register. Your application programs, Windows 98, or both could be disabled by a single error. Choose Run from the Start menu, then type REGEDIT into the Run window to check the registry in your system. In Windows, the Registry Editor will launch. Like Windows Explorer, the Registry Editor functions similarly. There is a tree in the left-hand column that you can use to navigate. The right-hand column will display the actual registry keys that are present under any given location in the register. Go to HKEY LOCAL MACHINE | Software | Microsoft | Windows | CurrentVersion | Run in the registry. You will probably see a number of keys in the right-hand column when you choose this registry site. These keys stand for applications that launch automatically when Windows has finished loading. These programs, as opposed to the Startup section of the Start menu, are typically lower-level ones connected to particular system operations. The program's name is displayed alongside it in the Task Manager. Additionally, you may view the actual command used to invoke the program. Make sense of the functions of each program with the help of using these two pieces of knowledge. Selecting the unnecessary programs and pressing the key delete will now eliminate them. Just keep in mind that deleting a registry key results in permanent deletion. When you press [Delete], the deletion happens instantly because the registry lacks a save feature. After making all of these modifications, close the Registry Editor and restart the computer. Next, determine whether any system errors are still present or not. Bad memory, or other types of hardware failureIf you have successfully followed all of the instructions and advice above but are still facing GPFs, your computer may have faulty or malfunctioning hardware. Random GPFs are frequently primarily caused by poor memory. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









