What is a Ring Topology?A ring topology is a network architecture in which devices are connected in a ring structure and send information to each other based on their ring node's neighbouring node. As compared to the bus topology, a ring topology is highly efficient and can handle heavier loads. Because packets may only travel in one direction, most Ring Topologies are referred to as one-way unidirectional ring networks. Generally, Bidirectional and Unidirectional are the two types of ring topology. On the basis of devices that are being linked together to form a network, several kinds of ring topology setups work differently. 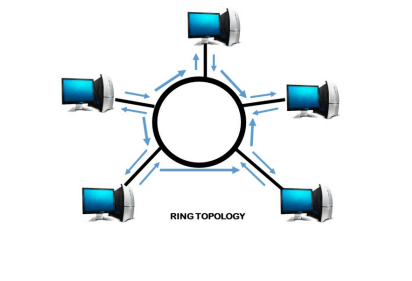
This topology may be used in LANs or WANs. Depending on the network card used in each computer, an RJ-45 network cable or a coaxial cable is used to connect computers in a ring topology. The advantages of a ring topology include, it does not need a central hub in order to function. Installation and troubleshooting with this type of network are also very easy as compared to other networks. A ring architecture has the drawback that if one node fails to send data, the entire network suffers. Therefore, some of the ring topology setups use a dual-ring structure to resolve this problem. In a dual-ring structure, the information is transmitted into clockwise and counter-clockwise directions. There is a backup way of transmission in case one transmission fails; these systems are known as redundant ring structures. How Does Ring Topology work?Below are given some steps that help you to understand how data is transmitted between nodes in a ring network.
How is ring topology formed?In a ring topology, each device is connected to two other devices, and several of these structures are linked together to form a circular route known as a ring network. To reach the data destination, the In-Ring Topology uses a one-to-one procedure; data is communicated from one device to the next, and the process is repeated until the data reaches the target. Sending node transmitted data to the destination node with the help of tokens. Therefore, it is called Token Ring Topology. It is also known as Active Topology since it requires all nodes to be active in order for transmission to continue. There may be modifications to data loss; when there are a lot of nodes, the tokens will have to leap through a lot of them to get to the target node. Repeaters are added on a regular basis to minimize data loss and to improve signal strength. Unidirectional Ring: A half-duplex network is one that permits data to be transferred in just one direction, either clockwise or counter-clockwise. Generally, most ring networks use the process to flow data in only one direction. Bidirectional Ring: It is also known as a dual-ring network, and it may be used to turn a unidirectional network into a bidirectional network by using two links between two network nodes. While sending data in one direction, if any of the intermediate nodes get fail down, dual rings offer alternate paths for any node to reach its destination. Why we Use Ring Topology?There are some factors to choose the network topology, which are as follows:
Increased data economy, excellent network performance, and network operations that are easy to administer are all factors in choosing the correct topology. As compared to another topology, there are five reasons to select Ring topology:
Applications of Ring Topology?
History of Ring TopologyEarly, the ring topology was most widely used in small buildings like offices, schools. However, in modern times, this type of technology is rarely used. For stability, performance, or support, it has been switched to other types of network. Advantages of Ring Topology
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
Next TopicWhat is Tree Topology
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










