What are the Processing Devices of the Computer?Before data is transmitted to an output device from an input device, such as a keyboard, it must pass through an intermediary step in a computer (e.g., a monitor). A processing device is any piece of hardware inside a computer that interprets and modifies incoming data at this level. The device for processing is the CPU. Any internal component of a computer that enables the interpretation and manipulation of incoming data is referred to as a processing device when this phase is being carried out. In this article, we'll walk you through the definition of processing devices for computers as well as their types, purposes, and other applications. The processing device is a physical element of the computer that assists in managing information storage and retrieval. Processing equipment is crucial to the processing processes of a computer. By following the program's instructions, these devices process data. Any instruction, whether it involves input-output activities, logical comparisons, or numerical computations, can be carried out by a CPU. They provide the coordination of all other computer units' tasks, and they make sure everything runs well. Computer processing device types:There are a number of different computer processing devices kinds; a description of each is provided below.
GPU(Graphics Processing Unit)
GPU stands for "Graphics Processing Unit". It is a computer-integrated circuit that aids in rendering visuals and images by employing to do quick mathematical calculations. It is employed in computers for both personal and business applications. Rendering of 2D and 3D images, videos, and animations is the duty of the GPU. GPU can accelerate machine learning due to its great processing capacity. Because a GPU can generate high-definition graphics and videos in parallel, it can enhance video editing and production performance. The use of GPU in crypto currencies like Bitcoin is due to its superior performance. Discrete and integrated GPUs are the two different types. Unlike discrete GPU, which is located on a separate circuit board, integrated GPU is installed next to the CPU. Microprocessor :
The microprocessor is the device's brain, which is installed as a single integrated circuit inside the computer. It is responsible for carrying out all mathematical and logical procedures. A microprocessor manages all of the different Arithmetic Logical Unit (ALU) functions, making it a control unit of a computer. In addition to basic computations like addition and subtraction, microprocessors are also capable of internal processing, device terminal communication, and I/O control. All calculations, including addition and subtraction, are handled by the microprocessor using the ALU, control unit, and register array. After the instructions have been carried out, store them in memory, and then send the output for display on output devices such as a computer monitor. Sound Card :
Input and output for audio are provided by the sound card. It is a motherboard-installed hardware element of the computer. The majority of sound cards come with at least one stereo line output and one analog line input. Ports for sound cards - Loudspeakers can be connected to digital out (yellow). Sound in or line in (blue): This connector is used to connect to external audio sources, such as record players, CD players, and so on. Pink microphone: It may be used with headphones or a microphone. Sound out or line out (Green): It is the main sound connection for speakers or headphones. It is used to connect an external MIDI keyboard or joystick (15-pin yellow connector). Video Card :
A video card is an extension card that is integrated into the motherboard of the computer. The terms "Display Adapter", "Graphics Card", "Video Adapter", "Video Board", and "Video Controller" are some of the various names for video cards. Without it, the user would not be able to view any images on the monitor, hence it is utilized to display the images there. For increased processing power and high-resolution graphics, most gamers prefer a video card. CPU (Central Processing Unit) :
The computer system's central processing unit (CPU) is a key component, which supports all processes involving the processing of data. It is in charge of overseeing how the computer's various parts operate. In order for a computer system to work well, the CPU is essential. It also aids in the smooth operation of all system elements. The system's hardware and software send instructions to the CPU, which manages all of them, processes them, and then outputs the results to things like a printer and monitor, among other things. Thus, we can say that the CPU (central processing unit) is the most significant component of the computer system. Clock :
The usage of a clock as a microchip inside the computer aids in controlling the timing and speed of all of its operations. The speed of a computer processor is also expressed in terms of clock speed; for example, 1 MHz represents one million cycles and 2 GHz represents two billion cycles. The system timer or system clock receives a regular pulse that aids in the accurate timekeeping of the computer. Chipset :
An array of integrated circuits makes up a chipset that are created and offered as a unit and works as a team to perform a single function. For instance, a chipset is a collection of all the microchips that a computer needs to provide the communications controller between the processor and memory as well as other components. It is possible to state that the computer's chipset aids in the control of all data flow. Motherboard :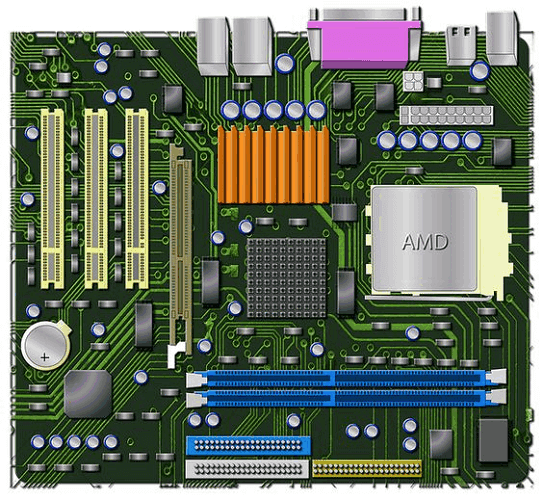
The motherboard is the primary circuit board of the computer system, which is also known as the "Mainboard or Logic board". Every motherboard has a chipset, which is a collection of chips and controllers. The motherboard, commonly referred to as the "HUB", is the foundation of the computer. The motherboard has sockets, ports, and connections for connecting all input and output peripherals as well as the CPU (central processing unit), memory (internal and external), and others. Data Bus :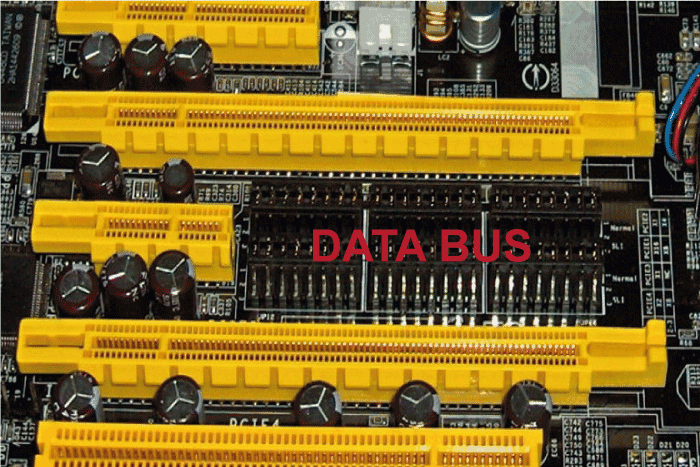
The data bus is a means of data transmission, which is a group of wires mounted on the motherboard and used by the CPU (central processing unit) to send data between all of the computer's components. It functions as the engine of the device. Moreover, two distinct computers can transfer data using a data bus. Bus controllers aid in controlling the speed of information transfer between all components of the computer.The internal and exterior data buses are two different types of data buses that are present in every computer system. Expansion Slots :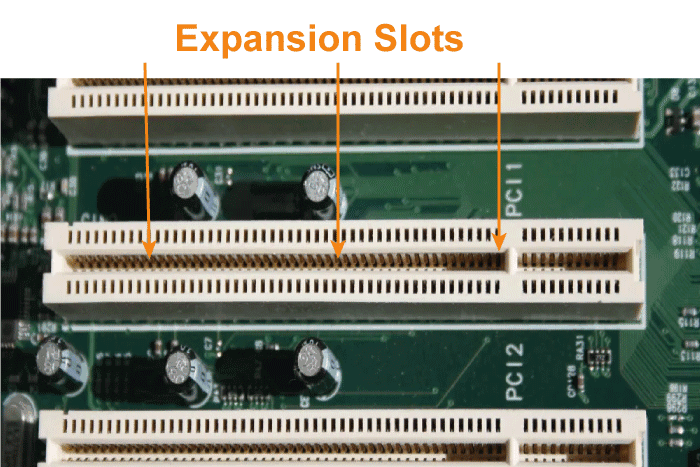
The term "expansion slots" refers to all motherboard slots that are used to insert expansion cards, such as video cards, network cards, or sound cards, to increase the capability of computers. In order to give the motherboard direct access to the computer hardware components, expansion cards can be plugged directly into expansion ports. PCI, AGP, AMR, CNR, ISA, EISA, and VESA are a few of the expansion slots available. Network Card :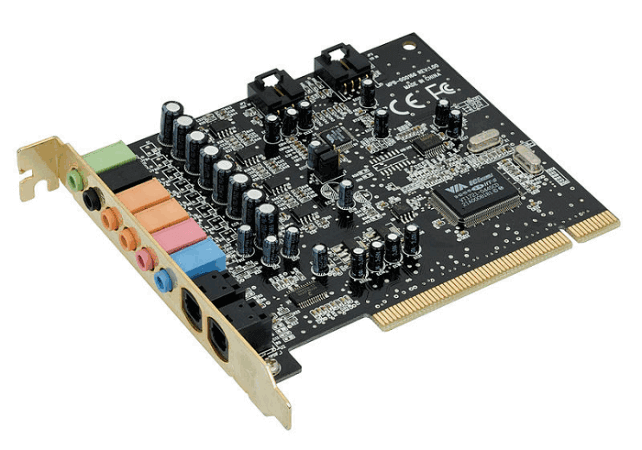
The physical part of a computer, known as a network card enables local area network (LAN) connection between other computers. Internet Protocol (IP) can be utilized if you want to communicate over a vast network. The phrase "Network interface controller, network adapter, or LAN adapter" is also another term for it. Address Bus :
An address bus is a collection of wires that only permits addresses to be stored. The address bus has a unidirectional flow of data, which means that an address may only be passed in one direction, from the CPU to Random Access Memory (RAM). The fundamental function of the address bus is to locate a particular address in the primary memory that can be read from or written to. Each position in the main memory has a specific, individual address, or "Addressability", that is used to identify it. Random Access Memory :
The main memory of a computer is called RAM (random access memory). The Purpose of Processing Devices:All coded data entered by users through input devices such as the mouse, keyboard, trackball, and other devices is processed by processing units in the computer system. This data are processed into information that is subsequently delivered to output devices like a display, speaker, printer, etc., after being transformed. Data is initially obtained from the input devices and then passed through an intermediate level before being output on the right output devices. For example, the Central Processor Unit (CPU) accepts the incoming data, does the necessary processing, including the computations, and then stores the results in the computer's memory. What are the three primary elements of a processing device?
Next TopicWhat is a Silicon Chip
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










