What is the nbtstat command??NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP) is a tool that displays protocol statistics and lives TCP/IP connections to assist in troubleshooting NetBIOS name resolution problems. Name resolution is often carried out when NetBIOS over TCP/IP is operating properly. It is accomplished using a local cache lookup, a WINS or DNS server query, an LMHOSTS or hosts file lookup, or another method. 
The NetBIOS name cache, and the NetBIOS name tables for the local and remote systems displays the NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) protocol statistics. This command also enables the NetBIOS name cache, and Windows Internet Name Service registered names to be refreshed (WINS). This command provides helpful information when used without any parameters. This command is possible only if the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) protocol is installed as a component in the characteristics of a network adapter in Network Connections. You can use the nbtstat command to diagnose NetBIOS over TCP/IP issues. The main goal of its design is to assist in solving NetBIOS name-resolving issues. Several iterations of Windows feature the command. There are various commands with nbtstat that provide a variety of possibilities, including local cache lookup, WINS Server query, broadcast, LMHOSTS lookup, and Hosts lookup. Its purpose is not to query DNS servers. NetBIOS over TCP/IP (NetBT) translates NetBIOS names to IP addresses when a network is operating normally. It is accomplished via a number of NetBIOS name resolution options, such as local cache lookup, WINS server query, broadcast, LMHOSTS lookup, Hosts lookup, and DNS server query. The command uses a number of case-sensitive switches to remove and correct preloaded entries. On the computer name supplied by name >, the nbtstat -a name > command executes a NetBIOS adapter status command. The local NetBIOS name table for that machine as well as the MAC address of the adapter card are returned by the adapter status command. Using an IP address as the target instead of a name, the nbtstat -A command does the same task. 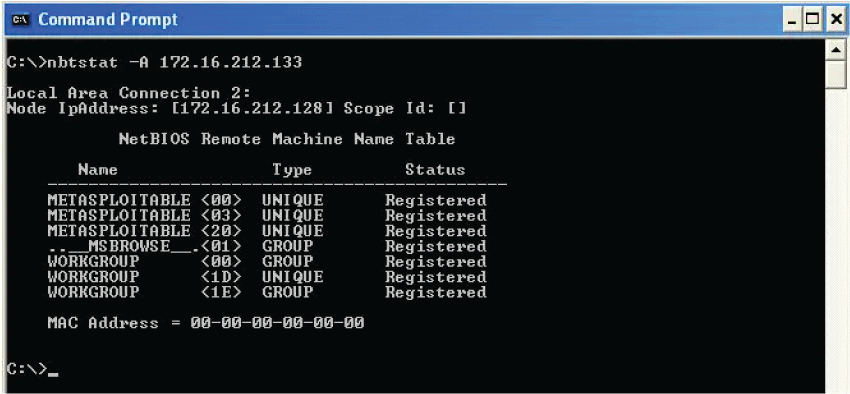
1. /a <remotename> : It shows the NetBIOS name table for a remote computer, where remote-name is the computer's NetBIOS name. The list of NetBIOS names for the NetBIOS programs operating on that computer is included in the NetBIOS name table. A remote name is entered as /a 2. /A <IPaddress> : The distant computer's IP address (in dotted decimal notation) is used to specify the remote computer, which then displays its NetBIOS name table. 3. /c : It shows the information in the NetBIOS name cache, the database of NetBIOS names, and the resolved IP addresses for those names. 4. /n : It gives a view of the local computer's NetBIOS name database. When a name is listed as registered, it means that it has been broadcast or registered with a WINS server. 5. /r : It shows the statistics for NetBIOS name resolution. 6. /R : The Lmhosts file's pre-tagged entries are then loaded after the NetBIOS name cache has been cleared of its previous entries. 7. /RR : It enables the local computer that has a WINS server registration to release and then renew its NetBIOS names. 8. /s : It tries to translate the destination IP address into a name while displaying NetBIOS client and server sessions. 9. /S : It lists the remote machines just by their destination IP address while displaying NetBIOS client and server sessions. 10. <interval> : It displays a set of statistics with a given pause between displays of that set of statistics, measured in seconds. To stop showing statistics, press CTRL+C on your keyboard. The information about the current configuration is printed only once by nbtstat if this option is left out. 11. /? : It shows help at the command prompt. 12. Interval : If a numerical interval is given, the program will repeatedly display the data set forth by the other choices, stopping for a given number of seconds in between each presentation. You have to press Ctrl+C key to stop the re-display of statistics. Example of nbtstat :The NetBIOS names of the hosts that have been registered on the system are displayed by nbtstat -n, and the current state of the NetBIOS name cache, which holds the mappings of NetBIOS names to IP addresses for other hosts on the network, is shown by nbtstat -c. |
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









