What is the Internet?Internet is a global network that connects billions of computers across the world with each other and to the World Wide Web. It uses standard internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to connect billions of computer users worldwide. It is set up by using cables such as optical fibers and other wireless and networking technologies. At present, internet is the fastest mean of sending or exchanging information and data between computers across the world. 
It is believed that the internet was developed by "Defense Advanced Projects Agency" (DARPA) department of the United States. And, it was first connected in 1969. Why is the Internet Called a Network?Internet is called a network as it creates a network by connecting computers and servers across the world using routers, switches and telephone lines, and other communication devices and channels. So, it can be considered a global network of physical cables such as copper telephone wires, fiber optic cables, tv cables, etc. Furthermore, even wireless connections like 3G, 4G, or Wi-Fi make use of these cables to access the Internet. Internet is different from the World Wide Web as the World Wide Web is a network of computers and servers created by connecting them through the internet. So, the internet is the backbone of the web as it provides the technical infrastructure to establish the WWW and acts as a medium to transmit information from one computer to another computer. It uses web browsers to display the information on the client, which it fetches from web servers. The internet is not owned by a single person or organization entirely. It is a concept based on physical infrastructure that connects networks with other networks to create a global network of billions of computers. As of 12 August 2016, there were more than 300 crores of internet users across the world. Set UpPhysical copper or optical fiber data transmission cables, as well as other networking technologies like LAN, WAN, and MAN, are used to set up the internet. Even the 2g, 3g, and 4g services, as well as Wi-Fi, need this physical cable arrangement in order to access the Internet connection. The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN), a US-based organization, is in charge of overseeing the management of the Internet and its related protocols, including IP addresses. How does internet work?Before understanding this let us understand some basics related to internet: The internet works with the help of clients and servers. A device such as a laptop, which is connected to the internet is called a client, not a server as it is not directly connected to the internet. However, it is indirectly connected to the internet through an Internet Service Provider (ISP) and is identified by an IP address, which is a string of numbers. Just like you have an address for your home that uniquely identifies your home, an IP address acts as the shipping address of your device. The IP address is provided by your ISP, and you can see what IP address your ISP has given to your system. A server is a large computer that stores websites. It also has an IP address. A place where a large number of servers are stored is called a data center. The server accepts requests send by the client through a browser over a network (internet) and responds accordingly. To access the internet we need a domain name, which represents an IP address number, i.e., each IP address has been assigned a domain name. For example, youtube.com, facebook.com, paypal.com are used to represent the IP addresses. Domain names are created as it is difficult for a person to remember a long string of numbers. However, internet does not understand the domain name, it understands the IP address, so when you enter the domain name in the browser search bar, the internet has to get the IP addresses of this domain name from a huge phone book, which is known as DNS (Domain Name Server). For example, if you have a person's name, you can find his phone number in a phone book by searching his name. The internet uses the DNS server in the same way to find the IP address of the domain name. DNS servers are managed by ISPs or similar organizations. Now after understanding the basics, let us see how internet works? 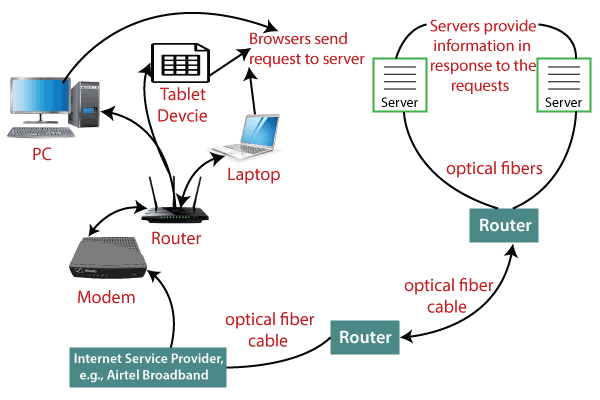
When you turn on your computer and type a domain name in the browser search bar, your browser sends a request to the DNS server to get the corresponding IP address. After getting the IP address, the browser forwards the request to the respective server. Once the server gets the request to provide information about a particular website, the data starts flowing. The data is transferred through the optical fiber cables in digital format or in the form of light pulses. As the servers are placed at distant places, the data may have to travel thousands of miles through optical fiber cable to reach your computer. The optical fiber is connected to a router, which converts the light signals into electrical signals. These electrical signals are transmitted to your laptop using an Ethernet cable. Thus, you receive the desired information through the internet, which is actually a cable that connects you with the server. Furthermore, if you are using wireless internet using wifi or mobile data, the signals from the optical cable are first sent to a cell tower and from where it reaches to your cell phone in the form of electromagnetic waves. The internet is managed by ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) located in the USA. It manages IP addresses assignment, domain name registration, etc. The data transfer is very fast on the internet. The moment you press enter you get the information from a server located thousands of miles away from you. The reason for this speed is that the data is sent in the binary form (0, 1), and these zeros and ones are divided into small pieces called packets, which can be sent at high speed. Uses of the internetGenerally speaking, the Internet may be used to exchange information with people all over the world, communicate across great distances, and locate information or answers fast on almost any subject. Here are some examples of specific uses for the Internet:
Other examples include:
Difference between the World Wide Web and the Internet
The World Wide Web (also known as the Web) and the Internet are fundamentally dissimilar from one another because the Web is a collection of information that can be accessed using the Internet, whereas the Internet is a global network of networks that offers access to almost all types of information. In other words, the Web is a service that was added to the Internet's foundation. The Web is the part of the Internet that gets the greatest traffic. One unique aspect of this is hypertext, a rapid cross-referencing method. The majority of websites feature text that highlights keywords or phrases by being a different color than the rest of the text. When a user selects one of these words or phrases, they will be sent to the chosen website or page. Buttons, graphics, and even particular areas of images are also utilized as hyperlinks. On the Internet, there are billions of pages of information. The most popular web browsers are Google Chrome, Firefox, and Internet Explorer. A web browser is used to surf the internet or do online browsing. A certain Web site's look may vary slightly depending on the browser being used. A certain browser's later or more updated versions have the potential to render more complicated features like music files, sound, animation, and virtual reality. Security and the InternetDue to the volume of private and public information collected online, customers are at risk for security attacks and data breaches. Crackers and hackers have access to networks and systems, and they are able to steal personal data, such as login passwords or information on bank and credit card accounts. Among the steps that may be taken to protect online privacy are:
Furthermore, the "dark web" is an additional component of the Internet. Standard browsers do not allow users to access the dark web, which is hidden. It instead makes use of the Tor and I2P browsers, which let users maintain complete anonymity. While this anonymity can be a fantastic way to safeguard a user's security and freedom of speech online or for the government to conceal confidential information, the dark web also fosters an environment that makes cybercrime, the transfer of illicit commodities, and terrorism easier. Social impact of the InternetBoth positive and negative effects of the Internet on society can be observed. On the one hand, some people claim that the Internet has raised the risk of withdrawal, social exclusion, alienation, and citing a rise in FOMO, or the fear of missing out, as evidence. On the other hand, some people also believe that the Internet has had the opposite impact on society, increasing sociability, civic participation, and the depth of connections. The Internet has changed how society communicates and interacts, whether the effects are positive or negative on society. The increased focus on personal growth is one example of change and the fall in a community that is determined by space, job, and family. People increasingly now build social connections on the basis of their unique projects, values, as well as interests. In addition to offline and in person, communities are being created by like-minded people through the Internet and the abundance of online settings it provides and produces. Social networking sites like Facebook and LinkedIn are the preferred platforms for both businesses and individuals wishing to carry out various tasks and connect with others. Internet Connection ProtocolsProtocols are a set of guidelines that aid in regulating the operation of any specific organization or technology. Three main categories of Internet Connection Protocols are discussed below:
History of the InternetThe forerunner of the Internet, the ARPANet, went live for the first time in 1969. The TCP/IP, open networking protocol suite, was adopted by the ARPANet in 1983, and the National Science Foundation Network (NSFN) developed the network to link university computer science departments across the US in 1985. When the hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) was developed in 1989, it enabled different computer platforms to connect to the same Internet sites, which dramatically improved communications over the network. The Mosaic Web browser was developed in 1993. Over the years of its existence, the Internet has remained a constant growth and development. For instance, IPv6 was created to provide for a significant future rise in the number of IP addresses that could be used. In a related development, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the rapidly developing environment where nearly any entity or device can be given a unique identifier (UID) and the capability to communicate data automatically over the Internet. Advantages of the Internet:
Disadvantages of the Internet
Different ways to Connect to the InternetThe various methods for connecting to the Internet are briefly discussed below:
Other things you can do on the InternetThe ability to communicate with anyone in the world virtually immediately is one of the best features of the Internet. With billions of users worldwide, email is one of the most established and widely used methods of online communication as well as information sharing with others. People can communicate with each other in a number of ways and create online communities with the help of using social media platforms. 
Also, you can use the Internet for a variety of additional purposes. There are multiple ways to stay up to date on news and do online shopping. You can take care of your financial affairs, meet new people, watch TV, or enhance new skills. With the help of Internet, you can do or learn anything online.
Next TopicIntranet
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share










