What is an Internal?A component that is installed within the computer is referred to as internal. An external device is a scanner, whereas an internal device is a motherboard. Any drive within the computer is referred to as an internal drive (for example, an internal hard disc). Additional illustrations of a computer's internal hardware are shown below. 1) Motherboard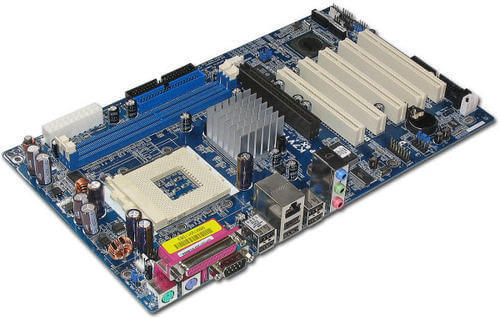
The motherboard is the physical core of the computer and serves as the point of contact for all other parts. A complicated electronic system's main circuit board is what it is. A motherboard offers the electrical connections via which the system's other parts can communicate. Numerous parts, including a CPU, RAM, firmware, internal and external buses, and random-access memory, are found on the motherboard. 2) CPU (Central Processing Unit)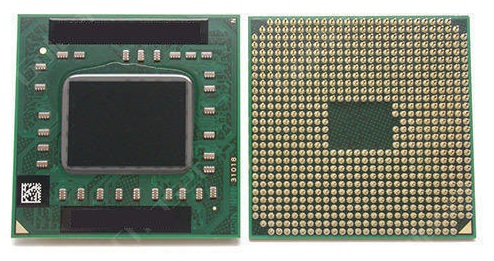
A device that can run computer programs is known as a central processing unit (CPU; it is sometimes simply referred to as a processor). It is commonly referred to as the computer's "brain." Fetch, decode, execute, and writeback are the four phases that practically all CPUs employ in their operations. In the first stage, fetch, an instruction is taken out of program memory. The instruction is divided into pieces at the decode stage that are significant to other CPU components. The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and the floating-point unit (FPU) are coupled during the execute stage in order to carry out the required operation. The execute phase's results are simply written back to some sort of memory in the last step, known as writeback. 3) RAM (Random Access Memory)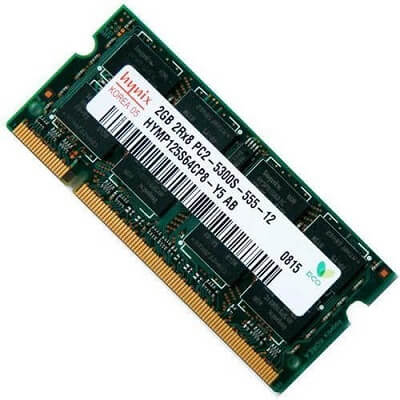
When a computer is turned off, its fast-access memory, known as random access memory (RAM), is cleaned. RAM is utilized to store active applications and is directly connected to the motherboard. RAM is a collection of integrated circuits that enables random access to the data that is being stored (why it is called random). There are several varieties of RAM. There are differences between these many kinds, such as readable vs read-only, static versus dynamic, volatile versus non-volatile, etc. 4) Firmware
Read-only memory (ROM) is used to load and operate firmware, which is controlled by the basic input-output system (BIOS). It is computer software that is integrated into a piece of hardware, such as a microcontroller. Firmware, as its name implies, sits in the middle between hardware and software. It is a computer program that, like software, is run by a microprocessor or microcontroller. However, it is also closely related to a hardware component and is not very significant. Most devices connected to current systems are standalone, specialized computers with their own operating systems. Some of these devices keep the software (or "firmware") in their own ROM. 5) Power Supply
The unit that provides power to all of the components in the computer is the power supply, as its name may imply. A transformer, voltage control, and a cooling fan are all housed within of its housing. For usage by the internal components, the power supply transforms around 100-120 volts of AC electricity into low-voltage DC power. The ATX form factor is supported by the majority of computer power supply. This makes it possible for various computer components to work with various power supplies. Additionally, ATX power supplies are made to switch on and off using a motherboard signal and enable contemporary features like standby mode. 6) Removable Media DevicesRemovable media is anything that you can insert into your computer and remove again. Removable media players come in a wide variety. The most common are likely CD and DVD drives, which are now found in practically every computer. There are certain modern disc drives, like Blu-ray, that can store a lot more data than standard CDs or DVDs. Floppy discs are one form of removable media that is losing importance. CD (Compact Disks) 
The most popular kind of removable media is CDs. Despite being cheap, they only last a short time. There are several distinct CD types. Although any kind of data may be stored on CD-ROMs, which stand for Compact Disc read-only memory, they are frequently used to transfer computer software. Another variety is CD-R, which can be read several times but only can be written once. CD-RW (rewritable) discs can be read and written several times. A CD-ROM drive and a CD writer are the two forms of CD-using hardware in a computer. The CD-ROM drive is used to read CDs. A CD may be read and written with a CD writer drive. In comparison to a CD-ROM drive, CD writers are significantly more common in modern PCs. Both types of CD drives are referred to as optical disc drives because they read or write data to or from a CD using laser light or electromagnetic waves. DVD 
Digital versatile discs, or DVDs, are another well-liked type of optical disc storage medium. Video and data storage are two of DVDs' primary applications. The majority of DVDs have the same size as compact discs. There are many distinct variants, much like CDs. Data on a DVD-ROM can only be read, not written. Once created, a DVD-R or DVD+R can serve as a DVD-ROM. Data on DVD-RAM, DVD-RW, or DVD+RW can be repeatedly deleted and rewritten. DVD-Video and DVD-Audio discs are terms used to describe appropriately prepared and organized video and audio information, respectively. The gadgets that use CDs and DVDs are quite similar. A DVD-ROM drive and a DVD writer exist, and they function in the same ways as a CD-ROM drive and a CD writer. Additionally, a DVD-RAM drive exists that reads and writes to the DVD-RAM variant of the format. Blu-Ray 
The optical disc storage format Blu-ray is more advanced. Data storage and high-definition video are their principal applications. The disc's dimensions are the same as those of a CD or DVD. The blue laser that reads and writes to the disc gives "Blu-ray" its name. Compared to CDs or DVDs, Blu-ray discs have substantially larger storage capacity. A dual-layer Blu-ray disc has a storage capacity of up to 50GB, which is almost six times as much as a dual-layer DVD. The equipment needed to read and write to Blu-ray discs is similar to that used for CDs. A Blu-ray disc can only be read by a BD-ROM drive, however, a Blu-ray disc can also be written to with a BD writer. Floppy Disks 
A floppy disc is a kind of data storage made up of a disc of a thin, flexible magnetic storage media (hence the name "floppy") enclosed in a square or rectangular plastic shell. A floppy disc drive reads and writes floppy discs. Floppy discs are becoming obsolete, and optical and flash drives are taking their place. Floppy drives are no longer often found in new computers, although they are still present in many older models. Despite their low cost, floppy discs are not practical to use due to their limited storage capacity when compared to flash drives, which offer more storage for the same price. What is an Internal Storage?Hardware, known as internal storage, preserves information within the computer for future use and continues to function even when the machine is not receiving electricity. Internal storage comes in a few distinct forms. The most common kind of internal storage is hard drives. The use of solid-state SSDs has gradually increased. When you want more storage than a single hard disc can provide, a disc array controller is frequently used. 1) HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
Using fast spinning platters with magnetic surfaces, a hard disc drive (HDD) is a non-volatile storage device that stores digitally encoded data. Nowadays, unless it has a brand-new solid-state drive, nearly every computer system comes with a hard disc. A typical desktop hard disc drive has a maximum data transmission rate of 1 Gbit/s and can hold 120 to 400GB of data. It also rotates at 7,200 rpm. SCSI, Serial Attached SCSI, Parallel ATA (commonly known as IDE), Serial ATA (SATA), and Fibre Channel are just a few of the bus types that may be used to access hard disc devices. 2) SSD (Solid State Drive)
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a type of data storage that keeps persistent data in solid-state memory. An SSD may readily replace a hard disc drive in any application since it mimics one. Due to their potential for being smaller than HDDs, SSDs have started to emerge in laptops. The reason why SSDs have not gained popularity as rapidly as HDDs is that they are now more costly per unit of capacity. 3) Disk Array Controller
The physical disc drives are managed by a disc array controller, which exposes them to the computer as logical units. Hardware RAID is nearly always used. A system known as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Drives) uses two or more hard disc drives at the same time to increase performance, reliability, and/or data capacity sizes. Additionally, a disc array controller offers more disc cache.
Next TopicWhat is an IP address
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









