How to enable or disable DHCP in Windows?
DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a common protocol for assigning IP addresses and other network settings to networked devices. Devices like laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles can be automatically assigned IP addresses in household and small business networks. By using DHCP, you can avoid manually configuring each device on your network, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
DHCP is typically enabled by default on most home routers and network devices. However, there can be instances where you have to turn off DHCP and assign IP addresses manually to particular devices. This can be useful for advanced network configurations, such as setting up a static IP address for a server or creating a DMZ (demilitarized zone) for security reasons.
How to enable or disable DHCP?
Step-by-step instructions for enabling or disabling DHCP on Windows
Windows 8 and Windows 10:
- To access the Power User menu, press the Windows key + X on your keyboard.
- Select "Control Panel"
- Select "Network and Sharing Center."
- On the left sidebar, select "Change adapter settings."
- Select "Properties" from the context menu when you right-click on the network device you want to enable DHCP for.
- Select "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" from the list of choices.
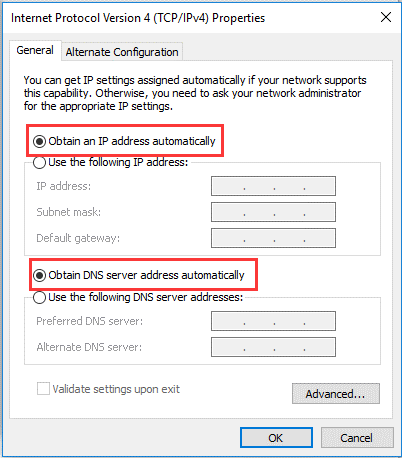
- Select "Obtain a DNS server address automatically" and "Obtain an IP address automatically" to enable DHCP.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Windows Vista and Windows 7:
- Launch the Control Panel by clicking the Start button.
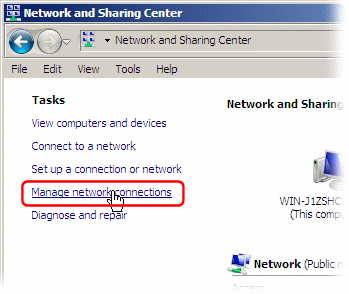
- Select "Network and Sharing Center."
Select "Manage network connections" from the left sidebar.
- Select "Properties" from the context menu when you right-click on the network device you want to enable DHCP for.
- Choose "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" from the menu.
- Select "Obtain a DNS server address automatically" and "Obtain an IP address automatically."
- Click OK to save the changes.
Windows XP:
- By selecting the Start button, you can open the Control Panel.
- From the context menu of the network adapter, you want to enable DHCP for, select "Network Connections," followed by "Properties."
- From the menu, choose "Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)."
- Select "Obtain a DNS server address automatically" and "Obtain an IP address automatically."
- To save the changes, click OK.
Note: Above instructions are for enabling DHCP on the specific version of Windows mentioned. Depending on your specific operating system version or service pack, you may encounter slight variations in the layout or wording. But the overall process will be similar.
If you want to disable DHCP and input your network settings instead, pick the Use the following IP address option and enter values for IP address, Subnet mask, and Default Gateway. Additionally, choose the Use the following DNS server address option and specify the preferred DNS server with a value. If you'd like, you may optionally provide a value for Alternate DNS server.
How to tell if I'm using DHCP?
The easy method of determining if you are using DHCP on your Windows computer is by using the "ipconfig /all" command from the Command Prompt. This command will display the detailed IP configuration information for all network adapters on your computer, including the DHCP status.
Open the Command Prompt by hitting the Windows key + R and typing "cmd," then type "ipconfig /all" and press the enter key to execute this command. Your computer's network adapters and their corresponding IP settings will be listed in the output.
Look for the section labeled "Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection" (or similar) and the DHCP Enabled line. If the DHCP is enabled, the line will read "Yes," meaning that the network adapter has DHCP enabled and your machine is using a dynamic IP address given to it by the DHCP server. If the DHCP is Enabled, the line says "No", which means that DHCP is disabled on that network adapter and your computer uses a static IP address that you have manually configured.
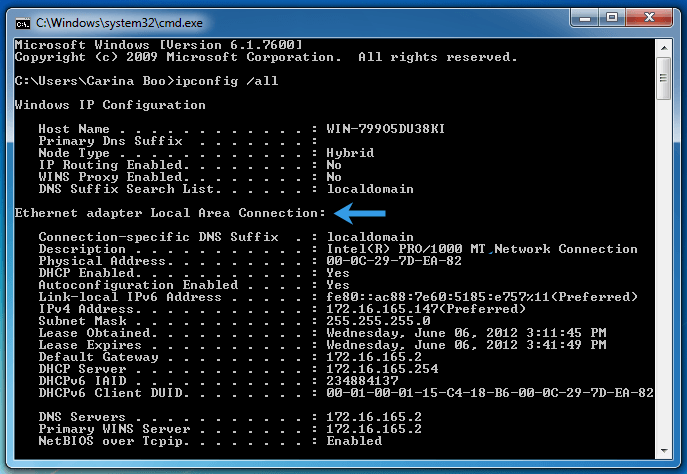
Note: DHCP Enabled line may not be present in the output if you are using a wireless network adapter. In this case, you should look for "Wireless LAN adapter Wi-Fi" (or similar) and look for the DHCP Enabled line.
Troubleshooting tips
There are a few important tips for resolving DHCP problems on Windows:
- Check the DHCP server: The first step in troubleshooting DHCP issues is ensuring the server is working properly. If the DHCP server is not operating or configured correctly, networked devices will not be able to receive IP addresses from it. Make that the DHCP server is operating properly by checking its settings.
- Check the network adapter: Make sure your computer's network adapter is working properly. You can do this by checking the adapter's settings in the Device Manager and ensuring that it is enabled and not experiencing any errors. Additionally, disabling and re-enabling the adapter to reset its settings.
- Check the IP configuration: Ensure your computer's IP configuration is set correctly. You can do this by using the "ipconfig" command in the Command Prompt and checking the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway. Make sure the DNS server addresses are right as well.
- Check the router: Check the DHCP settings on your router. Verify the IP address range of the DHCP server and that DHCP is enabled. Also, check the router's logs for any DHCP-related error messages.
- Examine the cables: Make sure that all cables are plugged in firmly and that neither the ports nor the cables they are plugged into have any physical problems.
- Restart your computer and router: Sometimes restarting your computer and router will cure DHCP problems. This can help to clear any temporary issues and refresh the network settings.
- Run network troubleshooter: A built-in network troubleshooter in Windows can automatically identify and resolve common network problems. Diagnose issues by going to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center.
Note: various factors can cause DHCP issues, and the troubleshooting steps will vary depending on the specific issue you are experiencing. However, by heeding the previous advice, you ought to be able to recognize and fix the most typical DHCP problems on Windows.
Advantages of DHCP in Windows:
- Automatic IP address assignment: DHCP eliminates the need for manual IP address configuration by automatically assigning IP addresses to devices on the network. This can save a significant amount of time and reduce the risk of errors.
- Dynamic IP addresses: DHCP allows for dynamic IP addresses, which means that IP addresses can be reassigned as needed. This is useful for networks with a high turnover of devices, such as public hotspots.
- Reduced network administration: DHCP can significantly reduce the amount of network administration required, as it eliminates the need to configure each device on the network manually.
- Centralized management: DHCP allows for centralized management of IP addresses, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot network issues.
- Increased security: By enabling network managers to restrict access to the network and assign unique IP addresses to particular devices, DHCP can assist increase security.
Disadvantages of DHCP in Windows:
- Limited Control over IP addresses: DHCP assigns IP addresses automatically, limiting network administrators' Control over IP addresses and their assignments.
- Dependence on DHCP server: DHCP requires a DHCP server to be running to assign IP addresses. If the DHCP server is down or not configured correctly, devices on the network cannot obtain IP addresses.
- Potential for IP address conflicts: If two or more networked devices are given the same IP address, DHCP may result in IP address conflicts.
- Reduced performance: DHCP can reduce the network's performance if the DHCP server becomes overloaded with requests.
- Vulnerability to DHCP spoofing: DHCP is vulnerable to DHCP spoofing attacks, in which an attacker sends fake DHCP responses to devices on the network, potentially causing them to connect to a rogue DHCP server. This can result in devices being assigned incorrect IP addresses and potentially compromising network security.
|



 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now









