What is a Local Drive?
A local Drive is a storage device which helps the users to store data in it. It is a device that is physically connected and installed within a computer. It stores data and files that can be accessed quickly by the computer's operating system and programs. A local drive is typically formatted with a specific file system that determines how data is organized and stored on the Drive.
Local Drive can be accessed directly by the devices without network or internet connectivity. Local drives provide a reliable and convenient way to store and access data on a device.
These drives can also be used for data backup, performance optimization, and portable data transfer. Local drives may be limited in storage capacity and more susceptible to data loss in case of hardware failure or other issues. Local drives provide a reliable and convenient way to store and access data on a device without relying on external resources or network connectivity.
They are commonly used for storing the operating system, applications, and personal files on a computer or device, as well as for data backup, performance optimization, and portable data transfer.
The capacity and performance of a local depends on the type of Drive and its specifications. Local drives require periodic maintenance, such as defragmentation or disk clean-up, to optimize their performance and prevent data loss. This can be done manually or automatically using built-in utilities in the operating system or third-party software.
Examples of Local Drive
Local drives can come in various forms and sizes.
Following are the different types of familiar Local Drive:
1) Internal Hard Disk Drive: An internal hard disk drive is a local storage device installed inside a computer or device. It consists of one or more spinning disks that store digital information magnetically and a read/write head that reads and writes data from and to the disks.
Internal HDDs are usually connected to a computer's motherboard using a SATA or SAS interface and are powered by the computer's power supply unit.
2) Solid State Drive: A solid-state drive is a local storage device that uses flash memory to store and access digital information. Normal Hard Disk Drives have a spinning Disk and a read/write head. At the same time, Solid State Drive has no moving parts. It Depends on electronic circuits to read and write data. This allows SSDs to access and transfer data much faster than HDDs, as no physical movement is involved.

3) External Hard Disk Drive: An external hard disk drive is a storage device designed to be connected to a computer or device using a USB, Thunderbolt, or other interface. It consists of a spinning disk that stores data magnetically and a read/write head that reads and writes data to and from the disk. External HDDs are typically enclosed in a protective case and are powered by a computer or an external power source.

4) USB flash Drive: It is also known as a thumb drive or USB stick. It is a small portable storage device. It has been designed to be connected to a computer or device using a USB interface. It consists of a flash memory chip that stores digital information and a USB connector that allows it to be inserted into a USB port.
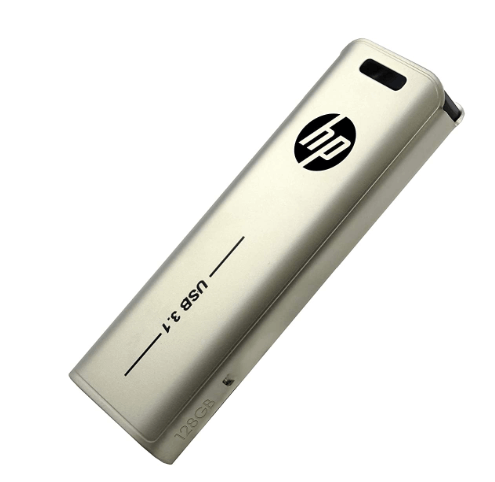

USB flash drives are used for many purposes. Some of the use of USB Flash drives are data storage, data backup, and data transfer. It is a prevalent example of a local drive. It is popular because it is tiny in size. It is Portable and straightforward to use. USB Flash drives are available in many storage capacities, from a few gigabytes to several terabytes. It is cheaper as compared to other types of storage devices.
USB flash drives can store digital files, such as documents, photos, music, and videos, and can be easily transferred between different computers or devices. It is used to boot operating systems or run software applications directly from the USB drive without installing them on a computer.
5. Memory card: It is also known as a flash memory card. It is a small storage device that is used to store digital information. Memory cards are used in portable devices such as cameras, smartphones, tablets, and other electronic devices to provide additional storage capacity. They are also used in some computers, particularly in laptops. It is an excellent way to expand the available storage.

Memory cards store data using solid-state technology, like USB flash drives and SSDs. They are available in different formats and sizes, such as SD, microSD, CompactFlash, Memory Stick, and more. Each format is designed for a specific device or user type and has its storage capacity, speed, and durability specifications.
Memory cards are popular due to their small size, portability, and compatibility with various devices. They are also relatively inexpensive and widely available. However, like other storage devices, memory cards can also be susceptible to data loss or corruption if not handled or stored correctly.
6. Optical disc: This type of storage media uses laser technology to read and write data. There are two main types of optical discs: CDs and DVDs. CDs and DVDs are made of plastic and coated with a reflective layer reflecting laser light. The data is encoded on the disc as a series of pits and lands, read by a laser in the disc drive. To write data onto a disc, a laser is used to heat the disc's reflective layer, which changes the reflective properties of the disc in specific areas.

While CDs and DVDs are still used today, they are becoming less common as newer technologies, such as USB flash drives and cloud storage, become more popular due to their higher storage capacity and faster read and write speeds.
Features of Local Drive
The following are some features of a local drive:
- Physical storage: A local drive is a physical device directly connected to your computer, such as a hard or solid-state drive. It provides a reliable and secure storage solution for your data and files.
- Capacity: The storage capacity of a local drive can range from a few gigabytes to several terabytes, depending on the size of the drive. This allows you to store a large amount of data, including documents, photos, videos, and software applications.
- Access speed: Local drives typically offer fast access speeds. This is important for applications that require high-speed data access, such as video editing, gaming, and database management.
- Data security: Local drives provide data security by allowing you to control access to your data physically. You can use passwords to protect your files and folders and even encrypt the data on the drive to prevent unauthorized access.
- Operating system installation: Local drives can be used to install and run operating systems, such as Windows or macOS, which allows you to use your computer independently without an internet connection.
- Backup and recovery: Local drives can be used to back up important data and files, which allows you to recover your data in case of a system failure or hardware malfunction.
- File organization: Local drives allow you to organize your files and data in a hierarchical directory structure, making finding and accessing your files more accessible.
Uses of Local Drive
The local disc in a computer system is a crucial component which is utilized for various tasks and functions. They have a wide range of benefits.
Here are a few applications for a local drive:
- Data storage is done on local discs. Documents, images, movies, audio files, and other types of data storage are all examples of data storage. Local drives come in a wide range of sizes. The capacity of various drive types varies. The capacity of a local disc can range from a few megabytes to many terabytes. It has a lot of data storage capacity.
- The operating system is stored on local discs. It may contain system files, driver files, and software programs. It enables the computer to boot up, run software, and do other functions.
- Software programs are installed on local discs. Productivity tools, multimedia software, and games may be included. When we install apps on the local disc, our system performs faster rather than the installation of applications on an external drive or network.
- Local drives are utilized to back up critical data. System files, papers, and programs are examples of data. It is an instrumental in retrieving data if hardware fails or the software becomes corrupted.
- Local drives can exchange files with other networks or computer users. It enables users to share documents and information.
- Media files can be streamed from local discs. It can encompass films, television series, and music.
- Local drives can be used as storage for Internet of Things (IoT) devices, which are network-connected devices that gather and transfer data. Local storage can assist in storing and processing data acquired by IoT devices.
- Local discs can store cache data of web browsers and other programs. By keeping frequently requested data on the local device, cache storage speeds up loading of web pages and programs.
Drawbacks of a Local Drive
Local drives are crucial components of contemporary computing, but you should be aware of several drawbacks before using a local drive. The following are some of the disadvantages of the local Drive:
- Local drives have varying storage capabilities and come in various sizes but also have limited storage capacity. If you need to save huge data, you will need to use an external drive or cloud storage services.
- Drops, bumps, and other events can cause physical damage to local drives. This can cause data loss. And, in some situations, It uses the costly services for data recovery.
- Local drives are susceptible to data corruption, which can result in data loss.
- Local drives can only be accessed from the device where they are installed. This might make accessing info from other devices or while traveling easier.
- Local drives can be stolen, resulting in data loss or unauthorized access to critical information.
- Purchasing local drives are relatively expensive. It would be costly to recover your data if it is lost due to physical damage or corruption.
- A local disc, such as a hard drive, is connected to the computer. As a result, if a user is away from his computer, he cannot access the hard drive's data.
- Regular maintenance, such as defragmentation, file cleaning, and software upgrades, are required for local drives. These chores can be time-consuming and disruptive to productivity.
- Sharing data saved on a local device takes a lot of work. Multiple users finding it difficult to access data from a local drive.
- Extending a local drive requires you to purchase or upgrade a new drive which can be costly and time-consuming.
How to Partition a Local Drive
Partitioning a local drive can be useful for organizing data, separating system files from user files, and improving performance by creating multiple partitions on a single physical drive.
Here are the steps to partition a local drive in Windows:
Step 1: Right-click the Start menu and select "Disk Management" from the context menu.
Step 2: In Disk Management, locate the Drive you want to partition and select it.
Step 3: Right-click on the partition you want to shrink and select "Shrink Volume." This will open a dialog box where you can enter the amount of space you want to shrink.
Step 4: You will see an unallocated space once you have shrunk the volume. Right-click on it and select "New Simple Volume." This will open a wizard to guide you through creating a new partition.
Step 5: In the wizard, specify the partition size, assign a drive letter, and choose a file system format.
Step 6: Follow the prompts in the wizard to complete the partitioning process.
In Mac OS, you can use the built-in Disk Utility tool to partition a local drive. Here are the steps:
Step 1: Open Disk Utility, to access Disk Utility, go to Applications > Utilities > Disk Utility.
Step 2: In Disk Utility, locate the drive you want to partition and then select it.
Step 3: Click on "Partition". After then, click on the "Partition" button in the toolbar.
Step 4: Create a new partition: Click on the "+" button to create a new partition.
Step 5: In the dialog box, specify the size, assign a name, and choose a file system format.
Step 6: Once you have specified the partition settings, click on the "Apply" button to complete the partitioning process.
How to Retrieve Data from Corrupted Local Drive
Data recovery from a failed local drive is a complex procedure, but the following ideas can be applied to retrieve Data from a Corrupted Local Drive:
- Before beginning any data recovery efforts, it is very important to find what is the actual cause of the local disc failure. Physical damage to the disc, malware or virus infection, or a logical failure of the file system are all common causes. If the cause of the failure is not known you must seek some expert.
- If the loss was caused by a logical or software error, data recovery software may be able to recover the lost data. Several data recovery software are as follows:
- EaseUS,
- Data Recovery Wizard,
- Recuva, and
- MiniTool Power Data Recovery.
These above four tools can scan the drive for recoverable files and allow you to recover them to another location.
- If the data recovery software cannot recover the lost data or if the reason for the failure is physical, professional data recovery services may be required. These services use specialized technology which uses its functions to recover data from failing local discs. They can, however, be costly, and there is no guarantee that all data can be recovered.
- If the failed local disc is not thoroughly damaged, connecting it to a different computer may allow you to recover some data. This can assist in establishing whether the issue is with the drive or the original machine.
Difference Between Local Drive and Cloud Drive
Local and cloud drives are two types of storage drives, each with its pros and downsides. Here are some critical distinctions between local and cloud drives:
- Location: Local discs are installed on your computer. On the other hand, cloud drives are not physically present within the computer. They are stored on remote servers that are only accessible via the Internet.
- Accessibility: Local drives can only be evaluated from the computer to which they are attached or present, but cloud drives can be evaluated from any computer with an internet connection. As a result, cloud drives are an excellent tool for remote work, collaboration, and file sharing across many devices.
- Storage capacity: The Storage of Local Drive is not Limited. Local drives typically offer more storage capacity than cloud drives.
- Cost: You must pay only once if you buy any Local drives. It has a one-time cost associated with purchasing. Whereas if you buy a cloud drive, the user will have to pay either every month or once a year with its monthly or annual subscription Fee. Purchasing a Local drive is cheaper than buying cloud storage.
- Safety: Local drives are safer than cloud drives. Because they are physically located on your computer, it protects against unauthorized access or data breaches. The user has complete control over the local disc. You have them in your possession. Cloud Drives are accessible from anywhere in the globe.
- Backup: If you wish to take backups on your local disc, manually back up your data to another location to prevent data loss. Cloud drives often provide automated backup and data redundancy, which means too many remote servers automatically back up your data for extra security.
- Speed: Local drives are faster than cloud storage when accessing and uploading data because they are physically attached to your computer's CPU and memory. Cloud drives rely on internet rates that might be unpredictable and sluggish.
- Control: Using a local disc, you have total control over your data and its management. A third-party supplier typically manages cloud drives, and you may need more control over how your data is kept and safeguarded.
- Reliance: A local drive does not require an online connection to access your data, but a cloud drive requires an internet connection to access your data. If your internet connection is down or slow, accessing and transferring data from a cloud drive may be more difficult or impossible.
Storage Capacities of Different Local Drives
- Hard Disk Drives: HDDs are available in a wide range of storage capacities, from 500 GB to 16 TB or more.
- Solid State Drives: These Drives are faster than HDDs because it uses flash memory. Its storage capacities range from 128 GB to 4 TB or more.
- Hybrid Drives: Hybrid drives typically have a smaller SSD cache and a larger HDD storage capacity, ranging from 500 GB to 4 TB or more.
- External Hard Drives: These are local drives connected to your computer via USB or other connection types. External hard drives are available in a wide range of storage capacities, from 500 GB to 16 TB or more.
How are local Drive Organised and Managed
The following are some examples of how local drives are organized and managed:
- File Systems: A file system organizes and manages the data stored on local discs. Local drives often employ the file systems NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. The file system governs how data on the local disc is stored and retrieved.
- Partitions: Partitioning a Local Drive means splitting a single hard drive's physical storage capacity into numerous logical drives or volumes. Each partition has its drive letter and appears in the operating system as a distinct entity. Partitioning can be advantageous for several reasons, including:
Partitioning helps you to organize data. You can retain various information in separate partitions or segregate your operating system files from your files. Or keep different types of files in separate partitions.
- Disk Management: The operating system provides tools for managing local drives, such as Disk Management on Windows and Disk Utility on Mac. These tools allow you to view information about the Drive, format or partition the Drive, and check for errors or bad sectors.
- Backup and Restore: It's important to regularly back up the data stored on a local drive to protect against data loss. Many operating systems provide built-in backup and restore tools to help manage this process.
- Disk Clean-up: Disk Clean-up is a tool that allows you to free up space on your local drive by deleting unnecessary files that are taking up space. Using your computer, you can create temporary files, caches, and other data that can accumulate over time and accepts valuable storage space on your local drive. This can slow down your computer and make storing new files or installing new software challenging.
It scans your local drive for these unnecessary files and presents you with a list of files that can be safely deleted. This includes temporary files, downloaded program files, recycle bin contents, and log files. You can then choose which files to delete, and Disk Clean-up will remove them from your local drive, freeing up space.
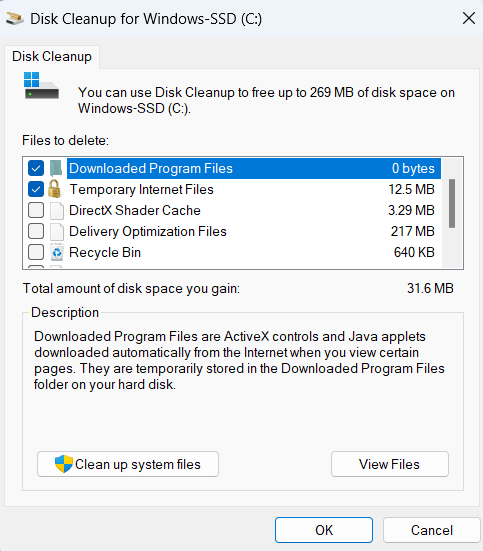
Note: Disk Clean-up is included with Windows operating systems and can be accessed by typing "Disk clean-up" in the Start menu search bar.
- Disk Defragmentation: They can become fragmented whenever you save files to a local drive. Disk Defragmentation is a process that helps us to optimize a local drive's performance by rearranging the fragmented data stored on it.
When you save files to a local drive, the data is sometimes stored in contiguous blocks. Instead of this, the operating system stores the data in the first available space on the drive. This can cause the data to become fragmented and scattered across different areas of the drive. When you access a file, the computer must read data from multiple parts of the drive, which can slow down the process.
Note: Disk Defragmentation is included with Windows operating systems and can be accessed by typing "Disk Defragmenter" in the Start menu search bar. On newer versions of Windows, this tool has been replaced by "Optimize Drives," which can perform similar functions, including optimizing the storage of Solid State Drives (SSDs).
|








 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now










