What is an internal IP address?Comparing your computer to other devices that might be using the intranet connection, external IP addresses identify your computer in a local network. Another name for an internal IP address is the local IP address. Typically, the first part of this IP address is 192.168. Following the number 8, there will be a period followed by a final run of three different numbers. Other devices linked to your intranet can see this IP address, but no internet-connected external devices can see it. Your device or network can only be identified by its IP address. 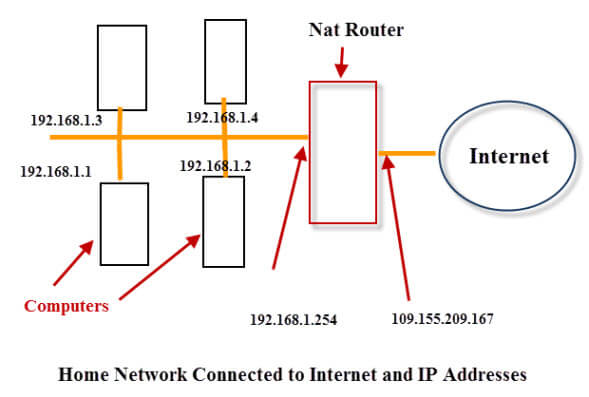
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) has established certain encoding standards to ensure that, despite their similar formatting, IP addresses differ from one another. A Network Address Translation (NAT) device gives you your own unique IP address, sometimes known as your internal or private address. By using private IP addresses, public or external IP addresses are effectively reserved for usage on public networks. Numerous devices, including computers, smart TVs, smartphones, tablets, video game consoles, and many others, are currently linked to the internet in many houses. Your ISP gives your router a single external IP address, which it uses to connect to all of your devices, instead of giving each of them a different external IP address to access the internet. Differences between internal and external IP addressesYour device's identification for its internal network, whether it is an ethernet connection or the connection between your device and your router, is often its internal IP address. Your internet service provider gives your router the external IP address that you have (ISP). Most people focus on their exterior IP address when considering IP addresses, but it's also crucial to consider your internal IP address. An external IP address is one that your ISP assigns to your device, as opposed to your internal IP address. In order to communicate information, such as social media updates, devices all across the internet can locate your device using its external IP address. In order to monitor your internet usage, including your browsing history and login details, and save it on their own servers, your ISP allocates various IP addresses to the devices that connect to your specific WiFi network. However, the router you use to access the internet is regarded as a part of your internal network. While selling this data to marketing firms, who use it for individualized advertisements on sites and social media, is the most harmful thing most ISPs do with it, doing so also leaves you open to data breaches if a hacker gains access to the ISP's server. When your devices access the network, this router also provides internal IP addresses to those devices. Instead of a different IP address for every device, this is typically the case. When you access the internet, anybody can see your external IP address. Still, everything you download from the internet is transferred to your device via the router using the internal IP address that was assigned to you and that no one can access without getting into your internal network. How to locate your internal IP address?Your internal IP address can be accessed using a variety of devices and operating systems, despite the fact that there are straightforward techniques to discover your exterior IP address. Here are a few of the more popular techniques:
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










