What is Back?The term back refers to any of the following: 1) The term "Back" can refer to the Back button. The back button is a common user interface feature in digital devices and applications. It allows users to return to their previous location or state within the interface. Clicking on the back button takes the user back to the last page visited, the previous screen in an application, or the previous state of an interface. The back button is a fundamental element of modern user interface design, providing users with a sense of control and familiarity and contributing to a more efficient and intuitive user experience. 
The back button has been around for decades, and its evolution has mirrored technological and user interface design changes. It was first introduced in web browsers, allowing users to navigate their browsing history easily. Since then, the back button has become ubiquitous in a wide range of digital applications, from file explorers to mobile devices and social media platforms. The back button is important because it simplifies the user experience and makes it more efficient. Instead of retracing their steps or using complex navigational tools to return to a previous location or state, users can click the back button to return to where they were. This saves time and reduces frustration, making it easier for users to accomplish their tasks and achieve their goals within the interface. Back Button in Different ApplicationsThe back button is a versatile user interface feature that plays an important role in various applications, including web browsers, mobile devices, and more. In this article, we'll explore the different applications of the back button and how it enhances the user experience in each context. Web Browsers:
In web browsers, the back button is a fundamental navigational tool that allows users to move backwards through their browsing history. This enables users to quickly return to a previous page, even if they've navigated through several different websites since then. The back button is particularly useful for users conducting research or reading a long article. It lets them easily refer to previous information without losing their place in browsing. Additionally, the back button is often accompanied by a forward button, allowing users to move forward through their browsing history. Mobile Devices:The back button is also a common feature on mobile devices, where screen real estate is at a premium. In mobile applications, the back button is typically used to return to a previous screen or state. This is particularly useful in complex applications with many screens or workflows as it enables users to quickly navigate between different sections of the app without starting over from the beginning. The back button is also useful for users who may accidentally tap a button or navigate to the wrong screen, as it provides a simple way to undo their actions and return to a previous state. 
Other Applications:The back button has been adapted for other applications, including media players, file explorers, and physical devices like remote controls. In these contexts, the back button is typically used to return to a previous screen or menu. It gives users a simple way to backtrack through their actions and make corrections if necessary. 2) When describing a physical object, the term "back" refers to the side of an object that is opposite to the front side. The back side of an object is typically the side that is not visible, or that faces away from the user. For example, the Back of a computer is where all the cables are connected, which is usually not visible from the front. The concept of the "back" of a physical object is important in understanding how the object functions and how it can be used. By examining the Back of an object, users can gain insight into the different types of connections available and how they can be used to achieve certain tasks. This knowledge can be particularly valuable for users setting up or configuring a new device, enabling them to make the right connections and ensure the device works properly. In addition to its practical applications, the concept of the "back" of a physical object can also be useful in aesthetic design. Designers often consider the appearance of an object's front and back when creating a product, and the back side can be just as important in terms of overall visual appeal as the front side. For example, some designers may incorporate distinctive features or textures on the back side of an object to make it more visually interesting or to create a sense of balance between the two sides. Examples of Objects with a "Back" SideThe concept of a "back" side is present in many physical objects we use daily. These objects include electronic devices, appliances, furniture, and even vehicles. Here are some examples of physical objects that have a "back" side: 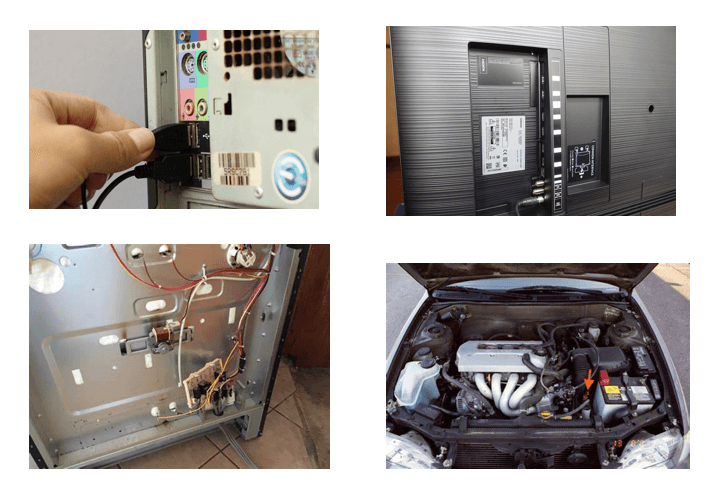
3) On an Android device, such as a tablet or smartphone, the term "back" refers to pressing a back button which returns you to the previous screen or exits the current menu. The back button on an Android device is a software or hardware button that allows you to go back to the previous screen or step into an app, undo an action, or exit a menu or dialogue. In most cases, the back button is represented by a left-pointing arrow or triangle icon and is located either on the bottom of the screen or on the device itself. 
The back button is a crucial component of the user interface in mobile devices, especially in Android, one of the most popular operating systems for smartphones and tablets. It enables users to navigate through apps and menus naturally and intuitively without memorizing complex hierarchies or using multiple gestures or taps. Moreover, the back button provides consistent and predictable behaviour across different apps and contexts, which makes it easier for users to learn and use their devices. The functionality of the Back Button on AndroidThe back button on an Android device serves multiple functions related to navigation within and between apps and system menus. This section will explore each of these functions in more detail.
Customization of the Back Button on AndroidOne of the benefits of using an Android device is the ability to customize the device's behaviour according to individual preferences. This extends to the functionality of the back button, which can be customized to suit different user needs. Options for Customizing the Back Button on Android:
Examples of Custom Back Button Configurations:
Next TopicWhat is an opto mechanical mouse
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









