What is an ATX-style connector?ATX-style connectors are electrical connectors that are often seen on computer motherboards and power supplies. It is a connector that supplies electricity to a computer system's components. The 24-pin ATX-style connector supplies electricity to the motherboard and other parts of the computer system. As a component of their Advanced Technology Extended (ATX) motherboard specification, it was created by Intel in 1995. It was the first significant upgrade to a desktop computer's power supply, motherboard, and casing in a very long time. It helped improve part standardization and interchangeability as a result. The standard specifies the dimensions, mounting locations, I/O panel, and power and connection connections of a computer case, a motherboard, and a power supply. Compared to earlier power supply connectors, the ATX-type connector is intended to be more reliable and efficient. It contains two rows of pins, with twelve pins in each row. Usually, the connector has a key that can only be used when placed into the motherboard in the proper direction. Additionally, it incorporates a locking system to guarantee that the connector is firmly fastened to the motherboard. An ATX-style connection has replaced the previous P8 and P9 AT-style connectors. It is one of the computer's largest connections. It links a power supply to a motherboard in the ATX format. The 20-pin cable is multi-coloured, as shown in the figure, and it can be recognized as P1. The image shows an ATX cable connector with a little clip-on top that clicks into place to secure the cable in place. It only connects in one direction, making it keyed. 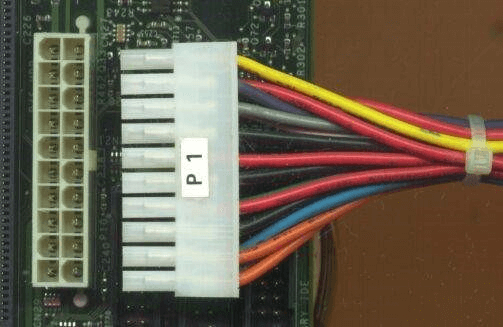
The four extra pins can be left unconnected when using a power supply with a 24-pin connection on a motherboard with a 20-pin connector. All 24 pins of a 24-pin connector on your motherboard must be connected. You will need to purchase a new power supply if yours lacks a 24-pin connector. MicroATX boards can be placed in various ATX chassis due to the full-size ATX board's dimensions of 12 by 9.6 inches (305 by 244 mm). The most common motherboard configuration is the ATX form factor. While reducing the board's size and the number of expansion slots, other smaller board standards (such as microATX, FlexATX, nano-ITX, and mini-ITX) keep the basic back layout. The motherboard, processor, memory, hard drive, video card, and other parts of the computer system are all powered by the ATX-style connector. The power connector offers +3.3V, +5V, and +12V as its three major power rails. Additionally, the connector offers -12V, -5V, and +5VSB power rails. The +3.3V rail, the memory by the +5V rail, and the hard drive and visual card by the +12V rail power the processor and other digital components. History of ATX Style ConnectorThe ATX specs have undergone numerous revisions since Intel released them in 1995. Version 2.2 of the ATX motherboard specification is the most recent. The latest ATX 12V power supply unit specification, 2.53, was released in June 2020. The EATX (Extended ATX) motherboard is a larger variant of the ATX motherboard, measuring 12 by 13 inches (305 x 330 mm). A few motherboards with dual CPU sockets have also been released simultaneously. Intel introduced the BTX (Balanced Technology Extended) standard as an alternative to ATX in 2004. BTX was no longer developed by Intel in 2006, despite several OEMs adopting the new standard. In 2022, the de facto standard for personal computers will still be the ATX architecture. ConnectorsThe AT standard was attached with major modifications on the back of the computer chassis. At first, AT cases just had a keyboard connector and expansion slots for card-back plates. Any additional onboard interfaces (such as serial and parallel ports) must be installed using flying leads in the vacant expansion slot positions and connected to connectors or brackets supplied by the casing. In contrast to ATX, which allowed any motherboard manufacturer to arrange these ports in any order they chose in a rectangular area on the back of the system, most manufacturers tended to stick to a few general patterns depending on the number of ports the motherboard supplied. One of the most common setups involves installing a snap-out panel, also known as an I/O plate or I/O shield, in the casing. I/O plates are frequently included with motherboards that are not built for a specific system; if necessary, they can be altered to fit the motherboard that is being installed. The computer will operate normally without the plate, but the enclosure will have open gaps that could weaken the EMI/RFI screening and let dirt and other foreign things in. An AT motherboard can be installed in an ATX chassis using panels. On some ATX motherboards, there is an integrated I/O plate accessible. Mini-DIN keyboard and mouse connectors akin to PS/2 became more common thanks to the ATX standard. Although PS/2 mouse connections were also present on some systems, serial port mice and 5-pin DIN keyboards were more commonly utilized with AT computers. The more modern Universal Serial Bus replaces PS/2-style keyboard and mouse ports on many modern motherboards. Current ATX motherboards are also gradually phasing out the old connector's 25-pin parallel connections and 9-pin RS-232 serial interfaces. In addition to Wi-Fi, onboard features include Ethernet, FireWire, eSATA, analog and S/PDIF audio, analog D-sub, DVI, HDMI, and video. The fact that the ATX specification was last updated when the power supply was frequently placed at the top rather than the bottom of computer enclosures is a significant fault. As a result, some common port locations have experienced problems, especially the 4/8 pin CPU power port, which is usually positioned at the board's top edge to allow for a top-mounted power supply. This makes it difficult to access cables from bottom-mounted power sources and occasionally results in the need for a unique hole in the backplane so the cable can enter from the back and curve around the board, which complicates insertion and wire management. Many power supply cables require the installation of extensions because they are too hard to bend, barely reach, or fail to reach owing to their configuration. Power SupplySeveral pins on the ATX power supply connector are used to power various computer components. The ATX connector comprises a 4-pin auxiliary connector and a 20-pin main connector. The processor receives additional power from the auxiliary connector and the main connector, which powers the motherboard. The +3.3V, +5V, and +12V power rails used to power various components in the computer are often marked on the main connection. One pin on standard PCI slots provides a reference voltage for some sound card types, while the 12 V supply provides the negative voltage for RS-232 ports. The 5 VSB supply powers the real-time clock and the ATX soft-power functionality while a PC is turned off to preserve the charge in the CMOS battery. 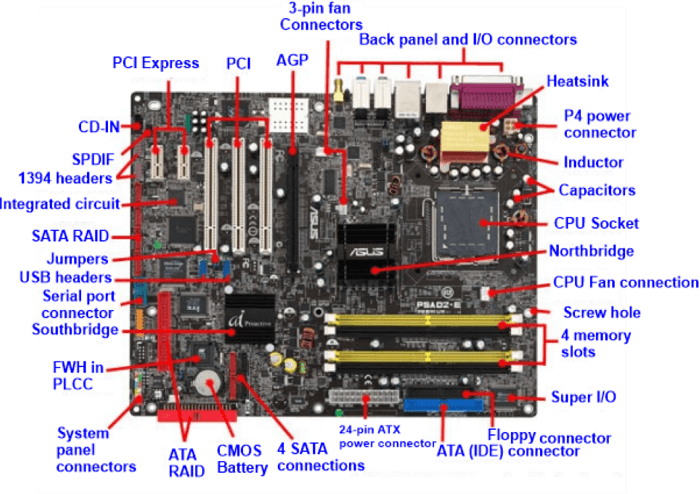
The primary 24-pin power supply connector, a larger version of the original 20-pin connector, and an extra 8-pin (or 4+4-pin) connector for additional CPU power are included in an ATX power supply along with (in modern systems) two motherboard connectors. A 20-pin MOLEX connector, MOLEX 39-29-9202, is located at the motherboard. The cable has a 20-pin MOLEX 39-01-2200 connector. The connector's pin pitch is 4.2 mm (one-sixth of an inch). There is also the Mini-ATX connector, a scaled-down variant of the ATX connector, and it is utilized in smaller computers and gadgets. Physical CharacteristicsOne of the main physical characteristics of the ATX-style connector is its size. It is a large, rectangular connector that measures about 15mm by 15mm and has 24 pins. There are 24 pins total, spread across three rows of 8. The ATX-style connector is typically found on a computer's motherboard and power supply. Another physical characteristic of the ATX style connector is its pinout, or arrangement of the individual pins. The pinout is used to provide power and signals to the motherboard. The ATX-style connector has a specific pinout to provide power and signals to the motherboard. The pins are arranged in three rows of 8, totalling 24 pins. The ATX-style connector is also keyed, which means it has a specific orientation that must be followed when connecting it to the motherboard or power supply. This helps to prevent incorrect connections and damage to the motherboard or power supply. The keyed design ensures that the connector can only be inserted one way, ensuring that the correct connection is made. A different color frequently denotes the function of each pin on an ATX-style connector. For example, the +3.3V and +5V pins may be colored red, while the ground pins may be colored black. This color coding helps identify each pin's function, making it easier to troubleshoot problems or make connections. 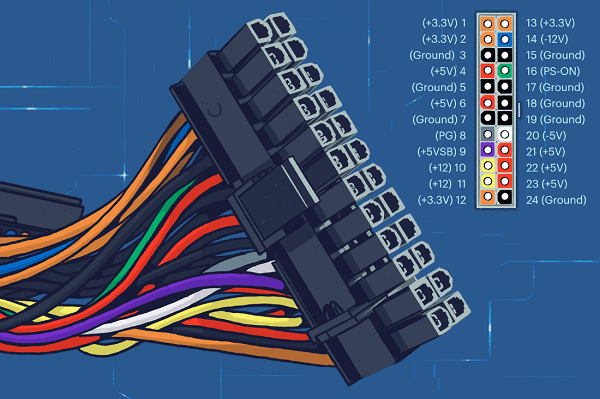
In addition to its size, pinout, and keyed design, the ATX-style connector also has a latch mechanism that helps secure it when it is connected to the motherboard or power supply. This latch mechanism helps ensure that the connector is firmly connected and prevents it from loose during operation. The latch can be released by pressing down on it or pulling it outwards, allowing the connector to be easily removed. The ATX-style connector is an important interface for computer motherboards and power supplies. Its size, pinout, keyed design, and latch mechanism all contribute to its function as a standard interface for these components. Its size and pinout help to provide a common interface for motherboard and power supply manufacturers, while its keyed design and latch mechanism ensure that the connector is securely connected and prevents damage to the motherboard or power supply. Applications of ATX Style Connector
In addition to these applications, the ATX-style connector may also be used in other computer systems, such as media centers, home theaters, and industrial control systems. Advantages and Disadvantages of ATX style connectorThere are several advantages to using the ATX-style connector as a standard interface for motherboards and computer power supplies. Some of advantages include the following:
However, there are also some disadvantages to using the ATX-style connector. Some of disadvantages include the following:
Overall, the ATX-style connector is a widely used and convenient interface for computer motherboards and power supplies. While it has some limitations, it offers several advantages in terms of compatibility, ease of use, and standardization.
Next TopicWhat is Auto Rotate
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









