What is MsconfigMSConfig (for Microsoft System Configuration Utility) is a built-in system configuration tool in Microsoft Windows operating systems. It allows users to control various system settings and startup programs that run when the computer boots up. You can configure several system settings using MSConfig, such as startup programs, boot options, system services, and tools that automatically load with the operating system. This tool is particularly useful for troubleshooting your Windows computer's startup issues or performance problems. MSConfig is typically accessed by typing "msconfig" into the Run box or search bar in Windows, pressing the Windows key + R, and typing "msconfig" into the Run dialogue box. You can configure various options and settings from there according to your needs. Built into Windows is a special "Microsoft System Configuration Utility" tool or simply "MSCONFIG." Designed to help you troubleshoot problems with your computer, MSCONFIG can also be used to ensure that your computer boots faster and crashes less. History of MsconfigMsconfig, short for Microsoft System Configuration Utility, is a tool included in Windows operating systems since Windows 98. The tool is designed to help users manage system startup processes, services, and other system configurations. Msconfig was first introduced in Windows 98 as a tool for diagnosing and troubleshooting startup issues. It allowed users to disable startup items, modify system settings, and troubleshoot issues with system services. In subsequent versions of Windows, Msconfig was updated to include additional features such as a "Services" tab for managing Windows services and a "Tools" tab for accessing various system utilities. Msconfig has been a valuable tool for advanced and novice users for many years. It provides a simple and user-friendly interface for managing system configurations and is often used by IT professionals to troubleshoot system issues. However, with the release of newer versions of Windows, some of the features of Msconfig have been replaced or supplemented by other tools and utilities. Today, Msconfig remains an important tool for managing system configurations and is still included in the latest versions of Windows, such as Windows 10. While its features may have changed over time, its continued presence in Windows is a testament to its usefulness and importance in system administration. How to Open Msconfig in WindowsTo open MSConfig in different versions of Windows, you can follow these steps:
You can also access MSConfig by typing "msconfig" in the search box on the Windows taskbar or by using the Command Prompt. To open MSConfig from Command Prompt, type "msconfig" and press Enter. Note: Some versions of Windows may require you to have administrative privileges to use MSConfig. If you encounter issues or error messages while using MSConfig, try running it as an administrator.Properties of MsconfigMSConfig has several properties that allow users to configure and control various system settings and startup programs. Here are some of the main properties of MSConfig: 1) General TabThe General tab allows you to configure the startup selection for your system. You can choose between Normal startup, Selective startup, or Diagnostic startup. You can also configure the timeout for the boot process and set the number of processors that should be used during boot. The General tab in MSConfig is where you can select the startup mode for your system, set the timeout for the boot process, and choose the number of processors that should be used during boot. Here's a brief overview of the properties available on the General tab: 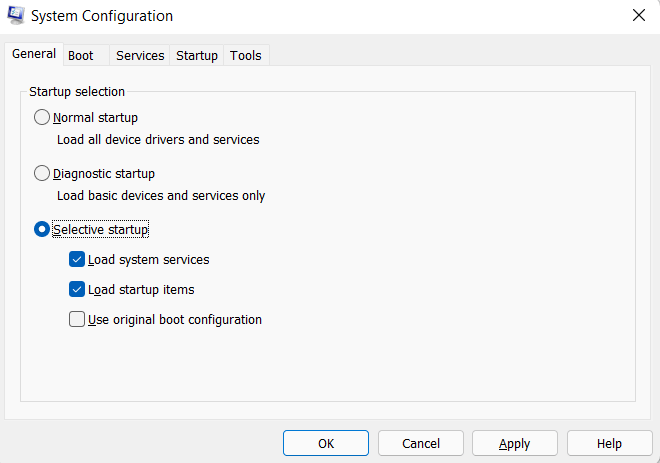
2) Boot TabThe Boot tab in MSConfig allows you to configure advanced boot options for your Windows computer. Here's a brief overview of the properties available on the Boot tab: 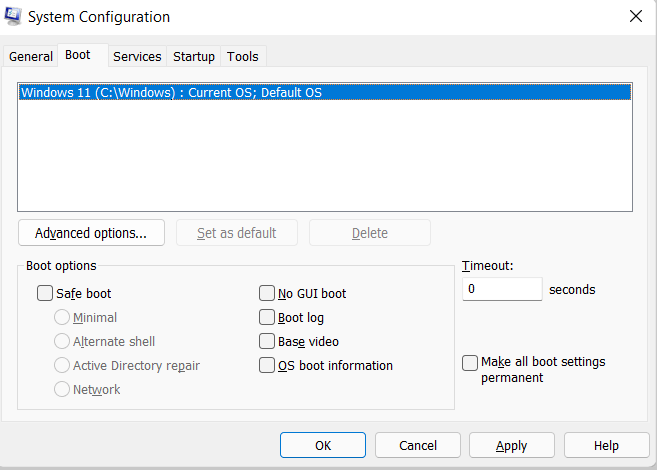
3) Services TabThe Services tab allows you to control system services that run in the background. You can enable or disable services or hide all Microsoft services to make it easier to identify third-party services.
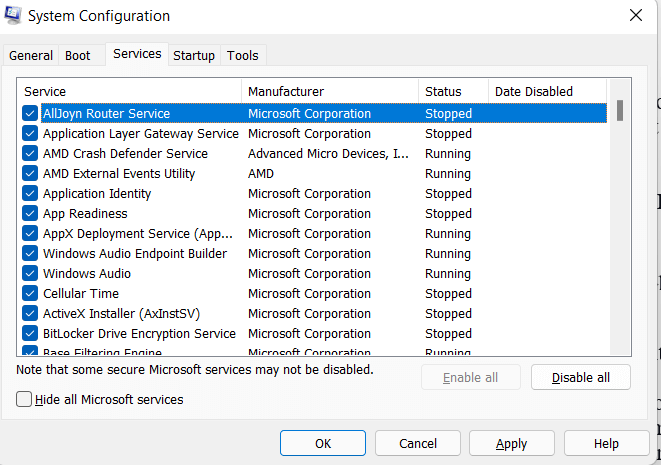
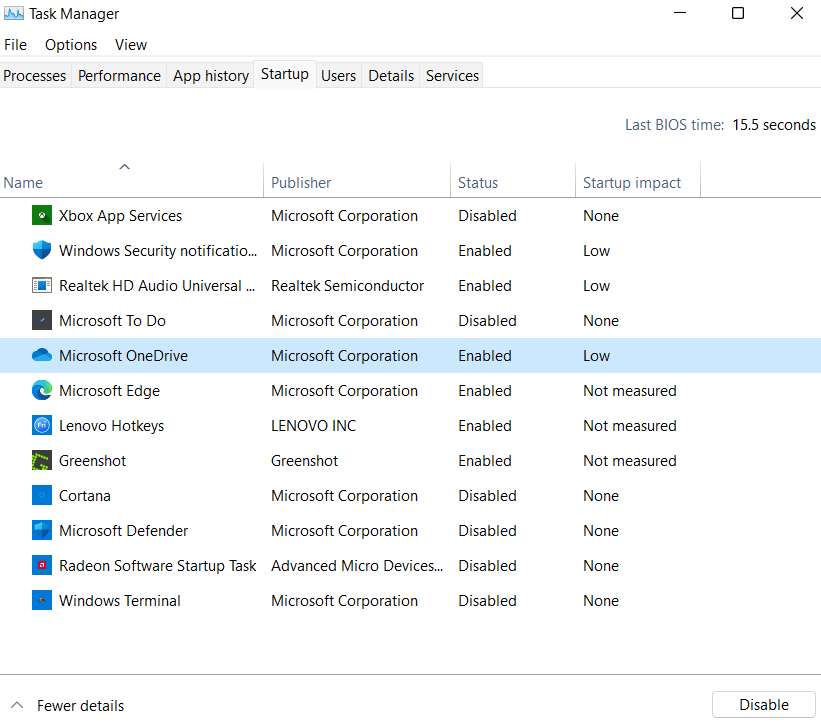
The Services tab in MSConfig allows you to manage and configure the services that are running on your Windows computer. By selecting the appropriate startup type and disabling unnecessary services, you can optimize the performance and stability of your system. However, it is important to use caution when changing these settings, as incorrect configuration can cause serious problems with your system. 4) Startup TabThe Startup tab allows you to manage programs that run at startup. You can disable or enable programs, change their startup type, or open the registry editor to view and edit the startup programs. The Startup tab in MSConfig displays a list of programs and applications that are set to run automatically when Windows starts up. Here's a brief overview of the properties available on the Startup tab:
5)Tools TabThe Tools tab provides quick access to several useful tools, such as System Configuration Utility, Event Viewer, Command Prompt, and Task Manager. The "Tools" tab in Msconfig (Microsoft System Configuration) is a feature available in Windows operating systems that allows users to access various system tools and utilities. This tab displays a list of tools that can be used to diagnose and troubleshoot issues related to Windows startup and system configuration. Some of the tools available on this tab may include: 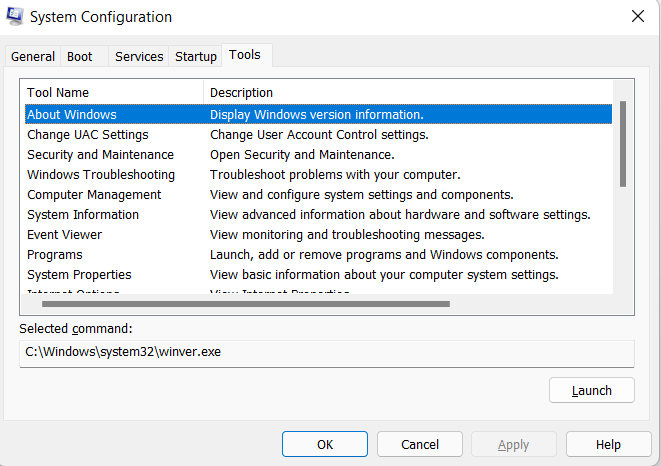
Use of MsconfigMSConfig is a powerful tool that can be used to manage and optimize the performance of your Windows computer. Here are some of the main uses of MSConfig: Troubleshooting: MSConfig is often used to troubleshoot issues related to startup programs, services, or system configurations that may be causing performance or stability problems on your Windows computer. By disabling non-essential startup programs or services, you can isolate the source of the issue and resolve it. Performance optimization: MSConfig can also be used to optimize the performance of your computer by disabling unnecessary startup programs or services that may be slowing down your system. By disabling these programs, you can reduce the startup time of your computer and free up system resources for other tasks. Security: MSConfig can be used to identify and disable malicious software or spyware that may be running on your system. By disabling these programs, you can prevent them from running at startup and potentially compromising your system. Customization: MSConfig can also be used to customize the behavior of your Windows computer by configuring advanced boot options, setting the number of processors to be used during boot, or changing the timeout settings for the boot process. How to Manage Startup Tab in MsconfigThe "Startup" tab in Msconfig (Microsoft System Configuration) displays a list of programs and services that are set to run automatically when your computer starts up. You can use this tab to manage and disable unnecessary startup programs, which can help to improve your computer's startup time and performance. Here are the steps to access the Startup tab in Msconfig:
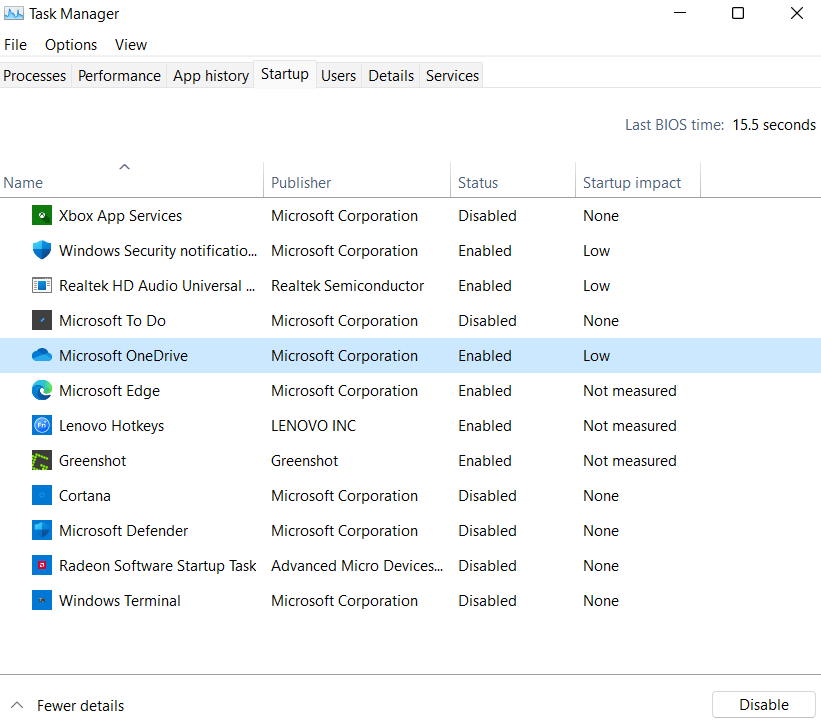
Note: Disabling the wrong startup programs can cause issues with your computer, so it's a good idea to research each program before disabling it. Additionally, some programs may re-enable themselves after being disabled in Msconfig, so you may need to disable them in their settings or uninstall them completely.
Next TopicWhat is Partition in Computer
|
 For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
For Videos Join Our Youtube Channel: Join Now
Feedback
- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share









